Maharashtra Board Class 12 Solutions for Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystems and Energy Flow – Download Free PDF with Solution
Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 explains what ecosystems are and how they are self-sustaining units. An ecosystem comprises various elements and factors. These elements and factors determine the uniqueness of an ecosystem and the organisms living in it. This chapter will explain how solar energy is trapped and how it flows in different forms in various ecosystems.
To understand the fundamental concepts of this chapter, focus on the Ecosystems and Energy Flow Class 12 Biology Solutions prepared by the subject matter experts of Vedantu. You will find the easiest explanation of all these concepts to make your preparation level better.
Access Maharashtra Board Solutions for Biology Class 12 Chapter 14 Ecosystems and Energy Flow
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which one of the following has the largest population in a food chain?
Producers
Primary consumers
Secondary consumers
Decomposers
Ans: The correct option is (d) Decomposers.
Decomposers such as bacteria and fungi form the largest population in a food chain. They obtain energy by breaking down the complex dead and decaying organic matter into simple inorganic forms. Thus, they play a very important role in cleaning the environment and making food available for producers.
2. The second trophic level in a lake is ______________.
Phytoplankton
Zooplankton
Benthos
Fishes
Ans: The correct option is (b) Zooplankton
In aquatic ecosystems such as lakes, the phytoplanktons are the primary producers or first trophic level. They are eaten by the zooplanktons that are primary consumers. Hence, zooplanktons form the second trophic level. The zooplankton is further eaten by other aquatic organisms such as fish and benthos. Hence, fishes and benthos represent higher trophic levels.
3. Secondary consumers are ______________.
Herbivores
Producers
Carnivores
Autotrophs
Ans: The correct option is (c) Carnivores.
In a food chain, the autotrophs such as green plants and algae are the primary producers. The primary consumers or herbivores feed on producers. Primary consumers are further consumed by secondary consumers. Secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores. When secondary consumers are consumed by other organisms then they are called tertiary consumers.
4. What is the % of photosynthetically active radiation in the incident solar radiation?
100%
50%
1-5%
2-10%
Ans: The correct option is (b) 50%.
Of the total solar radiation that falls on the surface of the earth, about 50% comes under the photosynthetically active radiation that can be absorbed by chlorophyll pigments. This photosynthetically active radiation has a wavelength of 400-700nm which favors the photosynthesis process. But, plants absorb only 2-10% of this radiation to carry out the photosynthesis process.
5. Give the term used to express a community in its final stage of succession.
End community
Final community
Climax community
Dark community
Ans: The correct option is (c) Climax community.
Succession is the process of the development of an ecological community in a barren or pre-colonized area. The first plant community that grows in that area is called the pioneer community while the stable community that forms the final stage of succession is called the climax community. There are various stages called successional stages that come between the pioneer and climax community.
6. After a landslide, which of the following types of succession occurs?
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Climax
Ans: The correct option is (a) Primary.
Primary succession occurs on a barren area or rocks that were never colonized by any habitat. This type of succession takes more time to reach the climax community as it starts from scratch. After the landslide, almost all the ecological communities that inhabit the area will be removed. Landslide exposes the new land and barren rocks on which pioneer species colonize. Hence, after a landslide, primary succession occurs.
7. Which of the following is most often a limiting factor of the primary productivity in any ecosystem?
Carbon
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
Sulphur
Ans: The correct option is (a) Carbon.
Primary productivity is the formation of organic compounds using carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere. This is generally done by plants through the photosynthesis process. As photosynthesis involves the utilization of carbon dioxide, water and sunlight, hence, carbon is the main limiting factor that can affect the primary productivity in an ecosystem.
Very Short Answer Question
1. Give an example of the ecosystem which shows an inverted pyramid of numbers.
Ans: The pyramid of numbers indicates the total number of organisms present at each trophic level. In an inverted pyramid of numbers, the number of producers is less than the number of organisms present at higher trophic levels. The tree ecosystem represents an inverted pyramid of numbers where the number of organisms increases when we move from lower to higher trophic levels. The first trophic level is represented by trees that are less in number. The next trophic level is formed by insects or birds that are more in number than trees.
