Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion - Exercise-wise Question Answers
Motion Class 9 NCERT solutions provide clear and step-by-step answers to all textbook questions from Class 9 Science Chapter 7. These Class 9 Motion NCERT solutions cover important topics such as motion, velocity, acceleration, and uniform circular motion, strictly based on the latest NCERT textbook. The Motion Class 9 questions answers include all exercises and in-text questions, helping students understand numerical and theory-based problems clearly. Students can access the Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion exercise question answer PDF for free. All Class 9 Science Chapter 7 question answer sets are prepared by subject experts and aligned with the latest CBSE Science syllabus.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion - 2025-26
Access Science Class 9 Motion Chapter 7 NCERT Solutions
1. An object has moved through a distance. Can it have zero displacement? If yes, support your answer with an example.
Ans: Yes. An object can have zero displacement if it has moved through a distance. Displacement is defined as the shortest distance from the initial point to the final point.
Hence, if the starting (initial) point is the same as the final point then the displacement of the object is zero.
Suppose a man is walking in a square park of length $20m$. He starts from point A and walks along all the corners of the park through points B, C and D and comes back to the same point A.
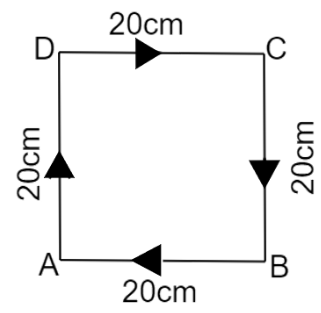
The total distance covered by the man$=20m+20m+20m+20m=80m$.
As the starting point and final point are same, the shortest distance between his initial and final position is zero
Therefore, the displacement is zero.
2. A farmer moves along the boundary of a square field of side $10m$ in $40s$ .What will be the magnitude of displacement of the farmer at the end of $2$ minutes $20$ seconds?
Ans: It is given that,
Farmer takes $40s$ to cover a square field of side $10m$.
$\Rightarrow Dis\tan ce=4\times 10=40m$
It is known that,$Speed=\frac{Dis\tan ce}{Time}$
$\Rightarrow Speed=\frac{40}{40}=1$
Therefore, speed of the farmer is $1m/s$.
In $2$minutes $20$seconds distance travelled is $Speed\times Time$.
$\Rightarrow Dis\tan ce=1\times (2\times 60+20)$
$\Rightarrow Dis\tan ce=140m$
Number of rounds farmer covered$=\frac{140}{40}=3.5$
After $2$minutes $20$seconds the farmer will be at the opposite end of starting point, completing $3$ and half rounds.
If the farmer starts from any corner of the field: The displacement will be equal to the diagonal of the field.
$\Rightarrow Displacement=\sqrt{{{10}^{2}}+{{10}^{2}}}=14.14m$
If the farmer starts from the middle point of any side of the field: The final point will be the middle point of the side opposite to the initial point.
\[\Rightarrow Displacement=10m\]
Therefore, the magnitude of displacement if the farmer starts at any corner is $14.14m$ and if the farmer starts from middle point of any side is $10m$.
3. Which of the following is true for displacement?
It cannot be zero.
Ans: Not true. When the initial and final position of the object is the same, then the displacement is zero.
Its magnitude is greater than the distance travelled by the object.
Ans: Not true. Displacement is the measure of the shortest distance between the initial and final position of an object.
Therefore, it is always smaller than or equal to the magnitude of distance travelled by the object.
4. An artificial satellite is moving in a circular orbit of radius \[\mathbf{42250km}\]. Calculate its speed if it takes $24$ hours to revolve around the earth?
Ans: It is given that,
Radius of the circular orbit, \[r=\mathbf{42250km}\]
Time taken by the satellite to revolve around earth, $t=24h$
Speed of the artificial satellite, $v=?$
It is known that,
$v=\frac{2\pi r}{t}$
$\Rightarrow v=\frac{2\times 3.14\times 42250}{24}$
$\Rightarrow v=1.105\times {{10}^{4}}km/h$
$\Rightarrow v=\frac{1.105\times {{10}^{4}}}{3600}km/s$
$\Rightarrow v=3.069km/s$
Therefore, the speed of the artificial satellite is $v=3.069km/s$.
5. Distinguish between speed and velocity.
Ans: The differences between speed and velocity are as follows:
Speed | Velocity |
|
|
6. Under what condition(s) is the magnitude of average velocity of an object added equal to its average speed?
Ans: It is known that,
\[Average\text{ }speed=\frac{Total\text{ }distance\text{ }covered}{Total\text{ }time\text{ }taken}\]
\[Average\text{ }velocity=\frac{Displacement}{Total\text{ }time\text{ }taken}\]
Therefore, the magnitude of average velocity of an object is equal to its average speed when total distance covered is equal to the displacement.
