
Urea
A.is an amide of carbonic acid
B.is diamide of carbonic acid
C.gives carbonic acid on hydrolysis
D.Resembles carbonic acid
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Urea is the most widely known waste product of many living organisms. It is also a major component of human urine and animal waste. Urea is a natural product of nitrogen and protein metabolism and is prepared by heating carbon dioxide ($C{{O}_{2}}$) and ammonia ($N{{H}_{3}}$). To solve this problem first we have to know the structure of urea.
Complete answer:Urea is the major nitrogenous end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in human beings, animals, and some fishes. When proteins are broken down, amino groups i.e $-N{{H}_{2}}$groups are removed from an amino acid that partly comprises proteins. Further, these amino groups are converted to ammonia $(N{{H}_{3}})$. As we know ammonia is very much toxic to our body system, thereby it must be converted to urea and excreted through urine.
Urea can be made commercially by combining liquid carbon dioxide and liquid ammonia under high pressures and elevated temperatures. At first ammonium carbamate is formed which then further decomposes to urea and water at low pressures.
$\begin{align}
& 2N{{H}_{3}}+C{{O}_{2}}\to N{{H}_{2}}COON{{H}_{4}} \\
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,(Ammonium\,\,carbamate) \\
\end{align}$
$\begin{align}
& N{{H}_{2}}COON{{H}_{4}}\to N{{H}_{2}}CON{{H}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O \\
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,(Urea) \\
\end{align}$
When both the hydroxyl groups $(-OH)$ of carbonic acid (${{H}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}$) are replaced by $-N{{H}_{2}}$ groups then the formed structure of diamide is called urea. Hence urea is a diamide of carbonic acid.
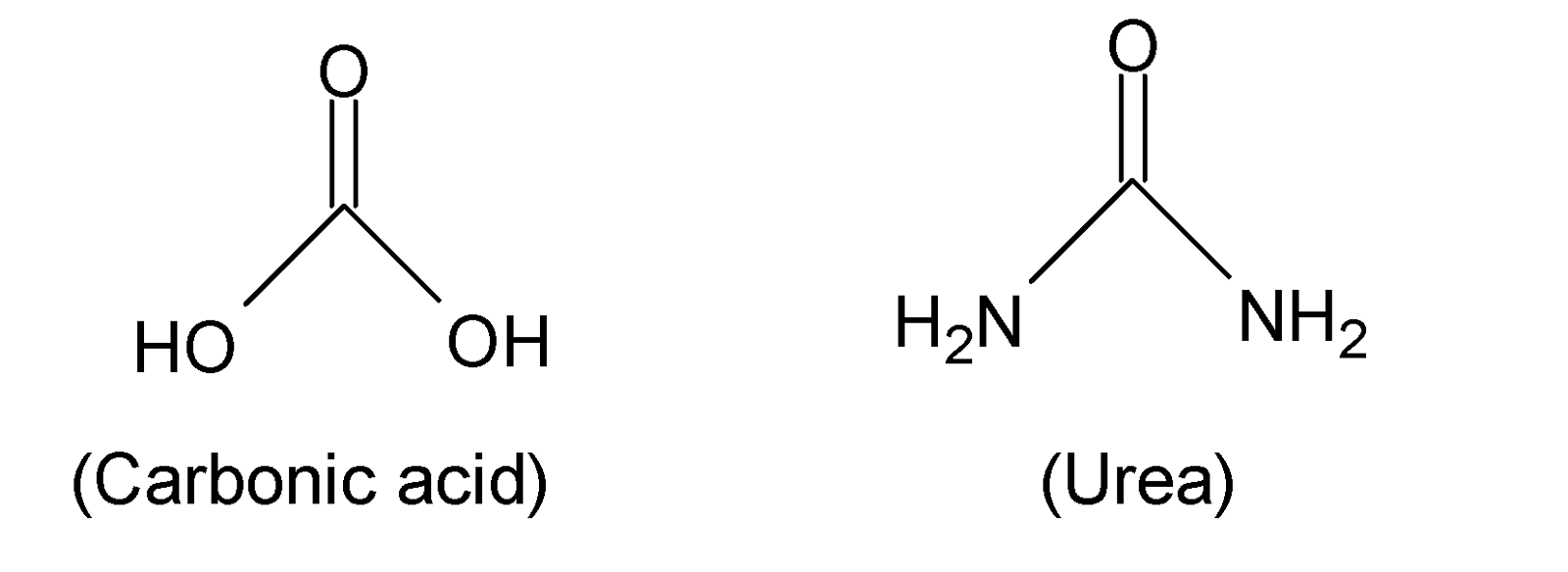
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: As urea contains a high amount of nitrogen, hence it can be used as fertilizer. It makes a long-lasting fertilizer and gradually releases ammonia into the soil. Nitrogen in urea is in non-protein form and hence it can be utilized in animals like sheep, and cattle. A major portion of animal protein requirements can be taken in this way.
Complete answer:Urea is the major nitrogenous end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in human beings, animals, and some fishes. When proteins are broken down, amino groups i.e $-N{{H}_{2}}$groups are removed from an amino acid that partly comprises proteins. Further, these amino groups are converted to ammonia $(N{{H}_{3}})$. As we know ammonia is very much toxic to our body system, thereby it must be converted to urea and excreted through urine.
Urea can be made commercially by combining liquid carbon dioxide and liquid ammonia under high pressures and elevated temperatures. At first ammonium carbamate is formed which then further decomposes to urea and water at low pressures.
$\begin{align}
& 2N{{H}_{3}}+C{{O}_{2}}\to N{{H}_{2}}COON{{H}_{4}} \\
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,(Ammonium\,\,carbamate) \\
\end{align}$
$\begin{align}
& N{{H}_{2}}COON{{H}_{4}}\to N{{H}_{2}}CON{{H}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O \\
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,(Urea) \\
\end{align}$
When both the hydroxyl groups $(-OH)$ of carbonic acid (${{H}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}$) are replaced by $-N{{H}_{2}}$ groups then the formed structure of diamide is called urea. Hence urea is a diamide of carbonic acid.

Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: As urea contains a high amount of nitrogen, hence it can be used as fertilizer. It makes a long-lasting fertilizer and gradually releases ammonia into the soil. Nitrogen in urea is in non-protein form and hence it can be utilized in animals like sheep, and cattle. A major portion of animal protein requirements can be taken in this way.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




