
Convert chloro benzene to phenol.
Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint: We know that Dow's process is one of the ways of conversion of chlorobenzene to phenol. To obtain phenol from chlorobenzene, first we have to react with chlorobenzene with sodium hydroxide, then phenoxide ion forms. The acidification of phenoxide ions results in phenol.
Complete answer:
In Dow's process, hydrolysis of chlorobenzene results in phenol. First step is treating chlorobenzene with aqueous sodium hydroxide at a temperature of 623 K and pressure of 300 bar to convert it into sodium phenoxide.
Now, we write the reaction of formation of sodium phenoxide ion by reaction of chlorobenzene with sodium hydroxide.

The next step is the acidification of phenoxide ions. This can be done by reacting phenoxide ion with hydrochloric acid. The result of this reaction is the production of phenol.
Now, we write the reaction of production of phenol by acidification of phenoxide ions.

Hence, by Dow’s process, we are able to convert chloro benzene to phenol by Dow’s process.
Additional information:
When one hydrogen atom of the benzene ring is replaced by a hydroxide ion, then the compound is known as phenol. Phenols are commonly used as intermediates in industrial synthesis and in household products. For example, phenol is used as a disinfectant (in low concentrations) in household and mouthwash cleaners. Phenol was probably the first antiseptic surgery. Phenol is also known as carbonic acid, hydroxybenzene and phenolic acid.
Note:
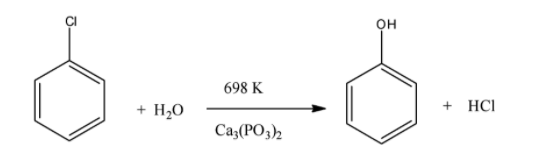
Another way to convert chlorobenzene to phenol is by reacting phenol with steam at 698 K in presence of calcium phosphate. The reaction gives phenol and hydrochloric acid.
Complete answer:
In Dow's process, hydrolysis of chlorobenzene results in phenol. First step is treating chlorobenzene with aqueous sodium hydroxide at a temperature of 623 K and pressure of 300 bar to convert it into sodium phenoxide.
Now, we write the reaction of formation of sodium phenoxide ion by reaction of chlorobenzene with sodium hydroxide.

The next step is the acidification of phenoxide ions. This can be done by reacting phenoxide ion with hydrochloric acid. The result of this reaction is the production of phenol.
Now, we write the reaction of production of phenol by acidification of phenoxide ions.

Hence, by Dow’s process, we are able to convert chloro benzene to phenol by Dow’s process.
Additional information:
When one hydrogen atom of the benzene ring is replaced by a hydroxide ion, then the compound is known as phenol. Phenols are commonly used as intermediates in industrial synthesis and in household products. For example, phenol is used as a disinfectant (in low concentrations) in household and mouthwash cleaners. Phenol was probably the first antiseptic surgery. Phenol is also known as carbonic acid, hydroxybenzene and phenolic acid.
Note:
Another way to convert chlorobenzene to phenol is by reacting phenol with steam at 698 K in presence of calcium phosphate. The reaction gives phenol and hydrochloric acid.

Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