7. What does the odometer of an automobile measure?
Ans: The distance covered by an automobile is recorded by the odometer of an automobile.
8. What does the path of an object look like when it is in uniform motion?
Ans: An object has a straight-line path when it is in uniform motion.
9. During an experiment, a signal from a spaceship reached the ground station in five minutes. What was the distance of the spaceship from the ground station? The signal travels at the speed of light, that is,\[3\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}\].
Ans: It is given that,
Time taken by a signal to reach ground from a spaceship $=5\min =5\times 60=300\sec $
Speed of the signal is equal to speed of light\[=3\times {{10}^{8}}m{{s}^{-1}}\]
It is known that,
\[Speed=\frac{Distance\text{ travelled}}{Time\text{ }taken}\]
$\Rightarrow Distance\text{ travelled = Speed}\times \text{Time taken}$
$\Rightarrow Distance\text{ travelled = 3}\times \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{8}}\times 300=9\times {{10}^{10}}m$
Therefore, the distance of the spaceship from the ground station is $9\times {{10}^{10}}m$.
10. When will you say a body is in
uniform acceleration?
Ans: When the magnitude and the direction of acceleration of a body is constant i.e., velocity changes at an equal rate then the body is said to be in uniform acceleration.
non-uniform acceleration?
Ans: When the acceleration of a body changes in magnitude or direction or both i.e., velocity changes at an unequal rate then the body is said to be in non-uniform acceleration.
11. A bus decreases its speed from \[80km{{h}^{-1}}\]to \[60km{{h}^{-1}}\]in $5s$. Find the acceleration of the bus.
Ans: It is given that,
Initial speed of the bus, $u=80km/h$
$\Rightarrow u=80\times \frac{5}{18}m/s=22.22m/s$
Final speed of the bus, $v=60km/h$
$\Rightarrow v=60\times \frac{5}{18}m/s=16.66m/s$
Time taken to decrease speed, $t=5s$
It is known that,
Acceleration,$a=\frac{v-u}{t}$
$\Rightarrow a=\frac{16.66-22.22}{5}$
$\Rightarrow a=-1.112m/{{s}^{2}}$
Therefore, the acceleration of the bus is $-1.112m/{{s}^{2}}$. The negative sign indicates that the velocity of the car is decreasing. Decreasing acceleration is called retardation.
12. A train starting from a railway station and moving with uniform acceleration attains a speed $40km/h$ in $10$ minutes. Find its acceleration.
Ans: It is given that,
Initial velocity of the train, $u=0$ (Train is starting from rest)
Final velocity of the train, $v=40km/h$
$\Rightarrow v=40\times \frac{5}{18}m/s=11.11m/s$
Time taken, $t=10\times 60=600s$
It is known that,
Acceleration,$a=\frac{v-u}{t}$
$\Rightarrow a=\frac{11.11-0}{600}$
$\Rightarrow a=0.0185m/{{s}^{2}}$
Therefore, the acceleration of the train is $0.0185m/{{s}^{2}}$.
13. What is the nature of the distance-time graphs for uniform and non-uniform motion of an object?
Ans: The distance-time graph for uniform motion of an object is a straight line.
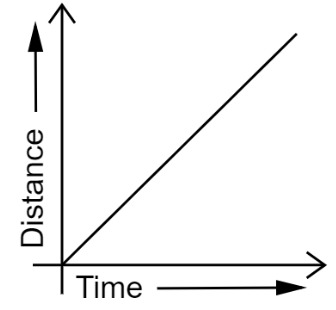
The distance-time graph for non-uniform motion of an object is a curved line.
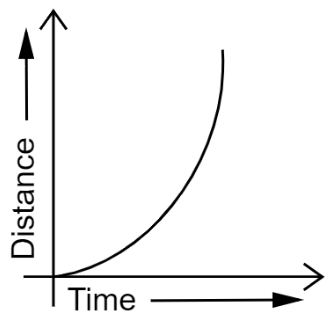
14. What can you say about the motion of an object whose distance-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis?
Ans: A straight line parallel to the x-axis in a distance-time graph indicates that the position of the object does not change with time.
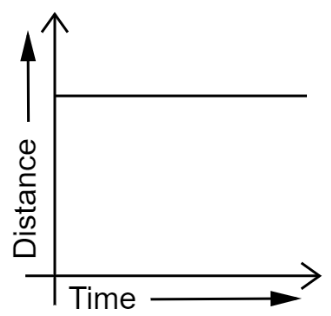
Therefore, the object is said to be at rest.
15. What can you say about the motion of an object if its speed-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis?
Ans: A straight line parallel to the time axis in a speed-time graph indicates that the speed of the object does not change with time.
