
Which of the following is steam volatile?
(A) o-Nitrophenol
(B) p-nitrophenol
(C) Both of them
(D) Neither of them
Answer
242.7k+ views
Hint: Any compound that can be distilled with steam distillation process, is called steam volatile compound. One of the compounds from o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol forms a special type of bond which lowers its melting and boiling point from the other.
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
As shown in the hint part, steam volatile compound is a compound that can be distilled by steam distillation process. Now during steam distillation, the compound needs to have its melting point under the boiling point of water so that steam will pass through the solution and the compound will melt if it is in solid state and can be separated from impurities by distillation.
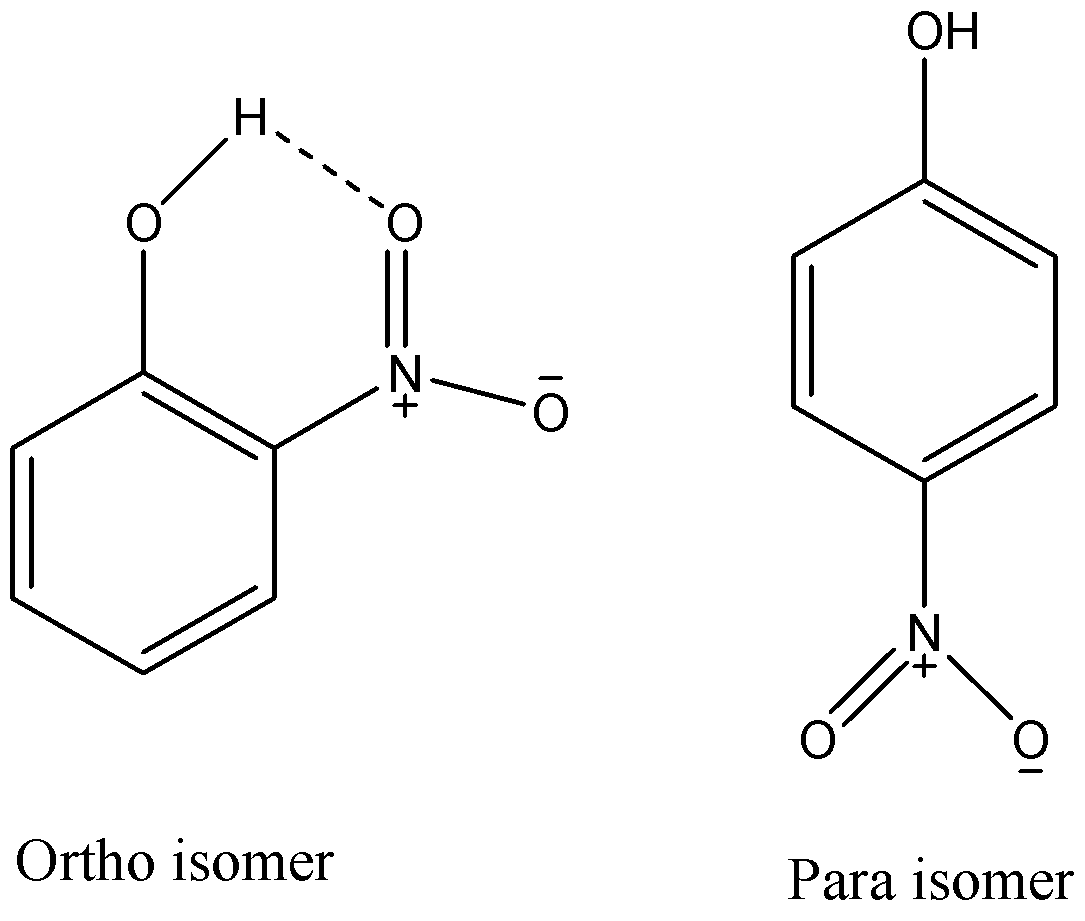
From the above given structures, we can see that ortho isomer has an intramolecular hydrogen bonding while para isomer cannot show it. As hydrogen atoms of o-nitrophenol are involved in intramolecular hydrogen bonding, they cannot effectively form hydrogen bonds with other molecules and hence it will have lower melting and boiling point then the para-isomer.
It is also practically proved that o-nitrophenol has M.P of \[{45^ \circ }C\] and p-nitrophenol has M.P of \[{119^ \circ }C\]. So, as o-nitrophenol has a lower melting point, it will easily melt and get converted to its vapours to get distilled by steam. While p-nitrophenol has a melting point higher than water’s boiling point and hence it will not be distilled with steam distillation. So, we can say that only o-nitrophenol is steam volatile.
Hence correct answer is (A) o-Nitrophenol
Note: Remember that volatile compound and steam volatile compounds are totally different terminologies. Do not get confused with intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen bonding as both are different and have different effects on the melting point of a compound.
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
As shown in the hint part, steam volatile compound is a compound that can be distilled by steam distillation process. Now during steam distillation, the compound needs to have its melting point under the boiling point of water so that steam will pass through the solution and the compound will melt if it is in solid state and can be separated from impurities by distillation.

From the above given structures, we can see that ortho isomer has an intramolecular hydrogen bonding while para isomer cannot show it. As hydrogen atoms of o-nitrophenol are involved in intramolecular hydrogen bonding, they cannot effectively form hydrogen bonds with other molecules and hence it will have lower melting and boiling point then the para-isomer.
It is also practically proved that o-nitrophenol has M.P of \[{45^ \circ }C\] and p-nitrophenol has M.P of \[{119^ \circ }C\]. So, as o-nitrophenol has a lower melting point, it will easily melt and get converted to its vapours to get distilled by steam. While p-nitrophenol has a melting point higher than water’s boiling point and hence it will not be distilled with steam distillation. So, we can say that only o-nitrophenol is steam volatile.
Hence correct answer is (A) o-Nitrophenol
Note: Remember that volatile compound and steam volatile compounds are totally different terminologies. Do not get confused with intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen bonding as both are different and have different effects on the melting point of a compound.
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




