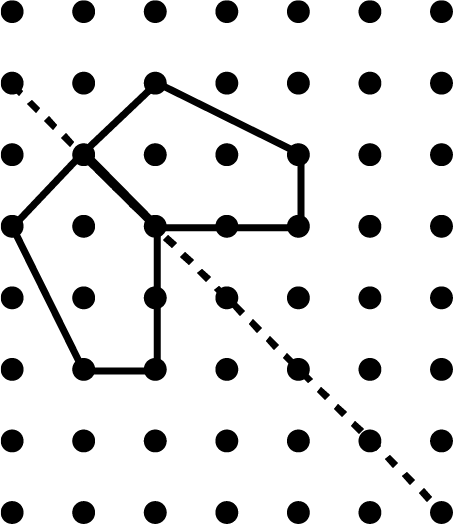
Symmetry - Exercise-wise Questions and Answers For Class 7 Maths - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Maths Chapter 12 Symmetry - 2025-26
1. Where can I find the correct, step-by-step NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 12, Symmetry?
You can find comprehensive and accurate NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 12 for the academic year 2025-26 on Vedantu. These solutions provide detailed, step-by-step answers for all questions in exercises 12.1, 12.2, and 12.3, helping you understand the correct CBSE methodology for solving problems related to line and rotational symmetry.
2. What is the best way to use the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 12 to score well in exams?
For effective exam preparation, first attempt to solve the Chapter 12 exercises yourself. Afterwards, use the Vedantu NCERT Solutions to verify your answers and, more importantly, to understand the problem-solving method. Pay close attention to how the solutions identify the centre of rotation, angle of rotation, and lines of symmetry, as these steps are crucial for marks.
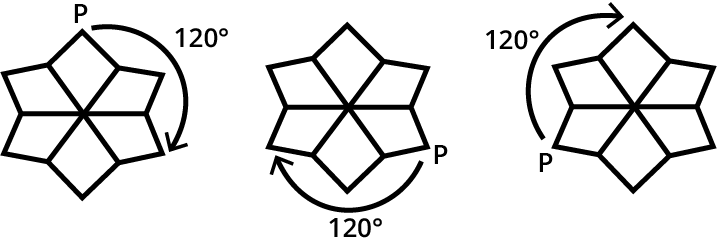
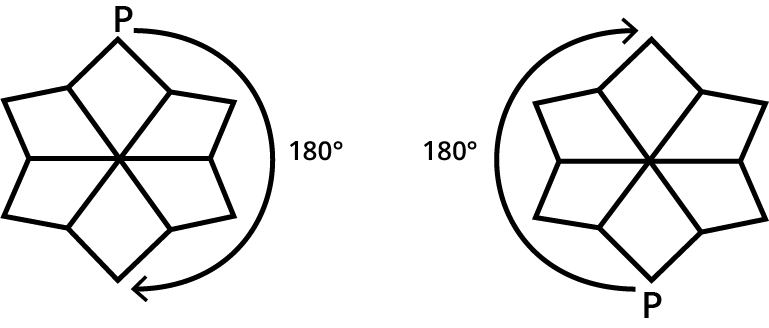
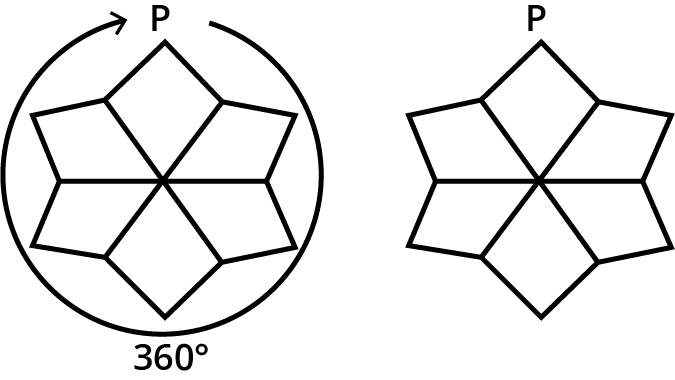
3. How do the NCERT Solutions explain the method for finding the order of rotational symmetry?
The NCERT Solutions explain a clear, step-by-step method to determine the order of rotational symmetry. The process is as follows:
- First, identify the centre of rotation, which is the fixed point around which the figure turns.
