
Fractions And Decimals - Exercise-wise Questions and Answers For Class 7 Maths - Free PDF Download
Here are the NCERT solutions for fractions and decimals Class 7. In order to improve their exam scores, students can practice answering various kinds of questions linked to this chapter either online or by downloading these files. In previous lessons, students have learned how to add and subtract decimals as well as fractions. In this lesson, students will learn how to multiply and divide decimals, as well as fractions. These Class 7 Maths Chapter 2 Solutions, which include fractions and decimals, have been created by experts in the field to help students prepare for their exams.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentGlance on Maths Chapter 2 Class 7 - Fractions and Decimals
Basic calculations like adding, subtracting, comparing, and ranking fractions are covered in this chapter.
We work on word problems, such as applying concepts like fractions to real-life scenarios.
We cover higher-order thinking questions that test your ability to evaluate and resolve issues with decimals and fractions.
Focus on concepts like adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing fractions, and confidently convert between fractions and decimals.
This article contains chapter notes, important questions, and exercise links for Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals, which you can download as PDFs.
There are five exercises (31 fully solved questions) in class 7th maths chapter 2 Fractions and Decimal.
Access Exercise Wise NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2 Maths Class 7
Exercises Under NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals
Exercise 2.1: Multiplication of Fractions
Multiplying Fractions by Whole Numbers: Understanding how to multiply fractions by whole numbers.
Multiplying Two Fractions: Learning the method to multiply two fractions.
Multiplying Mixed Numbers: Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions and then multiplying them.
Exercise 2.2: Division of Fractions
Reciprocal of a Fraction: Introduction to the concept of reciprocals.
Dividing Fractions by Whole Numbers: Method to divide fractions by whole numbers using reciprocals.
Dividing a Fraction by Another Fraction: Understanding the steps to divide one fraction by another fraction.
Word Problems: Applying division of fractions to solve real-life problems.
Exercise 2.3: Multiplication of Decimal Numbers
This section in Maths Class 7 Chapter 2 covers the rules and methods for multiplying decimal numbers. It includes step-by-step instructions for aligning the decimal points and performing multiplication, followed by placing the decimal point in the product correctly. Practical examples and problems help reinforce the concept and provide practice in multiplying decimals in various contexts.
Exercise 2.4: Division of Decimal Numbers
This section focuses on dividing decimal numbers, explaining how to handle the decimal point in both the dividend and the divisor. It includes methods for converting the divisor into a whole number by multiplying both the dividend and the divisor by a power of ten. The section in Class 7 Fractions and Decimals provides numerous examples and exercises to practice the division of decimals, ensuring a clear understanding of the process.
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 2 – Fractions and Decimals
Exercise - 2.1
1. Which of the drawings $(a)\,to\,(d)$ show:
(i). $\text{2 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{5}}$
(a)

Ans: corresponds to $\text{(d)}$
Because, $2\times \dfrac{1}{5}=\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{5}$
(ii). $\text{2 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}$
(b)

Ans: corresponds to $\text{(b)}$
Because, $2\times \dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}$
(iii). $\text{3 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\dfrac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}$
(c)

Ans: corresponds to $\text{(a)}$
Because, $3\times \dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{2}{3}$
(iv). $\text{3 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}$
(d)
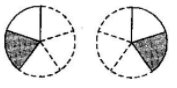
Ans: Corresponds to $\text{(c)}$
Because, $3\times \dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}$
2. Some pictures $\left( \text{a} \right)\,\text{to}\,\left( \text{c} \right)$ are given below. Tell which of them show:
(i). $\text{3 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{5}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}$
(a)
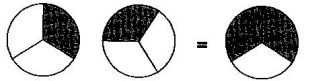
Ans: Corresponds to $\text{(c)}$
Because, $3\times \dfrac{1}{5}=\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{5}$
(ii). $\text{2 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}\text{=}\dfrac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}$
(b)
Ans: Corresponds to $\text{(a)}$
Because, $2\times \dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{3}$
(iii). $\text{3 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\text{=2}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}$
(c)

Ans: Corresponds to $\text{(b)}$
Because, $3\times \frac{3}{4}=\frac{3}{4}+\frac{3}{4}+\frac{3}{4}$
3. Multiply and reduce to lowest form and convert into a mixed fraction:
(i). $\text{7 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form and converting into a mixed fraction,
$7\times \frac{3}{5}=\frac{7\times 3}{5}=\frac{21}{5}=4\frac{1}{5}$
(ii). $\text{4 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form and converting into a mixed fraction,
$4\times \frac{1}{3}=\frac{4\times 1}{3}=\frac{4}{3}=1\frac{1}{3}$
(iii). $\text{2 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{6}}{\text{7}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form and converting into a mixed fraction,
$2\times \frac{6}{7}=\frac{2\times 6}{7}=\frac{12}{7}=1\frac{5}{7}$
(iv). $\text{5 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{2}}{\text{9}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form and converting into a mixed fraction,
$5\times \frac{2}{9}=\frac{5\times 2}{9}=\frac{10}{9}=1\frac{1}{9}$
(v). $\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 4}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form and converting into a mixed fraction,
$\frac{2}{3}\times 4=\frac{2\times 4}{3}=\frac{8}{3}=2\frac{2}{3}$
(vi) $\frac{\text{5}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 6}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form and converting into a mixed fraction,
$\frac{5}{2}\times 6=5\times 3=15$
(vii) $\text{11 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{4}}{\text{7}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form and converting into a mixed fraction,
$11\times \frac{4}{7}=\frac{11\times 4}{7}=\frac{44}{7}=6\frac{2}{7}$
(viii) $\text{20 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{4}}{\text{5}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form and converting into a mixed fraction,
$20\times \frac{4}{5}=4\times 4=16$
(ix) $\text{13 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form and converting into a mixed fraction,
$13\times \frac{1}{3}=\frac{13\times 1}{3}=\frac{13}{3}=4\frac{1}{3}$
(x) $\text{15 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form and converting into a mixed fraction,
$15\times \frac{3}{5}=3\times 3=9$
4. Shade:
(i). $\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}$ of the circles in box
(ii).