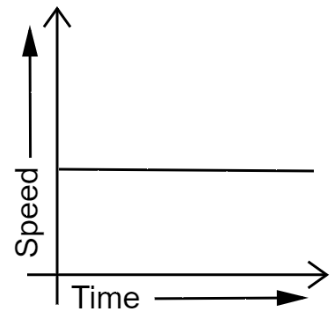
Therefore, the object is moving uniformly.
16. What is the quantity which is measured by the area occupied below the velocity-time graph?
Ans: The area of the velocity-time graph is displacement.
Consider the following figure which shows the velocity-time graph of a uniformly moving body.
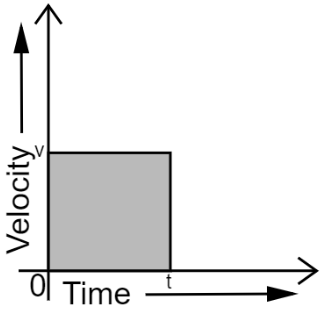
Let, the velocity of the body at time $t$ be $v$.
Area of the shaded region$=Length\times Breadth$
Where,
$Length=l$
$Breadth=v$
$\Rightarrow Area=vt=velocity\times time$ ……$(1)$
It is known that,
$Velocity=\frac{Displacement}{time}$
$\Rightarrow Displacement=Velocity\times Time$ ……$(2)$
From equations $(1)$and $(2)$
\[\Rightarrow Area=Displacement\]
Hence, the area occupied below the velocity-time graph measures the displacement of the body.
17. A bus starting from rest moves with a uniform acceleration of \[0.1m/{{s}^{2}}\]for $2$ minutes. Find
The speed acquired
Ans: It is given that,
Initial velocity of the bus, $u=0$ (Bus is starting from rest)
Acceleration of bus, $a=0.1m/{{s}^{2}}$
Time taken, $t=2\min =120\sec $
Final velocity of the bus, $v=?$
It is known that,
Acceleration,$a=\frac{v-u}{t}$
$\Rightarrow 0.1=\frac{v-0}{120}$
$\Rightarrow v=12m/s$
Therefore, the speed acquired is $v=12m/s$.
The distance travelled
Ans: It is known that,
From, third equation of motion:${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as$
$\Rightarrow {{(12)}^{2}}-{{(0)}^{2}}=2\times (0.1)\times s$
$\Rightarrow 144=0.2s$
$\Rightarrow s=720m$
Therefore, the distance travelled is $s=720m$.
18. A train is travelling at a speed of \[90km{{h}^{-1}}\]. Brakes are applied so as to produce a uniform acceleration of \[-0.5m{{s}^{-2}}\]. Find how far the train will go before it is brought to rest.
Ans: It is given that,
Initial speed of a train, $u=90km/h$
$\Rightarrow u=90\times \frac{5}{18}=25m/s$
Final speed of the train, $v=0$ (Train comes to rest finally)
Acceleration of train, $a=-0.5m/{{s}^{2}}$
Distance covered by the train, $s=?$
It is known that,
From, third equation of motion:${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as$
$\Rightarrow {{(0)}^{2}}-{{(25)}^{2}}=2\times (-0.5)\times s$
$\Rightarrow -625=-s$
$\Rightarrow s=625m$
Therefore, the train covers a distance of $625m$ before it comes to rest.
19. A trolley, while going down an inclined plane, has an acceleration of\[~2cm\text{/}{{s}^{2}}\]. What will be its velocity $3s$ after the start?
Ans: It is given that,
Initial velocity of the trolley, $u=0$ (Trolley is starting from rest)
Acceleration of the trolley, $a=2cm/{{s}^{2}}=0.02m/{{s}^{2}}$
Time taken, $t=3s$
Final velocity (after $3s$ of start) of the trolley, $v=?$
It is known that,
From, first equation of motion: $v=u+at$
$\Rightarrow v=0+0.02(3)$
$\Rightarrow v=0.06m/s$
Thus, the velocity of the trolley is $0.06m/s$ after $3s$ from the start.
20. A racing car has a uniform acceleration of \[4m{{s}^{-2}}\]. What distance will it cover in $10s$ after start?
Ans: It is given that,
Initial velocity of the racing car, $u=0$ (The racing car is initially at rest)
Acceleration of a racing car, $a=4m/{{s}^{2}}$
Time taken, $t=10s$
It is known that,
From, second equation of motion: $s=ut+\frac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow s=0+\frac{1}{2}(4){{(10)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow s=200m$
Therefore, the distance covered by racing car after $10s$ from start is $200m$.
21. A stone is thrown in a vertically upward direction with a velocity of \[5m\text{/}s\]. If the acceleration of the stone during its motion is \[10m/{{s}^{-2}}\] in the downward direction, what will be the height attained by the stone and how much time will it take to reach there?