Tree Ecosystem
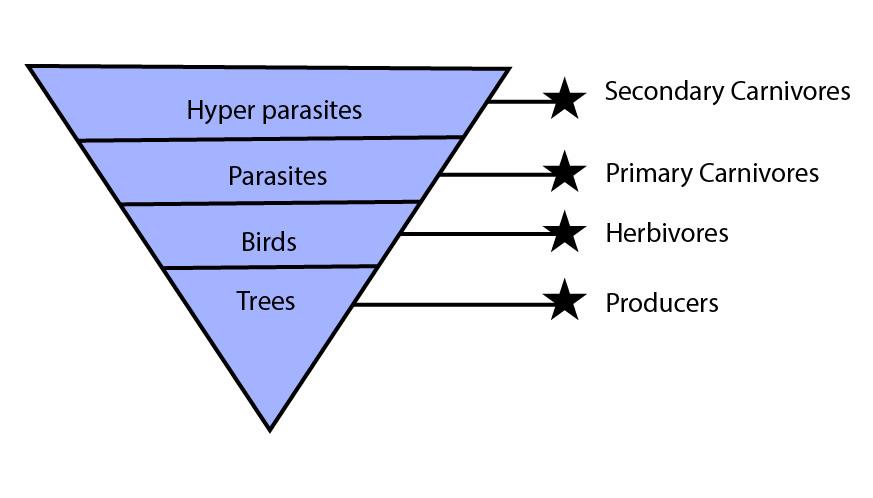
2. Give an example of an ecosystem which shows an inverted pyramid of biomass.
Ans: The pyramid of biomass depicts the total weight of all organisms at each trophic level. The pond ecosystem represents an Inverted pyramid of biomass where biomass increases at successive trophic levels from the base. In the pond ecosystem, the phytoplanktons form the base of the pyramid whose biomass is less than the organisms that are present above trophic levels. The zooplanktons form the next or second trophic level and their biomass is less than the organisms present above trophic levels. The higher trophic levels are occupied by fishes and benthos and their biomass is more than the lower trophic level organisms.
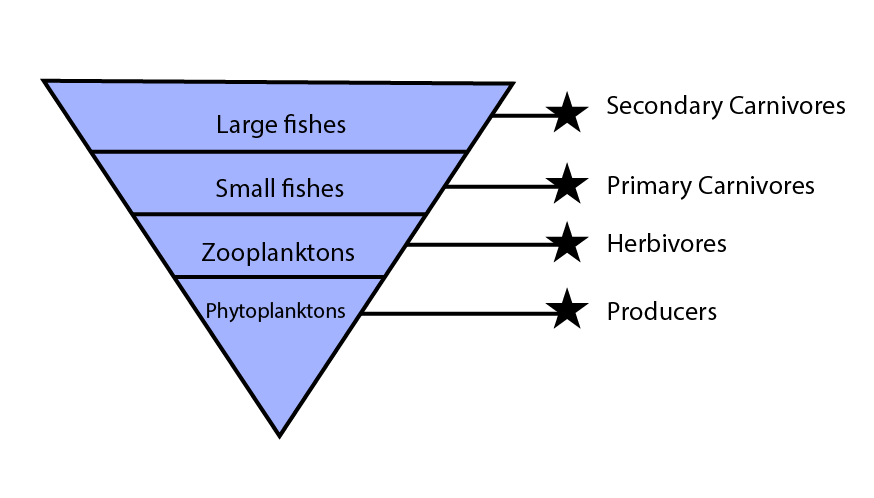
Pond Ecosystem
3. Which mineral acts as a limiting factor for productivity in an aquatic ecosystem?
Ans: Productivity is the formation of organic compounds using carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere. This is generally done by plants or primary producers through the photosynthesis process. But, in aquatic ecosystems, the plants and algae also require nutrients such as phosphorus for proper growth. The phosphorus generally enters the water bodies through the sedimentation process which is a very low process. Hence, in aquatic ecosystems, phosphorus acts as a limiting mineral that influences productivity.