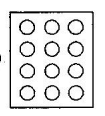
Ans: Half of the circles in the box are,
$\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\,\text{of}\,\text{12}\,\text{circles=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 12=6}\,\text{circles}$

(iii). $\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}$ of the triangles in box
(b)
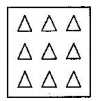
Ans: Two-third of the triangles in the box are,$\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\,\text{of}\,\text{9}\,\text{triangles=}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 9=2 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 3=6}\,\text{triangles}$

(iv). $\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}$ of the squares inbox
(v). (c)
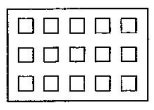
Ans: Three-fifth of the squares in the box are,
$\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}\,\text{of}\,\text{15}\,\text{squares=}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 15=3 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 3=9}\,\text{squares}$

5. Find
(a).$\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\,\text{of}\,\text{(i)}\,\text{24}\,\text{(ii)}\,\text{46}$
Ans:
(i) Calculating the value,
$\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\,\text{of}\,\text{24=12}$
(ii) Calculating the value,
$\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\,\text{of}\,\text{46=23}$
(b). $\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\,\text{of}\,\text{(i)}\,\text{18}\,\text{(ii)}\,\text{27}$
Ans:
(i) Calculating the value, $\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\,\text{of}\,\text{18=}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 18=2 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 6=12}$
(ii) Calculating the value, $\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\,\text{of}\,\text{27=}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 27=2 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 9=18}$
(c) $\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\,\text{of}\,\text{(i)}\,\text{16}\,\text{(ii)}\,\text{36}$
Ans:
(i) Calculating the value,
$\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\,\text{of}\,\text{16=}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 16=3 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 4=12}$
(ii) Calculating the value,
$\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\,\text{of}\,36\text{=}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 36=3 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 9=27}$
(d) $\frac{\text{4}}{\text{5}}\,\text{of}\,\text{(i)}\,\text{20}\,\text{(ii)}\,\text{35}$
Ans:
(i) Calculating the value,
$\frac{\text{4}}{\text{5}}\,\text{of}\,20\text{=}\frac{\text{4}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 20=4 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 4=16}$
(ii) Calculating the value,
$\frac{\text{4}}{\text{5}}\,\text{of}\,35\text{=}\frac{\text{4}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 35=4 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 7=28}$
6. Multiply and express as a mixed fraction:
(a) $\text{3 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 5}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{5}}$
Ans: Multiplying and expressing the term as mixed fraction,
$3\times 5\frac{1}{5}=3\times \frac{26}{5}=\frac{3\times 26}{5}=\frac{78}{5}=15\frac{3}{5}$
(b) $\text{5 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 6}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}$
Ans: Multiplying and expressing the term as mixed fraction,
$5\times 6\frac{3}{4}=5\times \frac{27}{4}=\frac{5\times 27}{4}=\frac{135}{4}=33\frac{3}{4}$
(c) $\text{7 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 2}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}$
Ans: Multiplying and expressing the term as mixed fraction,
$7\times 2\frac{1}{4}=7\times \frac{9}{4}=\frac{7\times 9}{4}=\frac{63}{4}=15\frac{3}{4}$
(d) $\text{4 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 6}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}$
Ans: Multiplying and expressing the term as mixed fraction,
$4\times 6\frac{1}{3}=4\times \frac{19}{3}=\frac{4\times 19}{3}=\frac{76}{3}=25\frac{1}{3}$
(e) $\text{3}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 6}$
Ans: Multiplying and expressing the term as mixed fraction,
$3\frac{1}{4}\times 6=\frac{13}{4}\times 6=\frac{13\times 3}{2}=\frac{39}{2}=19\frac{1}{2}$
(f) $\text{3}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 8}$
Ans: Multiplying and expressing the term as mixed fraction,
$3\frac{2}{5}\times 8=\frac{17}{5}\times 8=\frac{17\times 8}{5}=\frac{136}{5}=27\frac{1}{5}$
7. Find:
(a) $\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\,\text{of}\,\text{(i)}\,\text{2}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\,\text{(ii)}\,\text{4}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{9}}$
Ans:
(i) Calculating the value, \[\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\,\text{of}\,\text{2}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 2}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{11}}{\text{4}}\text{=}\frac{\text{11}}{\text{8}}\text{=1}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{8}}\]
(ii) Calculating the value, \[\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\,\text{of}\,\text{4}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{9}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 4}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{9}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{38}}{\text{9}}\text{=}\frac{\text{19}}{\text{9}}\text{=2}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{9}}\]
(b) $\frac{\text{5}}{\text{8}}\,\text{of}\,\text{(i)}\,\text{3}\frac{\text{5}}{\text{6}}\,\text{(ii)}\,\text{9}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}$
Ans:
(i) Calculating the value, \[\frac{\text{5}}{\text{8}}\,\text{of}\,\text{3}\frac{\text{5}}{\text{6}}\text{=}\frac{\text{5}}{\text{8}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 3}\frac{\text{5}}{\text{6}}\text{=}\frac{\text{5}}{\text{8}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{23}}{\text{6}}\text{=}\frac{\text{115}}{\text{48}}\text{=2}\frac{\text{19}}{\text{48}}\]
(ii) Calculating the value, \[\frac{\text{5}}{\text{8}}\,\text{of}\,\text{9}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\text{=}\frac{\text{5}}{\text{8}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 9}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\text{=}\frac{\text{5}}{\text{8}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{29}}{\text{3}}\text{=}\frac{\text{145}}{\text{24}}\text{=6}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{24}}\]
8. Vidya and Pratap went for a picnic. Their mother gave them a water bottle that contained $\text{5}$ liters of water. Vidya consumed $\frac{\text{2}}{\text{5}}$ of the water. Pratap consumed the remaining water.
(i). How much water did Vidya drink?
Ans: Water consumed by Vidya is,$\text{=}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{5}}\,\text{of}\,\text{5}\,\text{litres=}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 5=2}\,\text{litres}$
Hence, Vidya drank $2$ litres of water from the bottle.
(ii). What fraction of the total quantity of water did Pratap drink?
