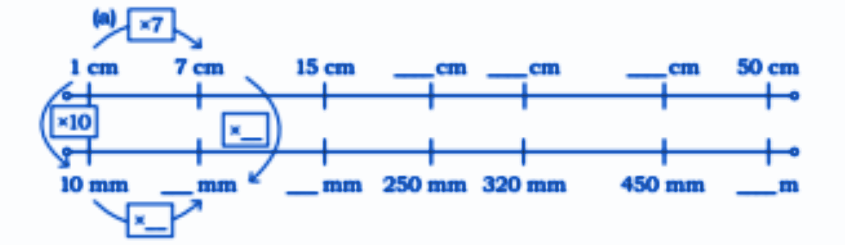
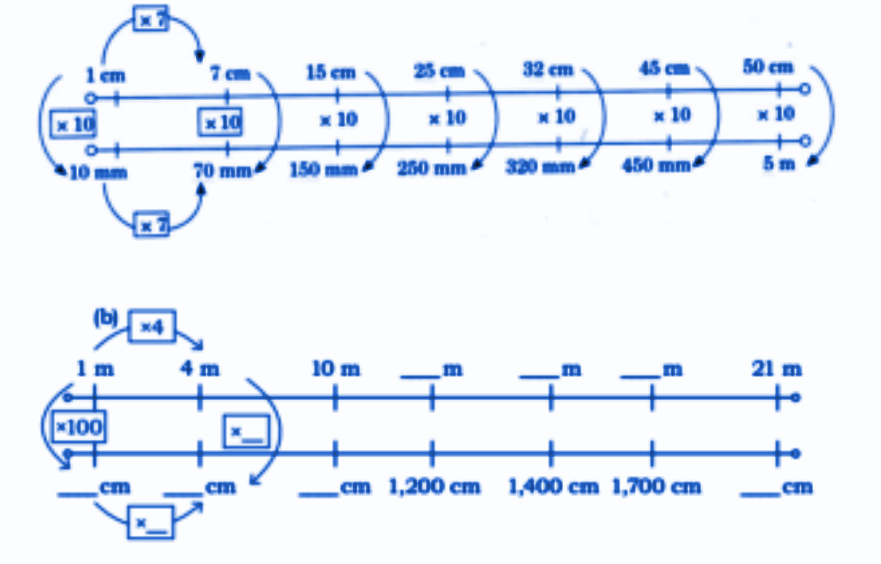
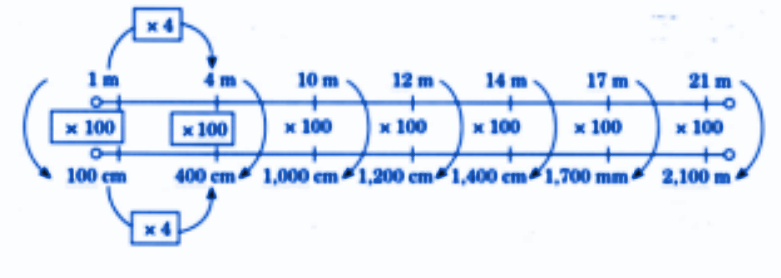
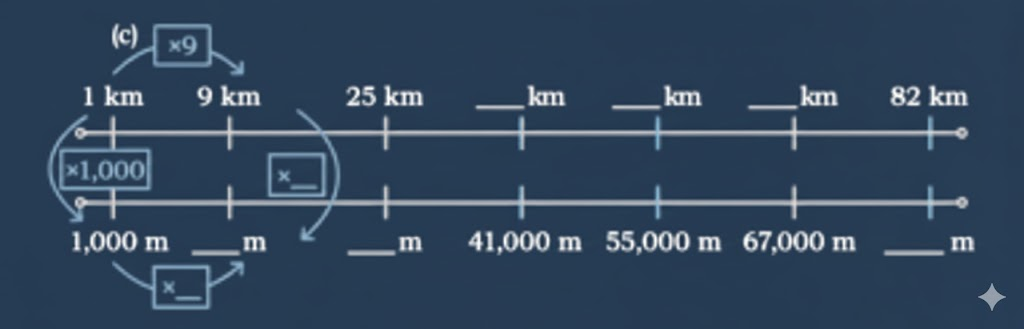
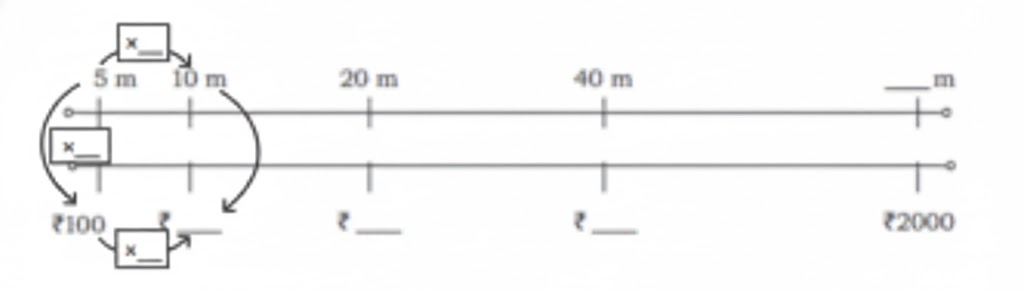
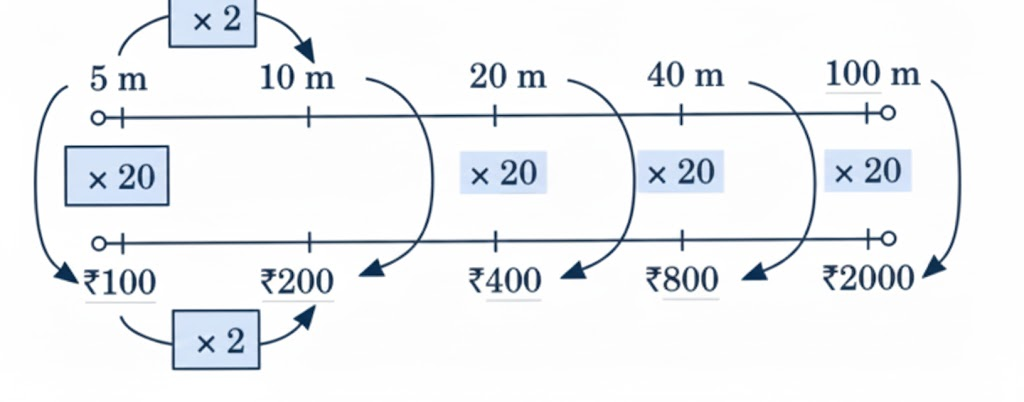
Stepwise Answers & Key Tips for NCERT Class 5 Maths Chapter 5
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 Far And Near - 2025-26
1. What topics are covered in NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 5 Far and Near?