Ans: It is given that,
Initial velocity of the stone, $u=5m/s$
Final velocity, $v=0$ (Stone comes to rest after reaching maximum height)
Acceleration of the stone is equal to acceleration due to gravity, $a=-10m/{{s}^{2}}$ (Negative sign because of downward direction)
Maximum height reached by the stone, $s=?$
It is known that,
From, first equation of motion: $v=u+at$
$\Rightarrow 0=5+(-10)t$
$\Rightarrow 5=10t$
$\Rightarrow t=0.5s$
From, third equation of motion: ${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as$
$\Rightarrow {{(0)}^{2}}-{{(5)}^{2}}=2(-10)s$
$\Rightarrow -25=-20s$
$\Rightarrow s=1.25m$
Therefore, the height attained by the stone is $1.25m$ in $0.5s$.
22. An athlete completes one round of a circular track of diameter $200m$ in $40s$. What will be the distance covered and the displacement at the end of $2$ minutes $20s$?
Ans: It is given that,
Diameter of a circular track, $d=200m$
Radius of the circular track, $r=\frac{d}{2}$
$\Rightarrow r=\frac{200}{2}=100m$
Circumference of the circular track, $c=2\pi r$
$\Rightarrow c=2\pi (100)=200\pi m$
Time taken to cover one round, $t=40s$
It is known that,
\[Speed=\frac{Distance\text{ travelled}}{Time\text{ }taken}\]
$\Rightarrow Speed=\frac{200\pi }{40}$
$\Rightarrow Speed=50\pi $
Athlete runs for $2$minutes $20$s: Time in seconds$=120+20=140s$
Total distance covered in \[140s=Speed\times Time\]
$\Rightarrow ~Distance=\frac{200\times 22\times 140}{40\times 7}=2200m$
Number of rounds$=\frac{140}{40}=3.5$
Athlete will be diametrically opposite to the point where he started after completing three rounds.
The displacement will be equal to diameter i.e.,$200m$
Therefore, the distance covered is $2200m$ and the displacement is $200m$at the end of $2$minutes $20$s.
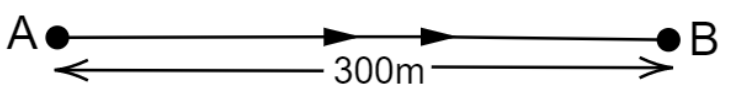
23. Joseph jogs from one end A to the other end B of a straight road of $300m$ in $2$ minutes $50$ seconds and then turns around and jogs $100m$ back to point C in another $1$ minute. What are Joseph’s average speeds and velocities in jogging
from A to B
Ans: It is given that,
Distance from A to B$=300m$
Time taken from A to B \[=2\min 50\sec =170\sec\]
It is known that,
\[Average\text{ }speed=\frac{Total\text{ }distance\text{ }covered}{Total\text{ }time\text{ }taken}\]
\[\Rightarrow Average\text{ }speed=\frac{300}{170}=1.765m/s\]
\[Average\text{ }velocity=\frac{Displacement}{Total\text{ }time\text{ }taken}\]
Displacement from A to B$=\mathbf{Distance}=300m$
\[Average\text{ }velocity=\frac{300}{170}=1.765m/s\]
Therefore, the average speed and average velocity of Joseph from A to B are same and is equal to $1.765m/s$.
from A to C?
Ans: It is given that,
Distance from A to B$=300m$
Distance from B to C$=100m$
Total distance from A to C$=300+100=400m$
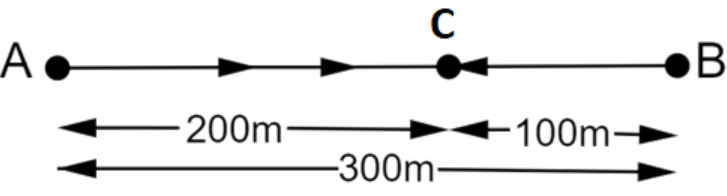
Time taken from A to B$=2\min 50\sec =170\sec $
Time taken from B to C$=1\min =60\sec $
Total time taken from A to C$=170+60=230\sec $
It is known that,
\[Average\text{ }speed=\frac{Total\text{ }distance\text{ }covered}{Total\text{ }time\text{ }taken}\]
\[\Rightarrow Average\text{ }speed=\frac{400}{230}=1.739m/s\]
\[Average\text{ }velocity=\frac{Displacement}{Total\text{ }time\text{ }taken}\]
Displacement from A to C$=AB-BC=300-100=200m$
\[Average\text{ }velocity=\frac{200}{230}=0.87m/s\]
Therefore, the average speed and average velocity of Joseph from A to C are $1.739m/s$ and $0.87m/s$ respectively.