Ans: Water consumed by Pratap \[\text{= }\left( \text{1-}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{5}} \right)\text{ }\]part of bottle
Pratap consumed $\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}\,\text{of}\,\text{5}\,\text{litres}\,\text{water=}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 5=3}\,\text{lites}$
Hence, Pratap drank $\frac{3}{5}$ part of the total quantity of water present in the bottle.
Exercise - 2.2
1. Find:
(i) $\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\,\text{of}$ (a) $\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}$ (b) $\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}$ (c) $\frac{\text{4}}{\text{3}}$
Ans:
(a) Calculating the value,
$\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 1}}{\text{4 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 4}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{16}}$
(b) Calculating the value,
$\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 3}}{\text{4 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 4}}\text{=}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{16}}$
(c) Calculating the value,
$\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{4}}{\text{3}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{4}}{\text{3}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 4}}{\text{4 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 3}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}$
(ii) \[\frac{\text{1}}{\text{7}}\,\text{of}\] (a) \[\frac{\text{2}}{\text{9}}\] (b) \[\frac{\text{6}}{\text{5}}\] (c) $\frac{\text{3}}{\text{10}}$
Ans:
(a) Calculating the value,
$\frac{\text{1}}{\text{7}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{2}}{\text{9}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{7}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{2}}{\text{9}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 2}}{\text{7 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 9}}\text{=}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{63}}$
(b) Calculating the value,
$\frac{\text{1}}{\text{7}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{2}}{\text{9}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{7}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{6}}{\text{5}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 6}}{\text{7 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 5}}\text{=}\frac{\text{6}}{\text{35}}$
(c) Calculating the value,
$\frac{\text{1}}{\text{7}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{2}}{\text{9}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{7}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{3}}{\text{10}}\text{=}\frac{\text{1 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 3}}{\text{7 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 10}}\text{=}\frac{3}{70}$
2. Multiply and reduce to lowest form (if possible):
(i) $\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 2}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form,
$\frac{2}{3}\times 2\frac{2}{3}=\frac{2}{3}\times \frac{8}{3}=\frac{2\times 8}{3\times 3}=\frac{16}{9}=1\frac{7}{9}$
(ii) $\frac{\text{2}}{\text{7}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{7}}{\text{9}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form,
$\frac{2}{7}\times \frac{7}{9}=\frac{2\times 7}{7\times 9}=\frac{2}{9}$
(iii) $\frac{\text{3}}{\text{8}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{6}}{\text{4}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form,
$\frac{3}{8}\times \frac{6}{4}=\frac{3\times 6}{8\times 4}=\frac{3\times 3}{8\times 2}=\frac{9}{16}$
(iv) $\frac{\text{9}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form,
$\frac{9}{5}\times \frac{3}{5}=\frac{9\times 3}{5\times 5}=\frac{27}{25}=1\frac{2}{25}$
(v) $\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{15}}{\text{8}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form,
$\frac{1}{3}\times \frac{15}{8}=\frac{1\times 15}{3\times 8}=\frac{1\times 5}{1\times 8}=\frac{5}{8}$
(vi) $\frac{\text{11}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{3}}{\text{10}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form,
$\frac{11}{2}\times \frac{3}{10}=\frac{11\times 3}{2\times 10}=\frac{33}{20}=1\frac{3}{20}$
(vii) $\frac{\text{4}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{12}}{\text{7}}$
Ans: Multiplying and reducing to lowest form,
$\frac{4}{5}\times \frac{12}{7}=\frac{4\times 12}{5\times 7}=\frac{48}{35}=1\frac{13}{35}$
3. Multiply the following fractions:
(i) $\frac{\text{2}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 5}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}$
Ans: Performing multiplication,
$\frac{2}{5}\times 5\frac{1}{4}=\frac{2}{5}\times \frac{21}{4}=\frac{2\times 21}{5\times 4}=\frac{1\times 21}{5\times 2}=\frac{21}{10}=2\frac{1}{10}$
(ii) $\text{6}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{7}}{\text{9}}$
Ans: Performing multiplication,
$6\frac{2}{5}\times \frac{7}{9}=\frac{32}{5}\times \frac{7}{9}=\frac{32\times 7}{5\times 9}=\frac{224}{45}=4\frac{44}{45}$
(iii) $\frac{\text{3}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 5}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}$
Ans: Performing multiplication,
$\frac{3}{2}\times 5\frac{1}{3}=\frac{3}{2}\times \frac{16}{3}=\frac{48}{6}=8$
(iv) $\frac{\text{5}}{\text{6}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 2}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{7}}$
Ans: Performing multiplication,
$\frac{5}{6}\times 2\frac{3}{7}=\frac{5}{6}\times \frac{17}{7}=\frac{85}{42}=2\frac{1}{42}$
(v) $\text{3}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{4}}{\text{7}}$
Ans: Performing multiplication,
$3\frac{2}{5}\times \frac{4}{7}=\frac{17}{7}\times \frac{4}{7}=\frac{68}{35}=1\frac{33}{35}$
(vi) $\text{2}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 3}$
Ans: Performing multiplication,
$2\frac{3}{5}\times 3=\frac{13}{5}\times \frac{3}{1}=\frac{13\times 3}{5\times 1}=\frac{39}{5}=7\frac{4}{5}$
(vii) $\text{3}\frac{\text{4}}{\text{7}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}$
Ans: Performing multiplication,
$3\frac{4}{7}\times \frac{3}{5}=\frac{25}{7}\times \frac{3}{5}=\frac{5\times 3}{7\times 1}=\frac{15}{7}=2\frac{1}{7}$
4. Which is greater:
(i) $\frac{\text{2}}{\text{7}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\,\text{or}\,\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{5}}{\text{8}}$
Ans: Calculating the greater term,
$\frac{\text{2}}{\text{7}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\,\text{or}\,\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{5}}{\text{8}}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{2}}{\text{7}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\,\text{or}\,\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{5}}{\text{8}}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{3}}{\text{14}}\,\text{or}\,\frac{\text{3}}{\text{8}}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{3}{14}<\frac{3}{8}$
Hence, $\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{5}}{\text{8}}$ is greater.