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 5 Far and Near include stepwise solutions for every exercise question, clarifications of key concepts, and explanations of diagrams. This chapter focuses on:
- Distance and measurement concepts
- Understanding maps and scales
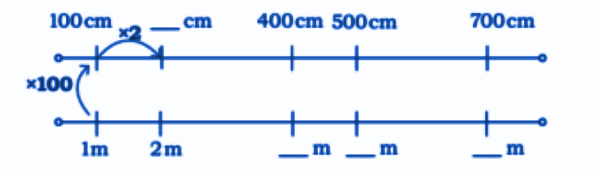
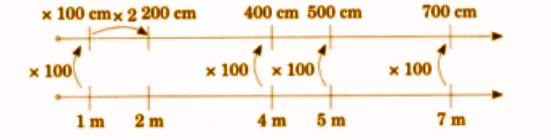
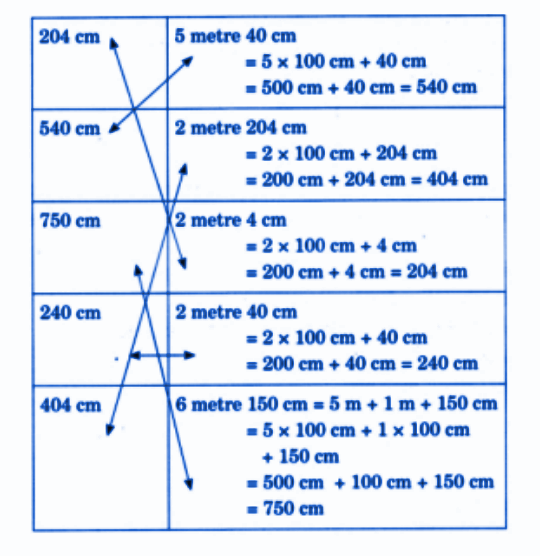
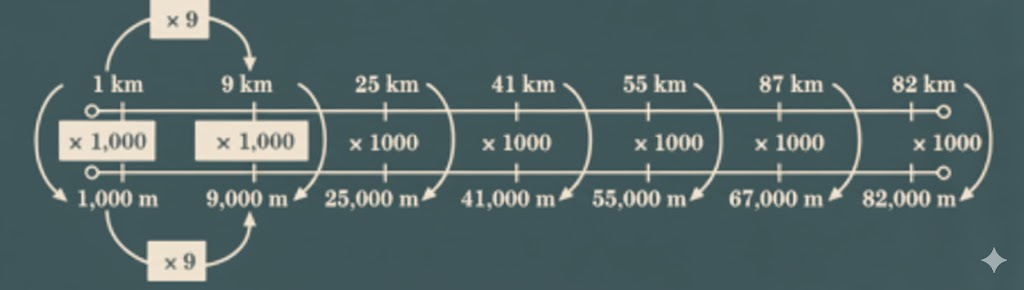
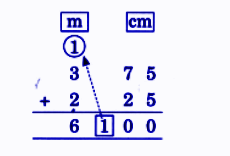
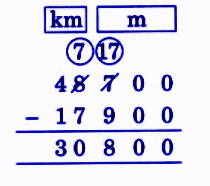
- Converting units (meters, centimeters, kilometers)
