
Which one of the following compounds when heated with KOH and a primary amine gives carbylamine test ?
A \[\text{CHC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\]
B \[\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{Cl}\]
C \[\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{OH}\]
D \[\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{CN}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Potassium hydroxide, sometimes known as caustic potash, is an inorganic chemical with the formula KOH. KOH is a typical strong base, along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH). It has numerous industrial and specialised uses, the majority of which make use of its caustic properties and acid reactivity.
Complete solution step by step:
The intermediate produced by the dehydrohalogenation of chloroform receives amine in the carbylamine reaction process. The name of this intermediary is dichlorocarbene. The Hofmann isocyanide synthesis is another name for the carbylamine reaction. Isocyanides are created through the reaction of a primary amine, chloroform, and a base. For this reaction, the dichlorocarbene intermediate is crucial. It is impossible to create isocyanides from secondary or tertiary amines via the carbylamine reaction. The carbylamine reaction can generally be expressed as –
\[R-N{{H}_{2}}~+\text{ }CHC{{l}_{3~}}+\text{ }3KOH\text{ }\to \text{ }RNC\text{ }\left( \text{Carbylamine} \right)\text{ }+\text{ }3KCl\text{ }+\text{ }3{{H}_{2}}O\]
The carbylamine reaction can be used as a chemical test because it only works for primary amines. The response is often referred to as Saytzeff's isocyanide test in this situation. In this process, chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide are used to heat the analyte. The isocyanide (carbylamine) is generated when a primary amine is present, as shown by an unpleasant odour. With secondary and tertiary amines, the carbylamine test does not produce a positive result.
Mechanism
The procedure entails mixing amine with dichlorocarbene, a reactive intermediate produced by chloroform's dehydrohalogenation. The isocyanide is created by two sequential base-mediated dehydrochlorination processes.
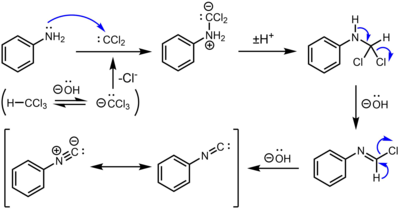
Hence option a is correct .
Note: The carbylamine reaction can be used as a chemical test for the presence of primary amines because it only reacts with primary amines. The carbylamine reaction is also known as the Hofmann's isocyanide test when used as a test. In this experiment, chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide are used to heat the test material. When primary amine is present, isocyanide (carbylamine) will develop and emit an exceedingly unpleasant odour, making it easy to detect. Since secondary and tertiary amines do not experience the carbylamine reaction, they do not produce an unpleasant smell when tested with Hofmann isocyanide.
Complete solution step by step:
The intermediate produced by the dehydrohalogenation of chloroform receives amine in the carbylamine reaction process. The name of this intermediary is dichlorocarbene. The Hofmann isocyanide synthesis is another name for the carbylamine reaction. Isocyanides are created through the reaction of a primary amine, chloroform, and a base. For this reaction, the dichlorocarbene intermediate is crucial. It is impossible to create isocyanides from secondary or tertiary amines via the carbylamine reaction. The carbylamine reaction can generally be expressed as –
\[R-N{{H}_{2}}~+\text{ }CHC{{l}_{3~}}+\text{ }3KOH\text{ }\to \text{ }RNC\text{ }\left( \text{Carbylamine} \right)\text{ }+\text{ }3KCl\text{ }+\text{ }3{{H}_{2}}O\]
The carbylamine reaction can be used as a chemical test because it only works for primary amines. The response is often referred to as Saytzeff's isocyanide test in this situation. In this process, chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide are used to heat the analyte. The isocyanide (carbylamine) is generated when a primary amine is present, as shown by an unpleasant odour. With secondary and tertiary amines, the carbylamine test does not produce a positive result.
Mechanism
The procedure entails mixing amine with dichlorocarbene, a reactive intermediate produced by chloroform's dehydrohalogenation. The isocyanide is created by two sequential base-mediated dehydrochlorination processes.

Hence option a is correct .
Note: The carbylamine reaction can be used as a chemical test for the presence of primary amines because it only reacts with primary amines. The carbylamine reaction is also known as the Hofmann's isocyanide test when used as a test. In this experiment, chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide are used to heat the test material. When primary amine is present, isocyanide (carbylamine) will develop and emit an exceedingly unpleasant odour, making it easy to detect. Since secondary and tertiary amines do not experience the carbylamine reaction, they do not produce an unpleasant smell when tested with Hofmann isocyanide.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