- Next, mentally or physically rotate the figure a full 360 degrees.
- Count how many times the figure looks identical to its starting position during this full rotation.
- This number represents the order of rotational symmetry. For example, a square has an order of 4.
4. What types of questions are covered in the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 12?
The solutions for Chapter 12 cover all concepts from the NCERT textbook, including:
- Identifying and drawing lines of symmetry in various geometric figures.
- Completing shapes that are partially drawn along a mirror line.
- Finding the centre of rotation, angle of rotation, and order of rotational symmetry.
- Solving problems on shapes that have line symmetry, rotational symmetry, both, or neither.
5. What is the key difference between line symmetry and rotational symmetry as explained in the solved problems for Chapter 12?
The key difference highlighted in the solved problems is the type of transformation. Line symmetry is related to reflection, where a figure is divided into two identical mirror halves by a line. Rotational symmetry, on the other hand, is about a figure looking the same after being turned around a central point by a certain angle. The solutions clarify this by providing examples, like a parallelogram which has rotational symmetry but no line symmetry.
6. How can the methods from the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 12 be applied to identify symmetry in real life?
The problem-solving techniques from Chapter 12 are directly applicable to the world around us. You can use the concept of line symmetry to analyse the design of a butterfly's wings or a building's facade. Similarly, the method for finding rotational symmetry helps you understand patterns in car wheels, windmills, and flowers. Mastering the solutions helps you see these mathematical principles in everyday objects.
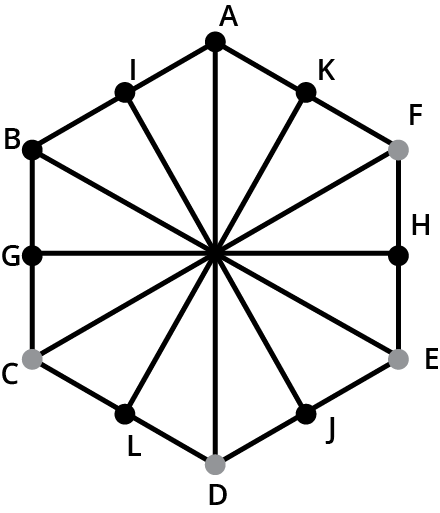
7. Why does a circle have infinite lines of symmetry but only one centre of rotation?
A circle has infinite lines of symmetry because any line that passes through its centre (a diameter) will divide it into two perfect mirror-image halves. Since an infinite number of such lines can be drawn, it has infinite lines of symmetry. However, all these rotations happen around a single fixed point: the centre. Therefore, it has only one centre of rotation, a concept that becomes clear when solving problems from the NCERT exercises.
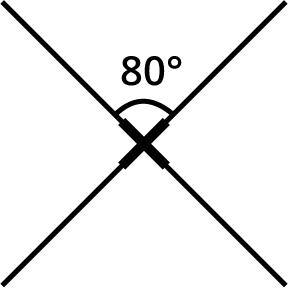
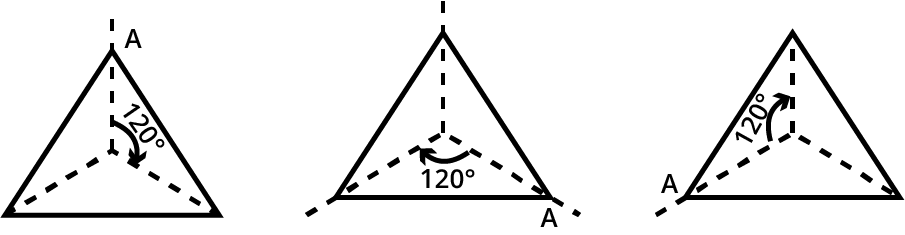
8. If a figure's smallest angle of rotation is 60°, how can I determine its order of rotational symmetry using the NCERT method?
The NCERT method establishes a relationship between the angle of rotation and the order. To find the order, you divide the total angle of a full turn (360°) by the smallest angle of rotation at which the figure looks the same.
Calculation:
Order of Rotational Symmetry = 360° / Smallest Angle of Rotation
Order = 360° / 60° = 6
Thus, the figure has an order of rotational symmetry of 6. This demonstrates how understanding the core concept helps solve problems without needing to draw the figure.