
Write the name of monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(i) Bakelite (ii) Neoprene.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Polymers are the materials made up of long, repeating chains of molecules. The polymers have unique properties, depending on the type of monomers being used for the formation of polymers.
Complete step by step solution:
(i) Bakelite: It is a copolymer made up of phenol and formaldehyde. Phenol – Formaldehyde resins are obtained by the reaction of phenol and formaldehyde in the presence of a basic catalyst. The reaction involves the formation of methylene bridges in ortho, para or both ortho and para positions of phenol. When the polymerisation of these substituted phenols take place, result into the formation of a linear polymer called Novalac which is used in paints. The reaction for this polymerisation is given below,
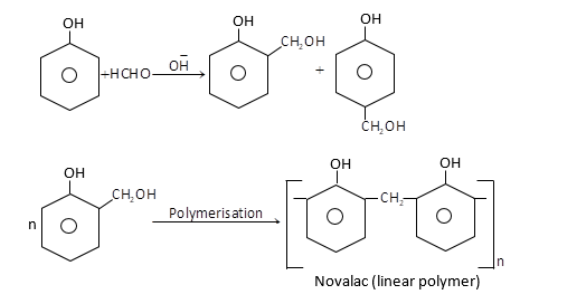
Novalac on heating with $HCHO$undergo cross linkage to form an infusible solid called bakelite.
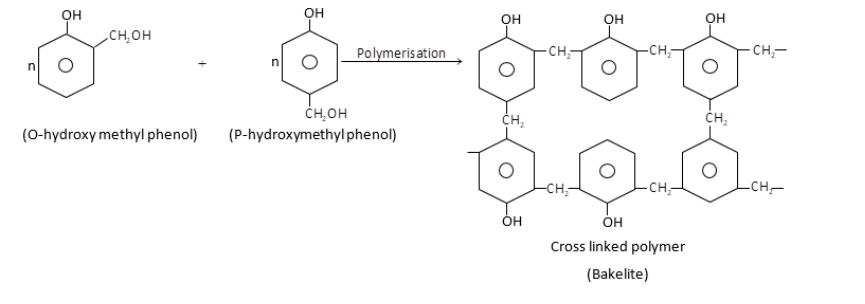
$\therefore $Monomers of bakelite are phenol and formaldehyde
(ii) Neoprene: Its monomer chloroprene is prepared from acetylene
\[\mathop {2CH \equiv CH}\limits_{acetylene} \mathop {\xrightarrow[{N{H_4}Cl}]{{C{u_2}C{l_2}}}}\limits_{\left( {343K} \right)} \mathop {{H_2}C = CH - C \equiv CH}\limits_{\left( {vinylacetylene} \right)} \xrightarrow{{HCl}}\mathop {{H_2}C = CH - C \equiv C{H_2}}\limits_{\left( {Chloroprene} \right)} \]
Chloroprene undergoes free radical polymerization to form neoprene. It polymerizes very rapidly and the reaction occurs by $1,{\text{ 4}}$- addition of one chloroprene to another.
Note: Neoprene was the first synthetic rubber manufactured on a large scale. It is also called diprene. The properties of neoprene are similar to natural rubber but neoprene is more resistant to action of oils, gasoline and other hydrocarbons. It is non – inflammable. Bakelite is used for making combs, fountain pens, electrical goods, etc. Soft Bakelite with low degree of polymerisation are used as binding glue for laminated, wooden plants and lacquers. Sulphonated bakelites are used as ion exchange resins.
Complete step by step solution:
(i) Bakelite: It is a copolymer made up of phenol and formaldehyde. Phenol – Formaldehyde resins are obtained by the reaction of phenol and formaldehyde in the presence of a basic catalyst. The reaction involves the formation of methylene bridges in ortho, para or both ortho and para positions of phenol. When the polymerisation of these substituted phenols take place, result into the formation of a linear polymer called Novalac which is used in paints. The reaction for this polymerisation is given below,

Novalac on heating with $HCHO$undergo cross linkage to form an infusible solid called bakelite.

$\therefore $Monomers of bakelite are phenol and formaldehyde
(ii) Neoprene: Its monomer chloroprene is prepared from acetylene
\[\mathop {2CH \equiv CH}\limits_{acetylene} \mathop {\xrightarrow[{N{H_4}Cl}]{{C{u_2}C{l_2}}}}\limits_{\left( {343K} \right)} \mathop {{H_2}C = CH - C \equiv CH}\limits_{\left( {vinylacetylene} \right)} \xrightarrow{{HCl}}\mathop {{H_2}C = CH - C \equiv C{H_2}}\limits_{\left( {Chloroprene} \right)} \]
Chloroprene undergoes free radical polymerization to form neoprene. It polymerizes very rapidly and the reaction occurs by $1,{\text{ 4}}$- addition of one chloroprene to another.
Note: Neoprene was the first synthetic rubber manufactured on a large scale. It is also called diprene. The properties of neoprene are similar to natural rubber but neoprene is more resistant to action of oils, gasoline and other hydrocarbons. It is non – inflammable. Bakelite is used for making combs, fountain pens, electrical goods, etc. Soft Bakelite with low degree of polymerisation are used as binding glue for laminated, wooden plants and lacquers. Sulphonated bakelites are used as ion exchange resins.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




