
A trolly falling freely on an inclined plane as shown in the figure. The angle of string of pendulum with the ceiling of trolley is $\left( \alpha \right)$ equal to-
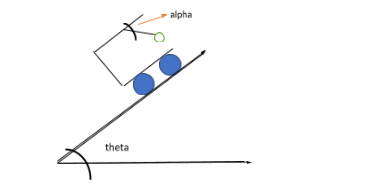
(A). ${\theta ^ \circ }$
(B). ${90^ \circ } - {\theta ^ \circ }$
(C). ${90^ \circ }$
(D). ${0^ \circ }$
Answer
529.4k+ views
- Hint: We will add the component of tension and component of weight and put it in the formula of force in order to solve this question. The formula for force is $F = ma$.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let T be the tension acting on the trolley.
So, the component of tension along the inclined plane is $T\cos \alpha $.
If m is the mass of the system of trolley, then the component of weight along the inclined plane is $mg\sin \theta $.
As we know that the acceleration of the trolley is equal to the acceleration of the bob in the trolley as bob is in the equilibrium in the frame of the trolley.
So, the net force along the plane will be-
$
\Rightarrow F = ma \\
\\
\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta + T\cos \alpha = ma \\
$
For the free falling trolly on an inclined plane, acceleration $a = g\sin \theta $ along the plane.
So, putting this value of acceleration in the above formula, we get-
$
\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta + T\cos \alpha = ma \\
\\
\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta + T\cos \alpha = mg\sin \theta \\
$
Cancelling $mg\sin \theta $ from both the sides, we get-
$
\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta + T\cos \alpha = mg\sin \theta \\
\\
\Rightarrow T\cos \alpha = 0 \\
\\
\Rightarrow \cos \alpha = 0 \\
\\
\Rightarrow \alpha = {90^ \circ } \\
$
Hence, option C is the correct option.
Note: In physics, tension is depicted as the pulling force transmitted axially by the methods for a string, a cable, chain, or comparative one-dimensional continuous object, or by each finish of a bar, truss member, or comparable three-dimensional object; tension may likewise be portrayed as the action-reaction pair of forces acting at each finish of said elements.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let T be the tension acting on the trolley.
So, the component of tension along the inclined plane is $T\cos \alpha $.
If m is the mass of the system of trolley, then the component of weight along the inclined plane is $mg\sin \theta $.
As we know that the acceleration of the trolley is equal to the acceleration of the bob in the trolley as bob is in the equilibrium in the frame of the trolley.
So, the net force along the plane will be-
$
\Rightarrow F = ma \\
\\
\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta + T\cos \alpha = ma \\
$
For the free falling trolly on an inclined plane, acceleration $a = g\sin \theta $ along the plane.
So, putting this value of acceleration in the above formula, we get-
$
\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta + T\cos \alpha = ma \\
\\
\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta + T\cos \alpha = mg\sin \theta \\
$
Cancelling $mg\sin \theta $ from both the sides, we get-
$
\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta + T\cos \alpha = mg\sin \theta \\
\\
\Rightarrow T\cos \alpha = 0 \\
\\
\Rightarrow \cos \alpha = 0 \\
\\
\Rightarrow \alpha = {90^ \circ } \\
$
Hence, option C is the correct option.
Note: In physics, tension is depicted as the pulling force transmitted axially by the methods for a string, a cable, chain, or comparative one-dimensional continuous object, or by each finish of a bar, truss member, or comparable three-dimensional object; tension may likewise be portrayed as the action-reaction pair of forces acting at each finish of said elements.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




