
What type of wave is represented by a density-distance graph?
A. Transverse wave
B. Longitudinal wave
C. Water wave
D. Light wave
Answer
240.6k+ views
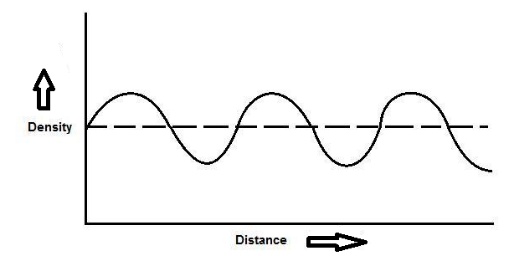
Hint: To solve this question, we need to know the basic theory related to the Longitudinal wave, Transverse wave, Water wave and Light wave. As we know the density-distance graph for a longitudinal wave at any point of time is drawn by plotting the particle density of the medium on the y -axis against distance on the x-axis as discussed below.
Complete step by step answer:
Mechanical waves are classified by their type of motion and fall into any of two categories: longitudinal or transverse.
Remember that both waves (transverse and longitudinal waves) can be periodic. A transverse wave propagates in such a way that the disturbance is always perpendicular to the direction of motion.
Light can be modeled as an electromagnetic wave. In this system, a varying electric field creates a changing magnetic field. This varying magnetic field then creates a change in the electric field.
Water waves involve a combination of both waves (longitudinal and transverse motions) and As a results water waves travel through the water. The radius of the water wave circles decreases as the depth into the water increases.
Therefore, we concluded that the Longitudinal wave is always represented by a density-distance graph. Longitudinal waves consist of compression and rarefaction in the medium.
Always remember that In the compression area air density is extremely higher than the normal air density while in case of rarefaction zone the air density is lower than the normal air density.
Therefore the correct option is B
Note: Always remember that in a density-distance graph, Compression refers to the region of high density or concentration or pressure and Rarefaction refers to the region of low density or concentration or pressure.
Complete step by step answer:
Mechanical waves are classified by their type of motion and fall into any of two categories: longitudinal or transverse.
Remember that both waves (transverse and longitudinal waves) can be periodic. A transverse wave propagates in such a way that the disturbance is always perpendicular to the direction of motion.
Light can be modeled as an electromagnetic wave. In this system, a varying electric field creates a changing magnetic field. This varying magnetic field then creates a change in the electric field.
Water waves involve a combination of both waves (longitudinal and transverse motions) and As a results water waves travel through the water. The radius of the water wave circles decreases as the depth into the water increases.
Therefore, we concluded that the Longitudinal wave is always represented by a density-distance graph. Longitudinal waves consist of compression and rarefaction in the medium.
Always remember that In the compression area air density is extremely higher than the normal air density while in case of rarefaction zone the air density is lower than the normal air density.
Therefore the correct option is B
Note: Always remember that in a density-distance graph, Compression refers to the region of high density or concentration or pressure and Rarefaction refers to the region of low density or concentration or pressure.

Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




