
Which one of the following statements is incorrect about soaps?
(A) Soaps are biodegradable
(B) Soaps are sodium salts of higher fatty acids
(C) Soaps are prepared from natural oils and fats
(D) Soaps can be used in acidic solutions
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Soap is a combination of sodium salts and higher fatty acids that are natural. These are chemical cleansers prepared from natural fats and oils which are obtained from plants and animals. These are salts and form insoluble fatty acid chains when acidified further.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Soaps are derivatives of fatty acids in the form of covalent salt made from common vegetable oils or natural fats. Soaps are the potassium or sodium salts of long-chain fatty carboxylic acids. They are surfactants i.e. these compounds reduce the surface tension between a liquid and another substance and thus help in the emulsification of oils in water.
Natural fats and oils present in soaps can be easily broken down into simpler molecules by microorganisms and so we can say that soaps are biodegradable.
Soaps are generally prepared by the process of saponification of fats and oils. This process involves heating oils and fats and reacting them with a liquid alkali or base to produce soap plus water along with glycerine. The carboxylate end of the soap molecule is hydrophilic (water-loving) whereas the hydrocarbon tail is hydrophobic (water-hating).
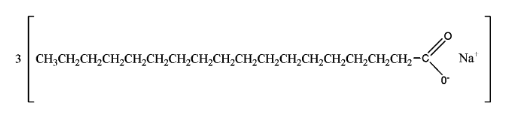
This is the structure of soap.
Soaps cannot be used in acidic conditions because they tend to lose their cleansing ability due to the formation of insoluble long-chain fatty acids. The pH of these fatty acids will then decrease to less than 7, which is bad for clothes.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note: Soaps do not work well with hard water that contains calcium or magnesium salts. It reacts with calcium and magnesium ions to form white precipitate which is referred to as scum and soap goes waste or can’t be used anymore.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Soaps are derivatives of fatty acids in the form of covalent salt made from common vegetable oils or natural fats. Soaps are the potassium or sodium salts of long-chain fatty carboxylic acids. They are surfactants i.e. these compounds reduce the surface tension between a liquid and another substance and thus help in the emulsification of oils in water.
Natural fats and oils present in soaps can be easily broken down into simpler molecules by microorganisms and so we can say that soaps are biodegradable.
Soaps are generally prepared by the process of saponification of fats and oils. This process involves heating oils and fats and reacting them with a liquid alkali or base to produce soap plus water along with glycerine. The carboxylate end of the soap molecule is hydrophilic (water-loving) whereas the hydrocarbon tail is hydrophobic (water-hating).
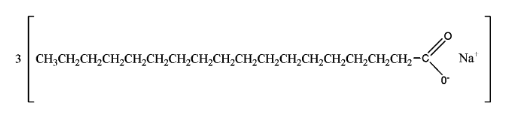
This is the structure of soap.
Soaps cannot be used in acidic conditions because they tend to lose their cleansing ability due to the formation of insoluble long-chain fatty acids. The pH of these fatty acids will then decrease to less than 7, which is bad for clothes.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note: Soaps do not work well with hard water that contains calcium or magnesium salts. It reacts with calcium and magnesium ions to form white precipitate which is referred to as scum and soap goes waste or can’t be used anymore.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