4. Name the reservoir and sink of carbon in the carbon cycle.
Ans: One main reservoir of carbon in the carbon cycle is the atmosphere while one major sink of carbon in the carbon cycle is the oceans. In the carbon cycle, the reservoirs store the carbon in various forms while sinks absorb the carbon. The atmosphere acts as a reservoir for carbon as it stores carbon in the form of gas i.e. carbon dioxide. The oceans act as a sink for carbon as they contain carbon in the form of dissolved carbon dioxide in water. Oceans are the largest sink of carbon.
Short Answer Questions
1. Distinguish between the upright and inverted pyramid of biomass.
Ans: The difference between the upright and inverted pyramid of biomass is given below:
S.No | Upright Pyramid of Biomass | Inverted Pyramid of Biomass |
In an upright pyramid of biomass, biomass decreases when we move from lower to higher trophic levels. | In an inverted pyramid of biomass, the biomass increases at successive trophic levels from the base. | |
The biomass of producers is more than the biomass of organisms present at higher trophic levels. | The biomass of producers is less than the biomass of organisms that are at present at higher trophic levels. | |
This type of biomass is found in the grassland ecosystem where the organisms at higher trophic levels are less than the biomass of organisms at lower trophic levels i.e. grasses. | This type of pyramid is found in the pond ecosystem where the biomass of organisms at higher trophic levels is more than the biomass of organisms at lower trophic levels i.e. phytoplanktons |
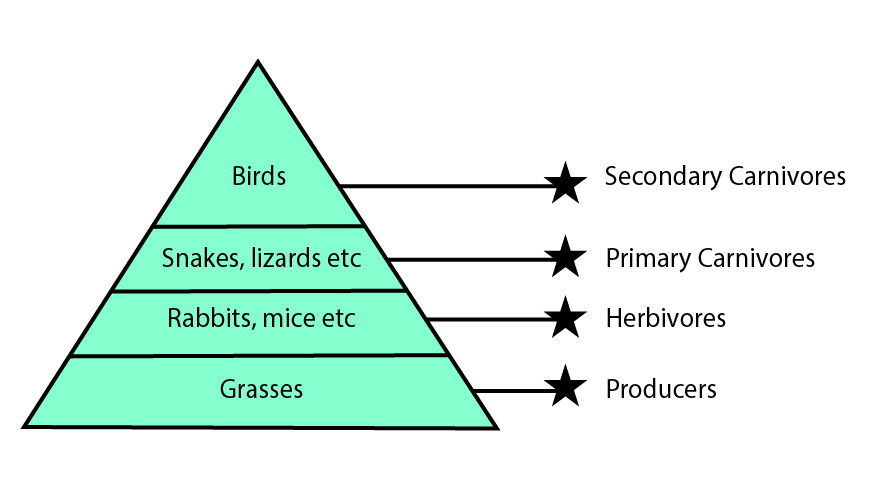
Upright Pyramid of Biomass

Inverted Pyramid of Biomass
2. Distinguish between food chain and food web.
Ans: The difference between food chain and food web is:
S.No | Food Chain | Food Web |
A food chain is a simple and single pathway that involves four to six trophic levels at a time. In a food chain, the organism at a higher trophic level eats the organism that is present at lower trophic levels. | A food web is a complex network of many interconnected food chains. It consists of different organisms at each trophic level. | |
2. | In a food chain, there is only one feeding option for organisms present at higher trophic levels. | There are many feeding options for the organisms that are present at higher trophic levels. |
3. | The food chain makes the ecosystem unstable because if one species is affected then all other species that feed on it will also be affected. | The Food web is found in all ecosystems and it makes the ecosystem stable because if one species is affected then it will not affect other organisms. |

Food Chain
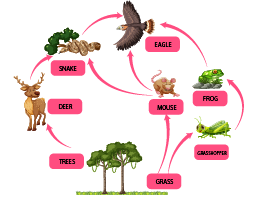
Food Web
Long Answer Questions.
1. Define ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of number and biomass.
Ans: Ecological pyramids: The ecological pyramids depict the connection between the different trophic levels on the basis of the number of organisms, the biomass of organisms and the energy available at each trophic level.
