
Which of the following figures represents the cross-section of an octahedral site-
A)
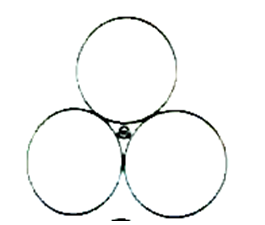
B)
C)
D)
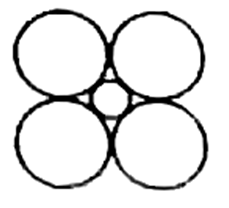
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The vacuum created by equilateral triangles with alternate apices is known as an "octahedral void." Tetrahedral voids are the empty spaces between four spheres that are arranged in a tetrahedral pattern.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
A place at the core of a cluster of six atoms that make up an octahedron is known as an octahedral site. In comparison to the tetrahedral site, the octahedral space is bigger. There is one octahedral site for each atom when atoms of the same size are grouped as tightly as feasible.
Consider this figure
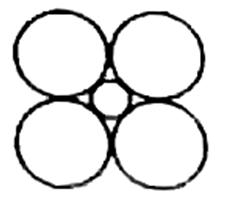
The cross section of an octahedral site is shown in this illustration. Octahedral layer refers to the interstitial void created by the union of two triangular voids from the first and second layers.
So the correct answer is option (D).
Note: We must keep in mind that the voids, which exist in crystal structures as empty spaces, are caused by the different atomic configurations. Tetrahedral and octahedral voids are the two basic categories of voids. Tetrahedral and octahedral voids differ in that tetrahedral void can only be observed in materials with tetrahedral crystal systems, whereas octahedral void can only be observed in materials with octahedral crystal systems. When six atoms, groups of atoms, or ligands are symmetrically positioned around a central atom to form the vertices of an octahedron, the shape of the compound is called octahedral molecular geometry. The prefix octa refers to the octahedron, which has eight faces. Although octahedral compounds typically have an atom in their centre and no links between the ligand atoms, the octahedron is one of the Platonic solids.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
A place at the core of a cluster of six atoms that make up an octahedron is known as an octahedral site. In comparison to the tetrahedral site, the octahedral space is bigger. There is one octahedral site for each atom when atoms of the same size are grouped as tightly as feasible.
Consider this figure

The cross section of an octahedral site is shown in this illustration. Octahedral layer refers to the interstitial void created by the union of two triangular voids from the first and second layers.
So the correct answer is option (D).
Note: We must keep in mind that the voids, which exist in crystal structures as empty spaces, are caused by the different atomic configurations. Tetrahedral and octahedral voids are the two basic categories of voids. Tetrahedral and octahedral voids differ in that tetrahedral void can only be observed in materials with tetrahedral crystal systems, whereas octahedral void can only be observed in materials with octahedral crystal systems. When six atoms, groups of atoms, or ligands are symmetrically positioned around a central atom to form the vertices of an octahedron, the shape of the compound is called octahedral molecular geometry. The prefix octa refers to the octahedron, which has eight faces. Although octahedral compounds typically have an atom in their centre and no links between the ligand atoms, the octahedron is one of the Platonic solids.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