(ii) $\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{6}}{\text{7}}\,\text{or}\,\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{3}}{\text{7}}$
Ans:
Calculating the greater term,
$\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{6}}{\text{7}}\,\text{or}\,\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{3}}{\text{7}}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{6}}{\text{7}}\,\text{or}\,\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{3}}{\text{7}}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{6}}{\text{14}}\,\text{or}\,\frac{\text{2}}{\text{7}}$ $\Rightarrow \frac{\text{6}}{\text{14}}>\frac{\text{2}}{\text{7}}$
Hence, $\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\,\text{of}\,\frac{\text{6}}{\text{7}}$ is greater.
5. Saili plants \[\text{4}\] saplings in a row in her garden. The distance between
two adjacent saplings is \[\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\] m. Find the
distance between the first and the last sapling.
Ans: Given: Saili plants \[4\] saplings in a row where the distance between two
adjacent saplings $=\frac{3}{4}$m.
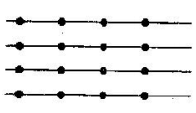
The number of gaps in saplings \[=\text{ }3\]
Hence,
The distance between the first and the last saplings$\text{=3 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\text{=}\frac{\text{9}}{\text{4}}\text{m=2}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\text{m}$
Therefore, the distance between the first and the last saplings is $\text{2}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{4}}\,\text{m}$
6. Lipika reads a book for $\text{1}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}$ hours every day.
She reads the entire book in \[\text{6}\] days. How many hours in all were
required by her to read the book?
Ans: Given: Time taken for reading a book by Lipika $=1\frac{3}{4}$ hours.
Lipika reads the entire book in $6$ days
Calculating the Total hours taken by Lipika to read the entire book,
$=1\frac{3}{4}\times 6=\frac{7}{4}\times 6=\frac{21}{2}=10\frac{1}{2}$ hours.
Hence, it would take $10$ hours to read the book.
7. A car runs $\text{16}$ km using \[\text{1}\] litre of petrol. How much
distance will it cover using $\text{2}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}$ litres of
petrol?
Ans: Given: A car covers the distance$\text{=16}\,\text{km}$ in $1$ litre of
petrol.
Calculating the distance covered by car in $2\frac{3}{4}$ litres of petrol,
Distance$\text{=2}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}\,\text{of}\,\text{16}\,\text{km=}\frac{\text{11}}{\text{4}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 16=44}\,\text{km}$
Therefore, car will cover a distance of $44$ km in $2\frac{3}{4}$ litres of petrol.
8. (a)
(i) Provide the number in the box , such that
$\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\text{=}\frac{\text{10}}{\text{30}}$
Ans: The number inside the box should be $\frac{2}{3}\times =\frac{10}{30}$
(ii) The simplest form of the number obtained in $$ is _____.
Ans: The simplest form of the number obtained in
$\frac{\text{5}}{\text{10}}\,\text{is}\,\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}$
(b)
(i) Provide the number in the box $$ , such that $\frac{3}{5}\times =\frac{24}{75}$.
Ans: The number inside the box should be $\frac{3}{5}\times =\frac{24}{75}$
(ii) The simplest form of the number obtained in is______.
Ans: The simplest form of the number obtained in
$\frac{\text{8}}{\text{15}}\,\text{is}\,\frac{\text{8}}{\text{15}}$
Exercise - 2.3
1. Find:
(i) $\text{12 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{3}}{\text{4}}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$12\div \frac{3}{4}=12\times \frac{4}{3}=16$
(ii) $\text{14 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{5}}{\text{6}}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$14\div \frac{5}{6}=14\times \frac{6}{5}=\frac{84}{5}=16\frac{4}{5}$
(iii) $\text{8 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{7}}{\text{3}}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$8\div \frac{7}{3}=8\times \frac{3}{7}=\frac{24}{7}=3\frac{3}{7}$
(iv) $\text{4 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{8}}{\text{3}}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$4\div \frac{8}{3}=4\times \frac{3}{8}=\frac{3}{2}=1\frac{1}{2}$
(v) $\text{3 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 2}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$3\div 2\frac{1}{3}=3\div \frac{7}{3}=3\times \frac{3}{7}=\frac{9}{7}=1\frac{2}{7}$
(vi) \[\text{5 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 3}\frac{\text{4}}{\text{7}}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
$5\div 3\frac{4}{7}=5\div \frac{25}{7}=5\times \frac{7}{25}=\frac{7}{5}=1\frac{2}{5}$
2. Find the reciprocal of each of the following fractions. Classify the
reciprocals as proper fraction, improper fractions and whole numbers.