24. Abdul, while driving to school, computes the average speed for his trip to be \[20km{{h}^{-1}}\]. On his return trip along the same route, there is less traffic and the average speed is \[40km{{h}^{-1}}\]. What is the average speed for Abdul’s trip?
Ans: It is given that,
Average speed of Abdul’s trip$=20km/h$
Let the distance travelled by Abdul to reach school and to return home be $d$.
Case 1: While driving to school
Let, total time taken be ${{t}_{1}}$.
\[Average\text{ }speed=\frac{Total\text{ }distance\text{ }covered}{Total\text{ }time\text{ }taken}\]
$\Rightarrow 20=\frac{d}{{{t}_{1}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{t}_{1}}=\frac{d}{20}$ ……$(1)$
Case 2: While returning from school
Let, total time taken be ${{t}_{2}}$.
\[Average\text{ }speed=\frac{Total\text{ }distance\text{ }covered}{Total\text{ }time\text{ }taken}\]
$\Rightarrow 40=\frac{d}{{{t}_{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}=\frac{d}{40}$ ……$(2)$
Average speed for Abdul’s trip$=\frac{Total\text{ }distance\text{ }covered\text{ }in\text{ }the\text{ }trip}{Total\text{ }time\text{ }taken}$
Where,
Total distance covered in the trip$=d+d=2d$
Total time taken$={{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}$
Substitute equation $(1)$ and $(2)$ in total time taken
Total time taken$=\frac{d}{20}+\frac{d}{40}$
\[\Rightarrow Average\text{ }speed=\frac{2d}{\frac{d}{20}+\frac{d}{40}}\]
\[\Rightarrow Average\text{ }speed=\frac{2}{\frac{2+1}{40}}=\frac{80}{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow Average\text{ }speed=26.67m/s\]
Therefore, the average speed for Abdul’s trip is $26.67m/s$.
25. A motorboat starting from rest on a lake accelerates in a straight line at a constant rate of $3.0m/{{s}^{2}}$ for $8.0s$. How far does the boat travel during this time?
Ans: It is given that,
The initial velocity of the motorboat, $u=0$( Motorboat is initially at rest)
Acceleration of the motorboat, $a=3m/{{s}^{2}}$
Time taken, $t=8s$
Distance travelled by the motorboat, $s=?$
It is known that,
From, second equation of motion: $s=ut+\frac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow s=0+\frac{1}{2}(3){{(8)}^{2}}$
\[\Rightarrow s=(3)(8)(4)\]
\[\Rightarrow s=96m\]
Therefore, the boat travels a distance of $96m$.
26. A driver of a car travelling at \[52km{{h}^{-1}}\] applies the brakes and accelerates uniformly in the opposite direction. The car stops in 5 s. Another driver going at \[3km{{h}^{-1}}\] in another car applies his brakes slowly and stops in $10s$. On the same graph paper, plot the speed versus time graphs for the two cars. Which of the two cars travelled farther after the brakes were applied?
Ans: Car A: Initial speed of the car, \[{{u}_{A}}=52km/h\]
\[\Rightarrow {{u}_{A}}=52\times \frac{5}{18}=14.4m/s\]
Time taken for the car to stop, ${{t}_{A}}=5s$
Final speed of the car becomes zero after $5s$ application of brakes.
Car B: Initial speed of the car, \[{{u}_{B}}=3km/h\]
\[\Rightarrow {{u}_{B}}=3\times \frac{5}{18}=0.833m/s\]
Time taken for the car to stop, ${{t}_{B}}=10s$
Final speed of the car becomes zero after $10s$ application of brakes.
Plot of the two cars on a speed-time graph is shown below:
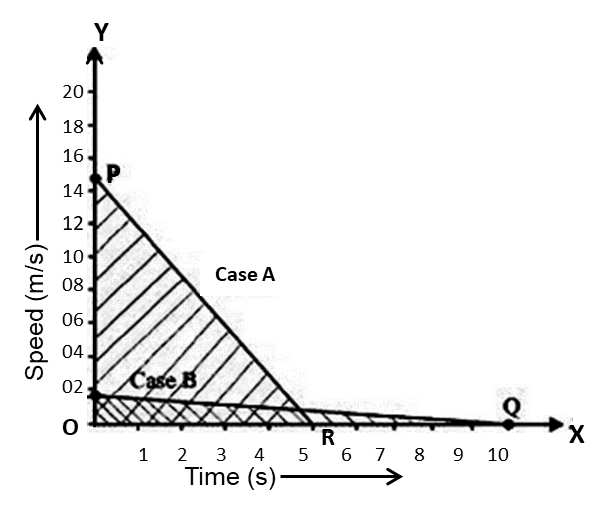
Distance covered by each car is equal to the area under the speed-time graph.
