
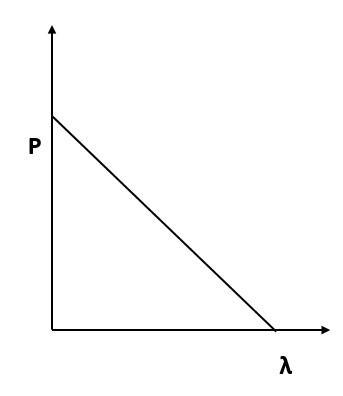
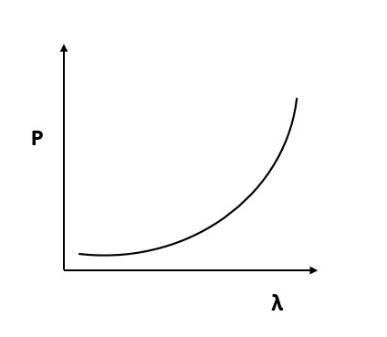
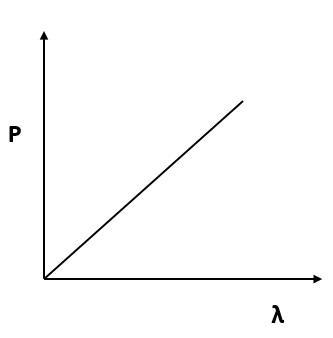
Which of the following figures represent the variation of particle momentum and the associated de-Broglie wavelength?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
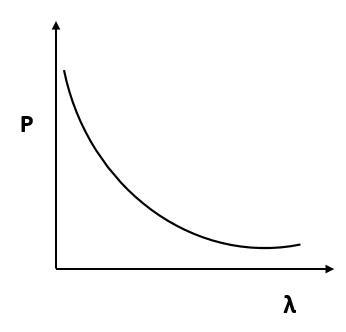




Answer
239.1k+ views
Hint: The relation between de Broglie wavelength and linear momentum is calculated from the energy of the photon. De Broglie’s equation equates de Broglie wavelength to the ratio of Planck’s constant and linear momentum.
Formula Used: The formulae used in the solution are given here.
Momentum of a photon is given by-
$P = \dfrac{E}{c} = \dfrac{h}{\lambda }$ where $E$ is the energy of the photon, $c$ is the speed of light in vacuum, $h$ is the Planck’s constant and $\lambda $ is the de Broglie wavelength.
Complete Step by Step Solution: The wavelength that is associated with an object in relation to its momentum and mass is known as de Broglie wavelength. A particle’s de Broglie wavelength is usually inversely proportional to its force.
Momentum of a photon is given by-
$P = \dfrac{E}{c} = \dfrac{h}{\lambda }$ where $E$ is the energy of the photon, $c$ is the speed of light in vacuum, $h$ is the Planck’s constant and $\lambda $ is the de Broglie wavelength.
According to de Broglie, $p = \dfrac{h}{\lambda }$ or $p\alpha \dfrac{1}{\lambda }$.
By this relation we can conclude that the linear momentum of a photon is inversely proportional to the de Broglie wavelength. The graph of $p$ vs $\lambda$ shall be a rectangular hyperbola.
It will look like,
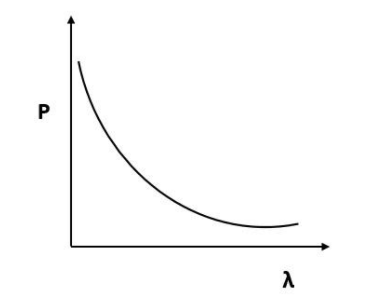
Hence, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: It is said that matter has a dual nature of wave-particles. De Broglie waves named after the discoverer Louis de Broglie, is the property of a material object that varies in time or space while behaving similar to waves. It is also called matter-waves. It holds great similarity to the dual nature of light which behaves as particle and wave, which has been proven experimentally.
The physicist Louis de Broglie suggested that particles might have both wave properties and particle properties. The wave nature of electrons was also detected experimentally to substantiate the suggestion of Louis de Broglie.
The objects which we see in day-to-day life have wavelengths which are very small and invisible, hence, we do not experience them as waves. However, de Broglie wavelengths are quite visible in the case of subatomic particles.
Formula Used: The formulae used in the solution are given here.
Momentum of a photon is given by-
$P = \dfrac{E}{c} = \dfrac{h}{\lambda }$ where $E$ is the energy of the photon, $c$ is the speed of light in vacuum, $h$ is the Planck’s constant and $\lambda $ is the de Broglie wavelength.
Complete Step by Step Solution: The wavelength that is associated with an object in relation to its momentum and mass is known as de Broglie wavelength. A particle’s de Broglie wavelength is usually inversely proportional to its force.
Momentum of a photon is given by-
$P = \dfrac{E}{c} = \dfrac{h}{\lambda }$ where $E$ is the energy of the photon, $c$ is the speed of light in vacuum, $h$ is the Planck’s constant and $\lambda $ is the de Broglie wavelength.
According to de Broglie, $p = \dfrac{h}{\lambda }$ or $p\alpha \dfrac{1}{\lambda }$.
By this relation we can conclude that the linear momentum of a photon is inversely proportional to the de Broglie wavelength. The graph of $p$ vs $\lambda$ shall be a rectangular hyperbola.
It will look like,

Hence, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: It is said that matter has a dual nature of wave-particles. De Broglie waves named after the discoverer Louis de Broglie, is the property of a material object that varies in time or space while behaving similar to waves. It is also called matter-waves. It holds great similarity to the dual nature of light which behaves as particle and wave, which has been proven experimentally.
The physicist Louis de Broglie suggested that particles might have both wave properties and particle properties. The wave nature of electrons was also detected experimentally to substantiate the suggestion of Louis de Broglie.
The objects which we see in day-to-day life have wavelengths which are very small and invisible, hence, we do not experience them as waves. However, de Broglie wavelengths are quite visible in the case of subatomic particles.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Step-by-Step Guide to Young’s Double Slit Experiment Derivation

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Essential Derivations for CBSE Class 12 Physics: Stepwise & PDF Solutions

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis




