
Two masses ${m_1}$and ${m_2}$ are suspended together by a massless spring of constant K. When the masses are in equilibrium, ${m_1}$is removed without disturbing the system. The amplitude of oscillations is
A. $\dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{K}$
B. $\dfrac{{{m_2}g}}{K}$
C. $\dfrac{{({m_1} + {m_2})g}}{K}$
D. $\dfrac{{({m_1} - {m_2})g}}{K}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:The problem is from the oscillations and waves section of physics. We have to apply the concepts of spring constant and vibrations to solve this problem. We can write the equation of motion for the two cases. When two masses are attached and when one mass is removed. After that from those two equations, we can find the amplitude of the oscillations.
Complete step by step solution:
The diagram is redrawn as
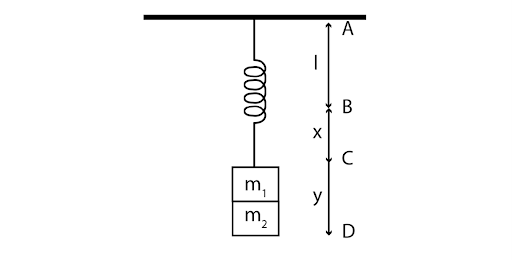
The length of the initial spring is $l$. When mass ${m_2}$ is attached to the spring and it stretches a distance x from point B to C. When mass \[{m_1}\] is attached to the spring and it stretches a distance y from point C to D. Then the equation of motion will be,
$({m_1} + {m_2})g = - k(x + y)$...........(1)
When mass ${m_1}$ is removed from the system, the equation of motion will become
${m_2}g = - kx$ …………(2)
By comparing and solving equations (1) and (2) we will get,
${m_1}g = - ky$
$\therefore y = - \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{k} = \left| {\dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{k}} \right|$
That is, the amplitude of the oscillation is $y = \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{k}$.
Hence, the correct option is option A.
Additional Information: The process of any quantity or measure fluctuating repeatedly about its equilibrium value in time is known as oscillation. A periodic change in an object's value between two values or around its central value is another way to define oscillation.
Note: The spring constant is defined as the stiffness of the spring. The equation of the spring constant is given as, \[k = - \dfrac{F}{x}\]. Where F = Force applied, x = displacement by the spring and k = spring constant.
Complete step by step solution:
The diagram is redrawn as

The length of the initial spring is $l$. When mass ${m_2}$ is attached to the spring and it stretches a distance x from point B to C. When mass \[{m_1}\] is attached to the spring and it stretches a distance y from point C to D. Then the equation of motion will be,
$({m_1} + {m_2})g = - k(x + y)$...........(1)
When mass ${m_1}$ is removed from the system, the equation of motion will become
${m_2}g = - kx$ …………(2)
By comparing and solving equations (1) and (2) we will get,
${m_1}g = - ky$
$\therefore y = - \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{k} = \left| {\dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{k}} \right|$
That is, the amplitude of the oscillation is $y = \dfrac{{{m_1}g}}{k}$.
Hence, the correct option is option A.
Additional Information: The process of any quantity or measure fluctuating repeatedly about its equilibrium value in time is known as oscillation. A periodic change in an object's value between two values or around its central value is another way to define oscillation.
Note: The spring constant is defined as the stiffness of the spring. The equation of the spring constant is given as, \[k = - \dfrac{F}{x}\]. Where F = Force applied, x = displacement by the spring and k = spring constant.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