- Reading and labelling diagrams
2. How can I score full marks using NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Chapter 5?
To score full marks in CBSE Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 Far and Near, follow these tips:
- Write stepwise answers using clear working
- Use correct definitions and units
- Include neatly labelled diagrams or maps where asked
- Highlight key points and box your final answer
- Revise with NCERT exercise-wise solutions and practice previous year questions
3. Are diagrams and definitions mandatory in NCERT Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 answers?
Including neat diagrams and exam-ready definitions is important for scoring well in Class 5 Maths Chapter 5. Diagrams are:
- Often required for map and measurement questions
- Required to be labelled accurately
- Help you earn easy step marks per CBSE marking scheme
Definitions are necessary when asked, especially for terms like distance, scale, or unit.
4. Where can I download the free PDF of Class 5 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 5?
You can download the free PDF of NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 Far and Near from trusted educational websites. The PDF includes:
- Exercise-wise and stepwise solutions
- Mapped to the latest 2025–26 CBSE syllabus
- Useful for offline study and last-minute revision
5. What is the CBSE marking scheme for Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 solutions?
The CBSE marking scheme for Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 awards marks for:
- Correct steps and method (step marking)
- Accurate final answer with correct unit
- Clear and neat diagrams/maps, if required
- Using keywords and completing all parts of multi-step questions
6. How to revise Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 Far and Near quickly before exams?
To revise NCERT Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 Far and Near efficiently:
- Go through exercise-wise NCERT solutions and key examples
- Revise key formulae and definitions
- Practice important diagrams and map labelling
- Use flash notes and a 1-day or 3-day revision plan
7. What are the most important questions and topics in Class 5 Maths Chapter 5?
The most important topics in Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 Far and Near for exams include:
- Conversion of units (cm, m, km)
- Interpreting maps and scales
- Calculation of distances using given data or diagrams
- Labelling maps and identifying places far and near
- Definitions and exercises with real-life applications
8. Are NCERT Solutions enough for Class 5 Maths exams?
NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths cover all essential concepts as per CBSE syllabus and are generally sufficient for exams. For best results:
- Practice all intext and back exercise questions
- Attempt exemplar, MCQs, and previous year questions
- Revise key formulae and definitions regularly
9. How to present long answers in Class 5 Maths according to CBSE marking?
To present long answers for Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 per CBSE marking scheme:
- Write stepwise with clear workings
- Use proper headings (e.g., Given, To Find, Solution)
- Box the final answer with correct units
- Draw neat diagrams if required and label them clearly
10. How do I avoid common mistakes in NCERT Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 solutions?
To avoid common mistakes in Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 Far and Near solutions:
- Always write correct units (cm, m, km) in answers
- Double-check all calculations
- Read map/scales carefully
- Draw and label diagrams neatly
- Follow stepwise solution as per marking scheme to avoid missing steps
11. How to label maps and diagrams in NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Chapter 5?
For map and diagram questions in Class 5 Maths Chapter 5 Far and Near:
- Use a scale when drawing distances
- Label locations and paths clearly and neatly
- Make arrows or legends if required
- Follow textbook conventions and practice with provided examples
12. Do examiners award partial marks for correct steps even if the final answer is wrong?
Yes, CBSE examiners usually award step marks for correct working, even if the final answer is incorrect, especially in Maths solutions. Ensure you:
- Show all steps clearly
- Write each calculation and conversion
- Attempt every part as per the question