Pyramid of numbers: The pyramid of numbers indicates the number of organisms present at each trophic level. It can be straight or upright. An example of an upright pyramid of numbers is a grassland ecosystem while an example of an inverted pyramid of numbers is an ecosystem on a tree.
Pyramid of Biomass:
The pyramid of biomass depicts the total weight of all organisms at each trophic level. It can be straight or upright.
An example of the upright pyramid of biomass is the grassland ecosystem while an example of an inverted pyramid of biomass is the pond ecosystem.
In a pond ecosystem, biomass of organisms at higher trophic levels is more than the biomass of organisms at lower trophic levels i.e. phytoplanktons.

Upright Pyramid of Biomass
2. What is primary productivity? Give a brief description of factors that affect primary productivity.
Ans: Primary productivity is the formation of organic compounds using carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere. This is generally done by plants or primary producers through the photosynthesis process.
The various factors that affect primary productivity are:
Sunlight: Sunlight is an important factor that
Water:
Availability of nutrients:
Number and type of plant species available in that ecosystem:
Temperature:
Type of soil:
3. Define decomposition and describe the processes and products of decomposition.
Ans: Decomposition is the process in which dead and decaying complex organic matter is broken down into simpler inorganic forms by decomposers such as bacteria and fungi.
Process of Decomposition: There are five steps involved in the decomposition process. These are fragmentation, catabolism, leaching, humification and mineralization.
In fragmentation, the dead and decayed matter is broken down into simpler pieces by decomposers or detritivores.
Catabolism includes the breaking down of complex dead matter into simpler forms.
Humification involves the formation of black-coloured humus.
Mineralisation is the process in which humus is degraded and nutrients are released into the soil.
During leaching, the nutrients are added into the soil with the seepage of water.
Products of decomposition: Nutrients, humus, water and carbon dioxide are the end products of the decomposition process.
4. Write important features of a sedimentary cycle in an ecosystem.
Ans: The minerals found in the Earth’s crust generally undergo a sedimentary cycle. Some important features of a sedimentary cycle in an ecosystem are:
By weathering and erosion processes, the minerals get unlocked from the earth’s crust and then participate in the sedimentary cycle.
The minerals enter the rivers or other water bodies and get deposited on the land where they get dissolved in the soil. The plants absorb some minerals according to their requirements and then they enter the higher trophic levels when eaten by consumers.
The sedimentary cycle is also called a less perfect cycle as sometimes, the minerals do not complete the circulation and get lost in the reservoir pool.
When compared to a gaseous cycle, the sedimentary cycle takes much time to complete the circulation.
Some examples of the sedimentary cycle are the phosphorus cycle, sulfur cycle etc.
5. Describe carbon cycle and add a note on the impact of human activities on carbon cycle.
Ans: Carbon forms 49% of the dry weight of living organisms. Hence, it constitutes the largest part of organic compounds in living forms. The whole carbon cycle generally involves five main processes: photosynthesis, respiration, sedimentation, combustion and decomposition.
The plants utilize atmospheric carbon dioxide to carry out the photosynthesis process and make their food.
This carbon then enters the food chain when primary consumers or herbivores eat the plants or their products.
When consumers respire, carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere.
Some amounts of carbon also enter the atmosphere through the decomposition process in which decomposers convert the dead organic matter into simpler forms and carbon dioxide is released.
Some amount of carbon is dissolved in ocean waters and the shells of marine organisms.
Fossil fuels, oils, rocks etc. act as a sink of carbon dioxide.
By combustion process, the carbon enters the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide.
The impact of human activities on the carbon cycle is:
The increasing burning of fossil fuels and rapid cutting of trees to fulfil human demands have significantly increased the carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere.
The increasing amount of carbon dioxide leads to increased sources of carbon. This impacts the carbon cycle.
