
Which of the following is a disadvantage of nylon?
(A) They do not shrink
(B) They are less resistant to sunlight
(C) They are resistant to insects and molds
(D) They can be easily dyed
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Nylons are polyamides which represents polyamide fibres. In polymer chemistry, the term polyamide refers to the category of condensation polymers which have amide linkages. These polyamides are synthesized by the condensation polymerization of dibasic acids with diamines or their equivalents. Polyamides are categorized into synthetic fibres and are featured by high tensile strength, abrasion resistance etc.
Complete step by step answer: There are many types of nylons. Two examples are nylon – 6 and nylon – 6, 6.
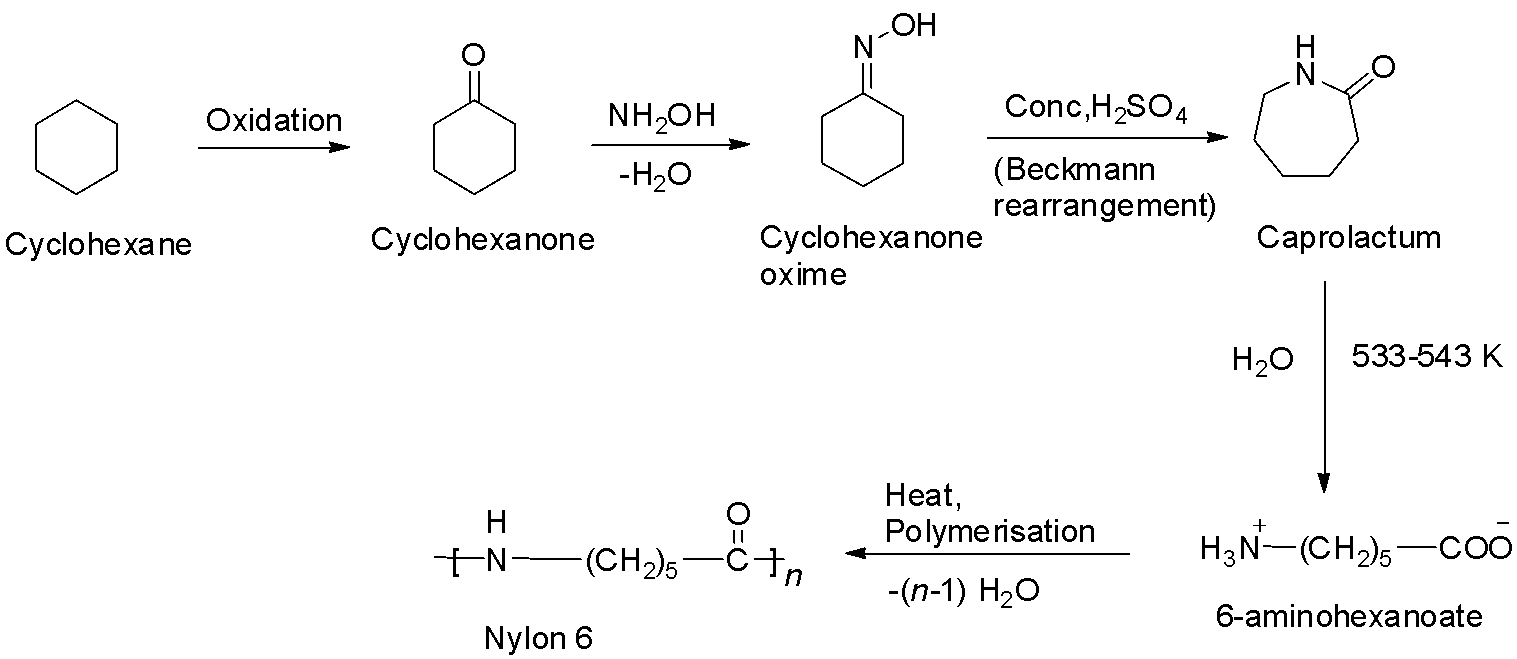
Nylon – 6 is a polyamide prepared from a single monomer called caprolactam. The caprolactum is manufactured from cyclohexane. When caprolactum is heated with water, it forms an aminocaproic acid that undergoes polymerization to give nylon – 6. The reaction is shown below.
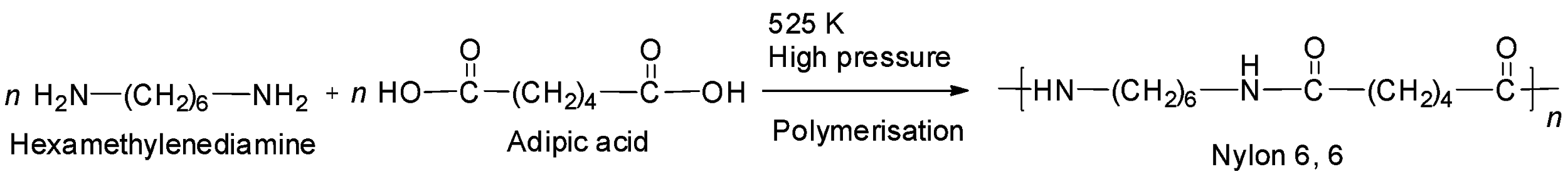
Nylon 6, 6 is also a polyamide formed by the condensation polymerisation of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid.
Although the nylon polymers have many advantages, they have certain disadvantages too. Among the disadvantages, the greatest disadvantage of nylon is its poor resistance to sunlight. After long exposure to the sunlight, the nylon fabric starts to turn yellow and its strength starts declining. So, it is not suitable for preparing outdoor clothing. Hence, option B is correct.
Nylon has poor heat resistance and when subjected to heat for a long time, it turns yellow and strength decreases. The fabric also starts to shrink. So, shrinking is a disadvantage of nylon. Hence, option A is wrong.
Nylon is a thermoplastic and so it is easily moldable. It also has insect-resistant properties and it has better dyeability than polyester. So, these are the advantages of nylon fibres and hence, options C and D are wrong.
Note: Some other disadvantages of nylon are poor moisture absorption and poor comfort, poor acid resistance and anti-oxidant properties, susceptibility to fuzzing after being used for a long time and susceptibility to crease.
Complete step by step answer: There are many types of nylons. Two examples are nylon – 6 and nylon – 6, 6.
Nylon – 6 is a polyamide prepared from a single monomer called caprolactam. The caprolactum is manufactured from cyclohexane. When caprolactum is heated with water, it forms an aminocaproic acid that undergoes polymerization to give nylon – 6. The reaction is shown below.

Nylon 6, 6 is also a polyamide formed by the condensation polymerisation of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid.

Although the nylon polymers have many advantages, they have certain disadvantages too. Among the disadvantages, the greatest disadvantage of nylon is its poor resistance to sunlight. After long exposure to the sunlight, the nylon fabric starts to turn yellow and its strength starts declining. So, it is not suitable for preparing outdoor clothing. Hence, option B is correct.
Nylon has poor heat resistance and when subjected to heat for a long time, it turns yellow and strength decreases. The fabric also starts to shrink. So, shrinking is a disadvantage of nylon. Hence, option A is wrong.
Nylon is a thermoplastic and so it is easily moldable. It also has insect-resistant properties and it has better dyeability than polyester. So, these are the advantages of nylon fibres and hence, options C and D are wrong.
Note: Some other disadvantages of nylon are poor moisture absorption and poor comfort, poor acid resistance and anti-oxidant properties, susceptibility to fuzzing after being used for a long time and susceptibility to crease.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