(i) $\frac{\text{3}}{\text{7}}$
Ans: Calculating the reciprocal and stating the type of the fraction,
Reciprocal of $\frac{\text{3}}{\text{7}}\text{=}\frac{\text{7}}{\text{3}}\to \text{Improper}\,\text{fraction}$
(ii) $\frac{\text{5}}{\text{8}}$
Ans: Calculating the reciprocal and stating the type of the fraction,
Reciprocal of$\frac{\text{5}}{\text{8}}\text{=}\frac{\text{8}}{\text{5}}\to \text{Improper}\,\text{fraction}$
(iii) $\frac{\text{9}}{\text{7}}$
Ans: Calculating the reciprocal and stating the type of the fraction,
Reciprocal of $\frac{\text{9}}{\text{7}}\text{=}\frac{\text{7}}{\text{9}}\to \text{Proper}\,\text{fraction}$
(iv) $\frac{\text{6}}{\text{5}}$
Ans: Calculating the reciprocal and stating the type of the fraction,
Reciprocal of $\frac{\text{6}}{\text{5}}\text{=}\frac{\text{5}}{\text{6}}\to \text{Proper}\,\text{fraction}$
(v) $\frac{\text{12}}{\text{7}}$
Ans: Calculating the reciprocal and stating the type of the fraction,
Reciprocal of $\frac{\text{12}}{\text{7}}\text{=}\frac{\text{7}}{\text{12}}\to \text{Proper}\,\text{fraction}$
(vi) $\frac{\text{1}}{\text{8}}$
Ans: Calculating the reciprocal and stating the type of the fraction,
Reciprocal of $\frac{\text{9}}{\text{7}}\text{=8}\to \text{Whole number}$
(vii) $\frac{\text{1}}{\text{11}}$
Ans: Calculating the reciprocal and stating the type of the fraction,
Reciprocal of $\frac{\text{1}}{\text{11}}\text{=11}\to \text{Whole number}$
3. Find:
(i) $\frac{\text{7}}{\text{3}}\text{ }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 2}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$\frac{7}{3}\div 2=\frac{7}{3}\times \frac{1}{2}=\frac{7\times 1}{3\times 2}=\frac{7}{6}=1\frac{1}{6}$
(ii) $\frac{\text{4}}{\text{9}}\text{ }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 5}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$\frac{4}{9}\div 5=\frac{4}{9}\times \frac{1}{5}=\frac{4\times 1}{9\times 5}=\frac{4}{45}$
(iii) $\frac{\text{6}}{\text{13}}\text{ }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 7}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$\frac{6}{13}\div 7=\frac{6}{13}\times \frac{1}{7}=\frac{6\times 1}{13\times 7}=\frac{6}{91}$
(iv) $\text{4}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}\text{ }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 3}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$4\frac{1}{3}\div 3=\frac{13}{3}\div 3=\frac{13}{3}\times \frac{1}{3}=\frac{13}{9}=1\frac{4}{9}$
(v) $\text{3}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 4}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$3\frac{1}{2}\div 4=\frac{7}{2}\div 4=\frac{7}{2}\times \frac{1}{4}=\frac{7}{8}$
(vi) $\text{4}\frac{\text{3}}{\text{7}}\text{ }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 7}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$4\frac{3}{7}\div 7=\frac{31}{7}\div 7=\frac{31}{7}\times \frac{1}{7}=\frac{31}{49}$
4. Find:
(i) $\frac{\text{2}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$\frac{2}{5}\div \frac{1}{2}=\frac{2}{5}\times \frac{2}{1}=\frac{2\times 2}{5\times 1}=\frac{4}{5}$
(ii) $\frac{\text{4}}{\text{9}}\text{ }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$\frac{4}{9}\div \frac{2}{3}=\frac{4}{9}\times \frac{3}{2}=\frac{2}{3}$
(iii) $\frac{\text{3}}{\text{7}}\text{ }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{8}}{\text{7}}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$\frac{3}{7}\div \frac{8}{7}=\frac{3}{7}\times \frac{7}{8}=\frac{3}{8}$
(iv) $\text{2}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{3}}\text{ }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{3}}{\text{5}}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$2\frac{1}{3}\div \frac{3}{5}=\frac{7}{3}\div \frac{3}{5}=\frac{7}{3}\times \frac{5}{3}=\frac{35}{9}=3\frac{8}{9}$
(v) $\text{3}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ }\frac{\text{8}}{\text{3}}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$3\frac{1}{2}\div \frac{8}{3}=\frac{7}{2}\div \frac{3}{8}=\frac{7}{2}\times \frac{3}{8}=\frac{7\times 3}{2\times 8}=\frac{21}{16}=1\frac{5}{16}$
(vi) $\frac{\text{2}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 1}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$2\frac{1}{3}\div \frac{3}{5}=\frac{2}{5}\div 1\frac{1}{2}=\frac{2}{5}\div \frac{3}{2}=\frac{2}{5}\times \frac{2}{3}=\frac{2\times 2}{5\times 3}=\frac{4}{15}$
(vii) $\text{3}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 1}\frac{\text{2}}{\text{3}}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$3\frac{1}{5}\div 1\frac{2}{3}=\frac{16}{5}\div \frac{5}{3}=\frac{16}{5}\times \frac{3}{5}=\frac{16\times 3}{5\times 5}=\frac{48}{25}=1\frac{23}{25}$
(viii) $\text{2}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{5}}\text{ }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 1}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{5}}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
$2\frac{1}{5}\div 1\frac{1}{5}=\frac{11}{5}\div \frac{6}{5}=\frac{11}{5}\times \frac{5}{6}=\frac{11}{6}=1\frac{5}{6}$
Exercise 2.4
1. Find:
(i) $\text{0}\text{.2 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 6}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[0.2\times 6=1.2\]
(ii) $\text{8 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 4}\text{.6}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[8\times 4.6=36.8\]
(iii) $\text{2}\text{.71 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 5}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[2.71\times 5=13.55\]
(iv) $\text{20}\text{.1 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 4}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[20.1\times 4=80.4\]
(v) $\text{0}\text{.05 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 7}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[0.05\times 7=0.35\]
(vi) $\text{211}\text{.02 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 4}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[211.02\times 4=844.08\]
(vii) $\text{2 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 0}\text{.86}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[2\times 0.86=1.72\]
2. Find the area of rectangle whose length is \[\text{5}\text{.7 cm}\] and
breadth is \[\text{3 cm}\text{.}\]
Ans: Given: The \[\text{Length of rectangle = 5}\text{.7 cm and Breadth of
rectangle = 3 cm}\]
Applying the area of rectangle formula,
\[\text{Area of rectangle = Length x Breadth}\]
\[\text{= 5}\text{.7 x 3 = 17}\text{.1 c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}\]
Hence, the area of rectangle is $\text{17}\text{.1}\,\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}$.
3. Find:
(i) \[\text{1}\text{.3 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 10}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
$1.3\times 10=13.0$
(ii) \[\text{36}\text{.8 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 10}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
$36.8\times 10=368.0$
(iii) \[\text{153}\text{.7 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 10}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
$153.7\times 10=1537.0$
(iv) \[\text{168}\text{.07 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 10}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
$168.07\times 10=1680.7$
(v) \[\text{31}\text{.1 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 100}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
$31.1\times 100=3110.0$
(vi) \[\text{156}\text{.1 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 100}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
$156.1\times 100=15610.0$
(vii) \[\text{3}\text{.62 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 100}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
$3.62\times 100=362.0$
(viii) \[\text{43}\text{.07 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 100}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
$43.07\times 100=4307.0$
(ix) \[\text{0}\text{.5 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 10}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
$0.5\times 10=5.0$
(x) \[\text{0}\text{.08 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 10}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
$0.08\times 10=0.80$
(xi) \[\text{0}\text{.9 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 100}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
$0.9\times 100=90.0$
(xii) \[\text{0}\text{.03 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 1000}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
$0.03\times 1000=30.0$
4. A two-wheeler covers a distance of\[\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ 55}\text{.3
km}\]
in one litre of petrol. How much distance will it cover in \[\text{10 litres}\] of
petrol?