Distance covered by car A: ${{s}_{A}}=\frac{1}{2}\times OP\times OR$
$\Rightarrow {{s}_{A}}=\frac{1}{2}\times 14.4\times 5$
$\Rightarrow {{s}_{A}}=36m$
Distance covered by car B: ${{s}_{B}}=\frac{1}{2}\times OS\times OQ$
\[\Rightarrow {{s}_{B}}=\frac{1}{2}\times 0.83\times 10\]
$\Rightarrow {{s}_{B}}=4.15m$
Area of $\Delta OPR$is greater than area of $\Delta OSQ$.
Therefore, the distance covered by car A is greater than the distance covered by car B. Thus, the car travelling with a speed of $52km/h$travels farther after the brakes were applied.
27. The following figure shows the distance-time graph of three objects A, B and C. Study the graph and answer the following:
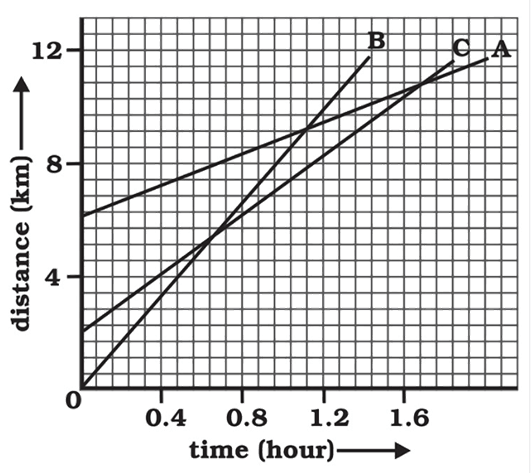
Which of the three is travelling the fastest?
Ans: It is known that,
$Speed=\frac{Distance}{Time}$

$\mathbf{Slope}\text{ }\mathbf{of}\text{ }\mathbf{graph}=\frac{y-axis}{x-axis}=\frac{Distance}{Time}=Speed$
Slope of the graph of object B is greater than objects A and C.
Therefore, object B is travelling the fastest.
Are all three ever at the same point on the road?
Ans: No, All the three objects A, B and C never meet at the same point.
Therefore, they were never at the same point on the road.
How far has C travelled when B passes A?
Ans: From the graph,
On distance axis:$7$small boxes $=4km$
$\Rightarrow \mathbf{1}\text{ }\mathbf{small}\text{ }\mathbf{box}=\frac{4}{7}km$
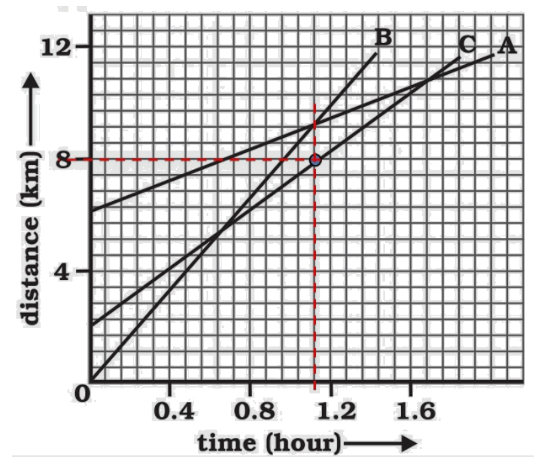
Initially, object C is $4$ blocks away from the origin$\Rightarrow \frac{16}{7}km$
Distance of object C from origin when B passes A is $8km$.
Distance covered by C$=8-\frac{16}{7}=5.714km$
Therefore, C has travelled a distance of $5.714km$ when B passes A.
How far has B travelled by the time it passes C?
Ans: From the graph,
Distance covered by B at the time it passes C$=9boxes$
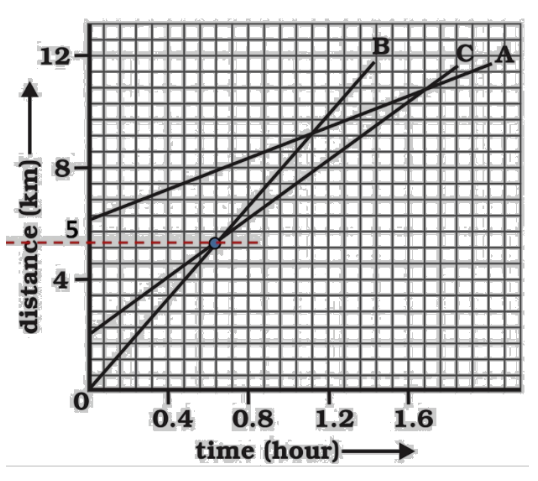
Distance$=9\times \frac{4}{7}=\frac{36}{7}=5.143km$
Therefore, B has travelled a distance of $5.143km$ when B passes A.