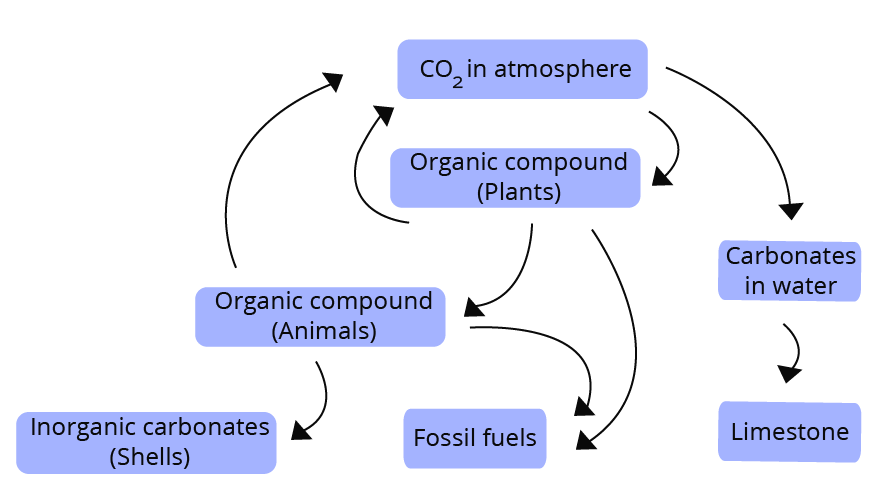
Carbon Cycle
Importance of Maharashtra Board Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystems and Energy Flow
As mentioned earlier, this chapter explains the various aspects of ecosystems, the units of a biosphere. In our world, we live in different ecosystems. Knowingly or unknowingly, we are a part of many ecosystems existing in our surroundings. In such ecosystems, plants and animals live in harmony.
An ecosystem can vary in size. It can be as small as a pond or as big as an ocean. The bigger the ecosystem the more the number of living beings in it. The two broadest divisions of ecosystems are aquatic and terrestrial. Aquatic ecosystems exist under or closer to water bodies. The terrestrial ecosystems exist on land and can be closer to a water body.
This chapter will explain the function and structure of an ecosystem. You will find out how an ecosystem is formed and how its balance is naturally maintained. The identification of an ecosystem is done by the specific plants and animals residing in it.
We will also learn that every ecosystem depends on the producers or the plants with the capability to trap sunlight and make food. The basis of an ecosystem is the producers. The food chain begins with them and ends with the predators or consumers. To understand these concepts clearly, follow the Maharashtra Board Class 12 Biology Solutions Chapter 14 Ecosystems and Energy Flow.
Benefits of Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystems and Energy Flow Solutions
These solutions have been prepared by the subject experts following the Maharashtra Board Class 12 Biology syllabus and focusing on the standards. It will help you correlate with the standards of the board exams and will help you prepare the syllabus faster.
The fundamental concepts of this chapter have been simplified in these notes. It means you will find the highest convenience in understanding these concepts.
Find out how the experts have compiled the answers to all the Ecosystem and Energy Flow Class 12 exercise questions. You can learn from the perfect answering formats suggested by the experts to score more in the exams.
Resolve all your doubts using these solutions and proceed to solve the Ecosystem and Energy Flow Class 12 MCQ. Practice answering sample questions to find out where you need to work more.
Download Ecosystem and Energy Flow Class 12 Exercise Solutions PDF
Get the free PDF version of these solutions and complete the study material for this chapter. Utilize the simpler explanation and presentation of the concepts to memorize and recall them during an exam. Learn how to score more from the answering techniques adopted by the experts.
FAQs on Maharashtra Board Class 12 Solutions for Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystems and Energy Flow
1. Why is solar energy a must for an ecosystem?
Solar energy is the prime source of energy that producers of an ecosystem harness to produce food and sustain the food chain.
2. Why are heterotrophs also needed in an ecosystem?
The consumption of producers and the control of their population are also mandatory for the balance of an ecosystem.
3. What is decomposition?
The process of breaking down complex organic material in dead matter into simpler ones for easy absorption is called decomposition.
4. What is energy flow in an ecosystem?
The flow of energy from the food-producing organisms to the consumers is called energy flow.
5. What is a biome?
It is a large community of plant and animal species covering a huge area. Example: A forest.