Ans: Given: In one litre a two-wheeler covers a distance\[\text{ = 55}\text{.3
km}\]
Since distance covered in one litre by a two-wheeler\[\text{ = 55}\text{.3 km}\]
\[\therefore \,\,\text{In 10 litrs, a two- wheeler covers a distance = 55}\text{.3 x 10 = 553}\text{.0 km}\]
Hence, $553$ km distance will be covered by two-wheeler in $10$ litres of petrol.
5. Find:
(i) $\text{2}\text{.5 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 0}\text{.3}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[\text{2}\text{.5 x 0}\text{.3 = 0}\text{.75}\]
(ii) $\text{0}\text{.1 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 51}\text{.7}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[\text{0}\text{.1 x 51}\text{.7 = 5}\text{.17}\]
(iii) $\text{0}\text{.2 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 316}\text{.8}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[\text{0}\text{.2 x 316}\text{.8 = 63}\text{.36}\]
(iv) $\text{1}\text{.3 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 1}\text{.3}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[\text{1}\text{.3 x 3}\text{.1 = 4}\text{.03}\]
(v) $\text{0}\text{.5 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 0}\text{.05}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[\text{0}\text{.5 x 0}\text{.05 = 0}\text{.025}\]
(vi) $\text{11}\text{.2 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 0}\text{.15}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[\text{11}\text{.2 x 0}\text{.15 = 1}\text{.680 }\]
(vii) $\text{1}\text{.07 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 0}\text{.02}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[\text{1}\text{.07 x 0}\text{.02 = 0}\text{.0214}\]
(viii) $\text{10}\text{.05 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 1}\text{.05}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[\text{10}\text{.05 x 1}\text{.05 = 10}\text{.5525}\]
(ix) $\text{101}\text{.01 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 0}\text{.01}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[\text{101}\text{.01 x 0}\text{.01 = 1}\text{.0101}\]
(x) $\text{100}\text{.01 }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ 1}\text{.1}$
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[\text{100}\text{.01 x 1}\text{.1 = 110}\text{.11 }\]
Exercise 2.5
1. Find:
(i) \[\text{0}\text{.4 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 2}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[0.4\div 2=\frac{4}{10}\times \frac{1}{2}=\frac{2}{10}=0.2\]
(ii) \[\text{0}\text{.35 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 5}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[0.35\div 5=\frac{35}{100}\times \frac{1}{5}=\frac{7}{100}=0.07\]
(iii) \[\text{2}\text{.48 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 4}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[2.48\div 4=\frac{248}{100}\times \frac{1}{4}=\frac{62}{100}=0.62\]
(iv) \[\text{65}\text{.4 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 6}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[65.4\div 6=\frac{654}{10}\times \frac{1}{6}=\frac{109}{10}=10.9\]
(v) \[\text{651}\text{.2 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 4}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[651.2\div 4=\frac{6512}{10}\times \frac{1}{4}=\frac{1628}{10}=162.8\]
(vi) \[\text{14}\text{.49 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 7 }\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[14.49\div 7=\frac{1449}{100}\times \frac{1}{7}=\frac{207}{100}=2.07\]
(vii) \[\text{3}\text{.96 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 4}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[3.96\div 4=\frac{396}{100}\times \frac{1}{4}=\frac{99}{100}=0.99\]
(viii) \[\text{0}\text{.80 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 5}\]
Ans: Calculating the value,
\[0.80\div 5=\frac{80}{100}\times \frac{1}{5}=\frac{16}{100}=0.16\]
2. Find:
(i) \[\text{4}\text{.8 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 10}\]
Ans: Performing the given calculation,
$4.8\div 10=\frac{4.8}{10}=0.48$
(ii) \[\text{52}\text{.5 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 10}\]
Ans: Performing the given calculation,
$52.5\div 10=\frac{52.5}{10}=5.25$
(iii) \[\text{0}\text{.7 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 10}\]
Ans: Performing the given calculation,
$0.7\div 10=\frac{0.7}{10}=0.07$
(iv) \[\text{33}\text{.1 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 10}\]
Ans: Performing the given calculation,
$33.1\div 10=\frac{33.1}{10}=3.31$
(v) \[\text{272}\text{.23 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 10}\]
Ans: Performing the given calculation,
$272.23\div 10=\frac{272.23}{10}=27.223$
(vi) \[\text{0}\text{.56 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 10 }\]
Ans: Performing the given calculation,
$0.56\div 10=\frac{0.56}{10}=0.056$
(vii) \[\text{3}\text{.97 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 10}\]
Ans: Performing the given calculation,
$3.97\div 10=\frac{3.97}{10}=0.397$
3. Find:
(i) \[\text{2}\text{.7 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 100}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$2.7\div 100=\frac{27}{10}\times \frac{1}{100}=\frac{27}{1000}=0.027$
(ii) \[\text{0}\text{.3 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 100 }\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$0.3\div 100=\frac{3}{10}\times \frac{1}{100}=\frac{3}{1000}=0.003$
(iii) \[\text{0}\text{.78 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 100}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$0.78\div 100=\frac{78}{10}\times \frac{1}{100}=\frac{78}{1000}=0.0078$
(iv) \[\text{432}\text{.6 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 100}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$432.6\div 100=\frac{4326}{10}\times \frac{1}{100}=\frac{4326}{1000}=4.326$
(v) \[\text{23}\text{.6 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 100}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,$23.6\div 100=\frac{236}{10}\times \frac{1}{100}=\frac{236}{1000}=0.236$
(vi) \[\text{98}\text{.53 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 100}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$98.53\div 100=\frac{9853}{10}\times \frac{1}{100}=\frac{9853}{1000}=0.9853$
4. Find:
(i) \[\text{7}\text{.9 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 1000}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$7.9\div 1000=\frac{79}{10}\times \frac{1}{1000}=\frac{79}{10000}=0.0079$
(ii) \[\text{26}\text{.3 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 1000}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$26.3\div 1000=\frac{263}{10}\times \frac{1}{1000}=\frac{263}{10000}=0.0263$
