
Which of the following statements are false?
This question has multiple correct options
(A) ${ Na }_{ 2 }{ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 }$ is less soluble than ${ K }_{ 2 }{ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 }$
(B) ${ CrO }_{ 4 }^{ 2- }$ is tetrahedral in shape.
(C) ${ Na }_{ 2 }{ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 }$ is a primary standard in volumetry.
(D) ${ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 }^{ 2- }$ has a Cr-O-Cr bond.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Dichromate means 2 atoms of chromium like Potassium dichromate. Dichromates are soluble in water and hence, they can act as an oxidizing agent in acidic, neutral, and alkaline medium.
Complete step-by-step answer:
> As we know that sodium ions have smaller sizes than potassium ions. Ongoing down the group, the solubility of dichromates of alkali metals decreases as the hydration enthalpy down the group decreases as compared to lattice energy. So, solubility also decreases.
> Hence, ${ Na }_{ 2 }{ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 }$ is more soluble than ${ K }_{ 2 }{ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 }$.
> Chromates are odorless and yellowish colored substances. They are generally insoluble in water. The structure of the chromate ion is shown below:
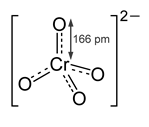
> The hybridization can be calculated by the following formula:
${ H=1/2(V+M-C+A) }$
where V = no. of valence electrons in an atom
M = number of monovalent atoms around the central atom
C = positive charge on cation
A = negative charge on an anion
So, put the values in the above formula:
${ H=1/2(6+0-0+2) }$
H = ${ 4 }$
Hence, ${ CrO }_{ 4 }^{ 2- }$ is tetrahedral in shape.
> The term primary standard refers to the pure elements/atoms free from hydrate ions which are used as a reference while secondary standards are prepared in the laboratory for experimental analysis.
> As ${ Na }_{ 2 }{ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 }$ is hygroscopic (which absorbs or attracts moisture from the atmosphere) in nature, so it cannot be used as a primary standard. This statement is not correct.
The structure of the dichromate ion is shown below:
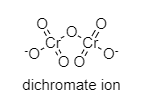
As we can see there is a Cr-O-Cr bond that is present, so this statement is correct.
The correct options are A and C.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option D as you may confuse between chromate and dichromate ions. But in dichromates Cr-O-Cr bond is present but in chromate ions, this bond is not present.
Complete step-by-step answer:
> As we know that sodium ions have smaller sizes than potassium ions. Ongoing down the group, the solubility of dichromates of alkali metals decreases as the hydration enthalpy down the group decreases as compared to lattice energy. So, solubility also decreases.
> Hence, ${ Na }_{ 2 }{ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 }$ is more soluble than ${ K }_{ 2 }{ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 }$.
> Chromates are odorless and yellowish colored substances. They are generally insoluble in water. The structure of the chromate ion is shown below:

> The hybridization can be calculated by the following formula:
${ H=1/2(V+M-C+A) }$
where V = no. of valence electrons in an atom
M = number of monovalent atoms around the central atom
C = positive charge on cation
A = negative charge on an anion
So, put the values in the above formula:
${ H=1/2(6+0-0+2) }$
H = ${ 4 }$
Hence, ${ CrO }_{ 4 }^{ 2- }$ is tetrahedral in shape.
> The term primary standard refers to the pure elements/atoms free from hydrate ions which are used as a reference while secondary standards are prepared in the laboratory for experimental analysis.
> As ${ Na }_{ 2 }{ Cr }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 7 }$ is hygroscopic (which absorbs or attracts moisture from the atmosphere) in nature, so it cannot be used as a primary standard. This statement is not correct.
The structure of the dichromate ion is shown below:

As we can see there is a Cr-O-Cr bond that is present, so this statement is correct.
The correct options are A and C.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option D as you may confuse between chromate and dichromate ions. But in dichromates Cr-O-Cr bond is present but in chromate ions, this bond is not present.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