28. A ball is gently dropped from a height of $20m$. If its velocity increases uniformly at the rate of $10m/{{s}^{2}}$, with what velocity will it strike the ground? After what time will it strike the ground?
Ans: It is given that,
Distance covered by the ball, $s=20m$
Acceleration of the ball, $a=10m/{{s}^{2}}$
Initial velocity of the ball, $u=0$ (Ball is initially at rest)
Final velocity of the ball, $v=?$
Time taken by the ball to strike ground, $t=?$
It is known that,
From, third equation of motion: ${{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}=2as$
$\Rightarrow {{(v)}^{2}}-{{(0)}^{2}}=2(10)(20)$
$\Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}=400$
$\Rightarrow v=20m/s$
From, first equation of motion: $v=u+at$
$\Rightarrow 20=0+(10)t$
$\Rightarrow 20=10t$
$\Rightarrow t=2s$
Therefore, the ball strikes the ground after $2s$ with a velocity of $20m/s$.
29. The speed-time graph for a car is shown as a figure.
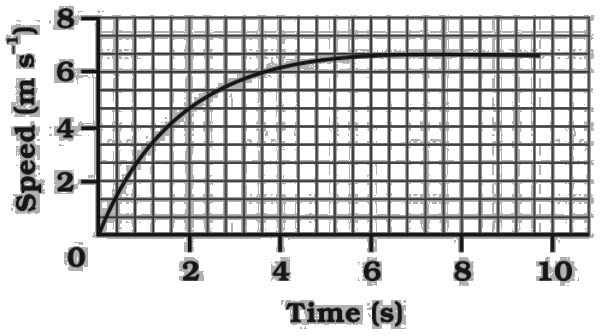
Find out how far the car travels in the first $4$seconds. Shade the area on the graph that represents the distance travelled by the car during the period.
Ans: Distance travelled by the car during the first $4$seconds is equal to the area of the shaded region on the graph.
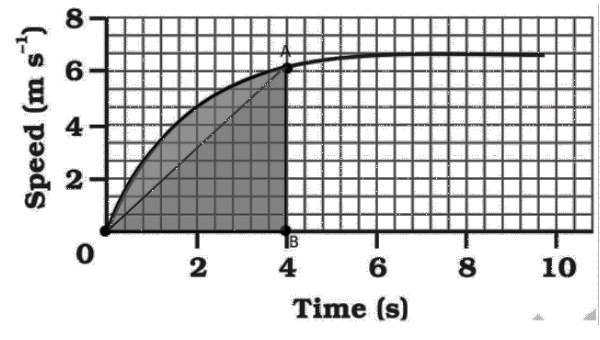
$Area=\frac{1}{2}\times 4\times 6=12m$
Therefore, the distance travelled by the car in first $4$seconds is $12m$.
Which part of the graph represents uniform motion of the car?
Ans: Horizontal line after $6$seconds represents the constant motion.
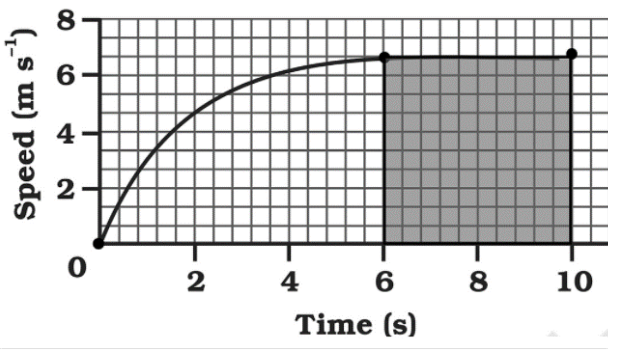
Therefore, the shaded part of the graph between time $6$seconds to $10$ seconds represent the uniform motion of the car.
30. State which of the following situations are possible and give an example for each of these:
An object with a constant acceleration but with zero velocity.
Ans: Possible.
For example, when a ball is thrown up at maximum height, it has zero velocity, although it will have constant acceleration due to gravity, equal to $9.8m/{{s}^{2}}$.
An object moving in a certain direction with an acceleration in the perpendicular direction.
Ans: Possible.
For example, when an object is moving in a circular track, its acceleration is perpendicular to the direction of velocity.
31. An artificial satellite is moving in a circular orbit of radius 42250 km. Calculate its speed if it takes 24 hours to revolve around the earth.