(iii) \[\text{38}\text{.53 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 1000}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$38.53\div 1000=\frac{3853}{10}\times \frac{1}{1000}=\frac{3853}{10000}=0.03853$
(iv) \[\text{128}\text{.9 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 1000}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$128.9\div 1000=\frac{1289}{10}\times \frac{1}{1000}=\frac{1289}{10000}=0.1289$
(v) \[\text{0}\text{.5 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 1000}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$0.5\div 1000=\frac{5}{10}\times \frac{1}{1000}=\frac{5}{10000}=0.0005$
5. Find:
(i) \[\text{7 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 3}\text{.5}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$7\div 3.5=7\div \frac{35}{10}=7\times \frac{10}{35}=\frac{10}{5}=2$
(ii) \[\text{36 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 0}\text{.2 }\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$36\div 0.2=36\div \frac{2}{10}=36\times \frac{10}{2}=18\times 10=180$
(iii) \[\text{3}\text{.25 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 0}\text{.5}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,$3.25\div 0.5=\frac{325}{100}\div \frac{5}{10}=\frac{325}{100}\times \frac{10}{5}=\frac{65}{10}=6.5$
(iv) \[\text{30}\text{.94 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 0}\text{.7}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$30.94\div 0.7=\frac{3094}{100}\div \frac{7}{10}=\frac{3094}{100}\times \frac{10}{7}=\frac{442}{10}=44.2$
(v) \[\text{0}\text{.5 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 0}\text{.25 }\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,$0.5\div 0.25=\frac{5}{10}\div \frac{25}{100}=\frac{5}{10}\times \frac{100}{25}=\frac{10}{5}=2$
(vi) \[\text{7}\text{.75 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 0}\text{.25}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$7.75\div 0.25=\frac{775}{100}\div \frac{25}{100}=\frac{775}{100}\times \frac{100}{25}=31$
(vii) \[\text{76}\text{.5 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 0}\text{.15}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$76.5\div 0.15=\frac{765}{100}\div \frac{15}{100}=\frac{765}{10}\times \frac{100}{15}=51\times 10=510$
(viii) \[\text{37}\text{.8 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 1}\text{.4}\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$37.8\div 1.4=\frac{378}{10}\div \frac{14}{10}=\frac{378}{10}\times \frac{10}{14}=27$
(ix) \[\text{2}\text{.73 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 1}\text{.3 }\]
Ans: Converting the terms in fraction form and calculating the value,
$2.73\div 1.3=\frac{273}{100}\div \frac{13}{10}=\frac{273}{100}\times \frac{10}{13}=\frac{21}{10}=2.1$
6. A vehicle covers a distance of \[\text{43}\text{.2 km}\] in
\[\text{2}\text{.4}\]litres of petrol. How much distance will it cover in one
litre
petrol?
Ans: Given:\[\,\,\,\text{In 2}\text{.4 litres of petrol, distance covered by the vehicle = 43}\text{.2 km}\]
Since,\[\,\,\,\text{In 2}\text{.4 litres of petrol, distance covered by the vehicle = 43}\text{.2 km}\]
\[\therefore \,\,\text{In 1 litre of petrol, distance covered by the vehicle = 43}\text{.2 }\!\!\div\!\!\text{ 2}\text{.4}\]
Performing the required calculations,
$=\frac{432}{10}\div \frac{24}{10}=\frac{432}{10}\times \frac{24}{10}$
$\text{=18}\,\text{km}$
Hence, the vehicle can cover \[\text{18 km}\] distance in one litre of petrol.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Chapter 2 Maths PDF Download
2.1 Introduction
In NCERT Solutions Class 7 Chapter 2 Maths, students will learn about fractions and decimals. In junior classes, students have learned about what is a fraction and its types: proper, improper, mixed fractions, etc. Now, in class 7, we are going to learn about multiplication and division of fractions. The concept of fractions mainly focuses on the ratios and proportions, how to distribute etc. At the same time, decimals are the accurate values obtained after the division.
2.2 Recollect
In NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths Chapter 2, students need to think again on the topics they have learned so far in the previous classes. These include representation of fractions on the number line, ordering of fractions, addition and subtraction of fractions, decimals and their additions, how to keep a point, etc. These are reminded in the first two exercises.
2.3 Multiplication of Fractions
In this section, students can understand how to multiply two fractions. If students have values like a and b, they can say ab is the product of a and b. If the values are like p/q, a/b then, how can we multiply? To multiply these fractions, it has two different methods. One is by using a whole number and the other is by using a portion.
2.3.1 Multiplication of Fractions Using the Whole Number
Here, let us see what Fraction tells us? It explains that a down part is a whole number (except zero) and the upper part is the integer. In a fraction, the down part is known as the denominator whereas the upper part is the numerator. We use a whole number to multiply fractions if they are the same. For instance, let's say we have p/q. Then we can multiply with the whole number as 3*p/q. It is also applicable for improper or mixed fractions. But students need to make them into simpler forms before multiplying.
2.3.1 Multiplication of Fractions Using the Fraction
In this section, students can learn how to multiply two fractions when they are dissimilar. Students use a fraction to multiply them. The formula for multiplying two fractions is,(product of numerators)/(product of denominators).
The resultant product is less than the two fractions if we multiply two proper fractions. On the other hand, the result is greater than the two fractions if we multiply two improper fractions.
2.4 Division of Fractions
Let's discuss the division of fractions. Students can divide a fraction by a whole number and a whole number by a fraction. Here is a particular case to keep in mind. If two fractions for which numerator and denominator are in reverse order, then they are called reciprocals to each other. Their product is always 1.
In the same way, while dividing mixed fractions with a whole number, students need to change the mixed fraction into improper fractions. Then it is easy to divide and solve. Next, we have to learn to divide a fraction with another fraction by changing one of the fractions into its reciprocal form.
The three concepts are explained differently in the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 2 PDF book available on Vedantu for students to go through if necessary.
2.5 Recalling Decimals
Decimals are the proper forms to represent the results obtained from multiplication and division. Placing the point in between numbers plays a vital role. One can express the heights, distances, weights, measuring values, interest rates, shares, and fractions, also using decimals. To change the place value of the point, we can multiply by 10,100,...... Let's have a glance at the addition and subtraction of decimals.
Overview of Deleted Syllabus for CBSE Class 7 Maths Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals
Chapter | Dropped Topics |
Fractions and Decimals | 2.1 - Introduction |
2.2 - How well have you learned about fractions | |
2.5 - How well have you learned about decimals. |
Class 7 Maths Chapter 2: Exercises Breakdown
Chapter 2 - Fraction and Decimals Class 7 Exercises in PDF Format | |
Exercise 2.1 | 8 Questions & Solutions |
Exercise 2.2 | 8 Questions & Solutions |
Exercise 2.3 | 4 Questions & Solutions |
Exercise 2.4 | 5 Questions & Solutions |
Exercise 2.5 | 6 Questions & Solutions |
Conclusion
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2 fraction and decimals Class 7 offers practice problems and clear explanations to help master these concepts. Students should focus on fraction addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division for both like and unlike denominators. They should also be able to convert between fractions and decimals easily and understand relative fraction sizes. By carefully working through NCERT Class 7 Maths Chapter 2 Exercises, students can improve their knowledge and prepare for exams.
Other Study Material for CBSE Class 7 Maths Chapter 2
S.No. | Important Links for Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals |
1 | |
2 | |
3 |
Chapter-Specific NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths
Given below are the chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths. Go through these chapter-wise solutions to be thoroughly familiar with the concepts.
S.No. | NCERT Solutions Class 7 Chapter-wise Maths PDF |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. | |
6. | |
7. | |
8. | |
9. | |
10. | |
11. | |
12. |
Important Related Links for NCERT Class 7 Maths
Access these essential links for NCERT Class 7 Maths, offering comprehensive solutions, study guides, and additional resources to help students master language concepts and excel in their exams.
S.No | Other CBSE Study Materials for Class 7 Maths |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6. | |
7. | |
8. | |
9. |
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Maths Chapter 2 Fractions And Decimals - 2025-26
1. How are the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 2 structured across the different exercises?
The NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2 are organised by exercise to match the textbook. This chapter contains seven exercises in total: Exercise 2.1 (8 questions), Exercise 2.2 (8 questions), Exercise 2.3 (8 questions), Exercise 2.4 (4 questions), Exercise 2.5 (9 questions), Exercise 2.6 (5 questions), and Exercise 2.7 (6 questions). Each solution provides a step-by-step method to ensure students can follow the correct procedure as per the 2025-26 CBSE guidelines.
2. What is the correct method for solving the multiplication of fractions as shown in the NCERT solutions for Chapter 2?
The NCERT solutions demonstrate a straightforward method for multiplying fractions. The process involves two main steps:
- First, multiply the numerators of the given fractions to find the numerator of the product.
- Second, multiply the denominators of the fractions to find the denominator of the product.
- Finally, simplify the resulting fraction to its lowest form if required.
3. How do the NCERT Solutions explain the correct way to compare two unlike fractions?
The solutions provide a clear, step-by-step approach for comparing fractions with different denominators. To solve these problems correctly, you must first find the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of the denominators. After finding the LCM, convert each fraction into an equivalent fraction with the LCM as the new common denominator. Once the denominators are identical, the fraction with the larger numerator is the greater of the two.
4. What is the step-by-step process for dividing a decimal number by another decimal as per the NCERT solutions?
The NCERT solutions break down this process to prevent common errors. The key step is to first convert the divisor (the number you are dividing by) into a whole number. This is done by multiplying both the divisor and the dividend by a power of 10 (such as 10, 100, or 1000). For example, to solve 8.25 ÷ 0.25, the solution shows multiplying both numbers by 100 to change the problem to 825 ÷ 25, which is much simpler to solve accurately.
5. Why is it important to show the step of finding the reciprocal when solving fraction division problems in an exam?
Showing the step of finding the reciprocal is crucial because it demonstrates a full understanding of the mathematical principle behind fraction division. According to CBSE evaluation norms, marks are often awarded for key methodical steps, not just the final answer. The NCERT solutions highlight this by explicitly converting a division problem (e.g., 1/2 ÷ 3/4) into a multiplication problem using the reciprocal (1/2 x 4/3) before solving. This ensures you secure marks for the correct method.
6. How do the detailed solutions for word problems in Chapter 2 help in building practical problem-solving skills?
The step-by-step solutions for word problems are designed to build skills beyond just calculation. By following them, you learn to:
- Translate a real-world scenario into a mathematical equation.
- Identify whether a problem requires addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division of fractions and decimals.
- Set up the calculation correctly and solve it methodically.
- Interpret the numerical answer back into the context of the problem. This develops foundational analytical and reasoning abilities.
7. What is a common mistake when converting mixed fractions to improper fractions, and how do the NCERT solutions prevent it?
A common error is to incorrectly combine the whole number and the fraction. The NCERT solutions reinforce the correct procedure: multiply the whole number by the denominator and then add the numerator. The result becomes the new numerator, while the denominator stays the same. For instance, for 3 1/4, the correct conversion is ((3 × 4) + 1) / 4 = 13/4. Following this procedural memory helps avoid mistakes in more complex problems.
8. What key decimal concepts from Exercise 2.5 are explained in the NCERT Solutions?
The NCERT Solutions for Exercise 2.5 primarily focus on the comparison of decimal numbers. The problems and solutions guide you on how to compare decimals by first checking the whole number part and then the digits in the tenths, hundredths, and thousandths places. Additionally, the solutions cover the practical application of expressing smaller units (like paise or metres) as decimals of larger units (like rupees or kilometres).
9. How can a student best use the NCERT Solutions for 'Fractions and Decimals' for effective self-study?
For effective self-study, you should first try to solve the NCERT exercise questions on your own. Afterwards, use the Vedantu NCERT Solutions to:
- Verify your method, not just the final answer.
- Identify and understand any steps where you made a mistake.
- Learn the most efficient and logical sequence for solving different types of problems.
- Observe the proper way to present answers, especially for word problems, to learn how to score full marks in exams.

