Ans. Given, the radius of the orbit = 42250 km
Therefore, circumference of the orbit = 2π42250km = 265571.42 km
Time is taken for the orbit = 24 hours
Therefore, speed of the satellite = 11065.4 km.h-1
The satellite orbits the Earth at a speed of 11065.4 kilometers per hour.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 7 - Motion
List of Topics Covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 7 - Motion | |
Topics | Subtopics |
Motion | Motion Along a Straight Line, Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion, Speed with Direction, |
Rate of Change of Velocity | |
Measuring the Rate of Motion | |
Graphical Representation of Motion | Distance-time graphs, Velocity-time graphs, |
Equations of Motions | |
Uniform Circulation Motion | |
Deleted Topics in Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion
Equations of Motion by Graphical Method
Equation for Velocity-Time Relation
Equation for Position-Time Relation
The equation for Position Velocity
Benefits of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion
NCERT Solutions motion class 9 questions answers uses a simple and easy-to-understand approach to teach students about various topics.
All the questions in the relevant NCERT textbooks are entirely solved for class 9 science chapter 7 question answer.
To assist students in their preparations, NCERT Solutions provides complete answers to NCERT solutions for class 9 science chapter 7 motion exercise.
These answers will come in handy for Science Olympiads, CBSE Term I exams, and other competitive exams.
A reference point or origin is required to explain the position of an object. To one observer, an object may appear to be moving while, to another, it appears to be motionless.
A convention, or a standard reference point or frame, is required to make observations easier. The reference frames of all objects must be the same.
Important Study Material Links for Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion
S.No. | Important Links for Class 9 Chapter 7 Science Study Material |
1. | |
2. | |
3. |
Conclusion
Motion class 9 NCERT solutions provide students with simple and detailed definitions and explanations of each concept covered in the chapter. Therefore, it is highly recommended that students download and refer to our comprehensive and expert-curated class 9 science ch 7 NCERT Solutions to get a gist of the chapter before the exam and to know how to answer the questions in the exam. Students can also refer to our plethora of other study resources related to this chapter, which are available for free on our website.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science - Other Chapter-Wise Links
Given below are the links for the other chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science. These solutions are provided by the Science experts at Vedantu in a detailed manner. Go through these chapter-wise solutions to be thoroughly familiar with the concepts.
S.No. | NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter-wise List |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | |
11 |
Important Study Material Links for Class 9 Science
S.No. | Important Links for Class 9 Science |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 |
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion - 2025-26
1. What will I learn from Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion?
In Motion Class 9, students learn how objects move and how this movement is measured. This chapter explains distance and displacement, speed and velocity, acceleration, and different types of motion in a clear and logical way. It also helps students understand motion through graphs and real-life examples.
2. Are NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 7 enough for CBSE exams?
Yes, Class 9 Motion NCERT Solutions are sufficient for CBSE exams as they are strictly based on the NCERT textbook. All Class 9 Science Chapter 7 questions and answers are explained step by step, which helps students write accurate and well-structured answers in exams.
3. How do NCERT Solutions help in solving Motion numericals easily?
The Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion exercise question answers explain every numerical problem using proper formulas, correct units, and logical steps. Regular practice with these solutions improves speed, accuracy, and confidence while solving numericals related to velocity, acceleration, and motion graphs.
4. What types of questions are covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion?
This chapter includes:
Conceptual questions
Numerical problems
Motion graph-based questions
Short and long answer questions
All these are covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 7 question answers as per the latest NCERT and CBSE pattern.
5. How can I score well in Motion Class 9 exams?
To score well in Class 9 Science Chapter 7, students should:
Clearly understand formulas and definitions
Practice Motion Class 9 questions answers regularly
Learn how to interpret distance-time and velocity-time graphs
Revise solved examples before exams
Using NCERT-based solutions ensures concept clarity and exam readiness.
6. Is Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion important for higher classes?
Yes, Motion Class 9 is a foundational chapter for Physics in higher classes. Concepts like velocity, acceleration, and graphs are used extensively in Class 10 and Class 11 Physics, making this chapter very important for future learning.
7. Can I download Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion exercise question answers PDF?
Yes, students can download the Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion exercise question answer PDF to study offline. PDF format helps in quick revision and makes exam preparation more convenient.
8. How should I start studying Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion?
Begin by understanding basic terms like distance, displacement, speed, and velocity. Then move on to numericals and graphs. Solving Class 9 Science Ch 7 Motion question answers regularly will help build strong fundamentals and improve problem-solving skills.
9. Are these Motion Class 9 questions useful for competitive exams?
Yes. The concepts covered in Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion are essential for exams like Olympiads and future entrance exams. NCERT-based preparation builds strong conceptual clarity needed for competitive exams as well.
10. Why should students rely on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 7?
NCERT Solutions present accurate, exam-oriented, and easy-to-understand explanations. They help students avoid common mistakes, improve logical thinking, and master all Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Motion questions and answers effectively.














 Watch Video
Watch Video
















