
Two masses ${\text{A}}$ and ${\text{B}}$ of ${\text{10kg}}$ and ${\text{5kg}}$ respectively are connected within a string passes over a frictionally pulley fixed at a corner of a table. As shown in figure. The Coefficient of ${\text{A}}$ with the table is $0.20.$ The minimum value of mass of ${\text{C}}$ that may be placed on the on ${\text{A}}$ to prevent it from moving is equal to:
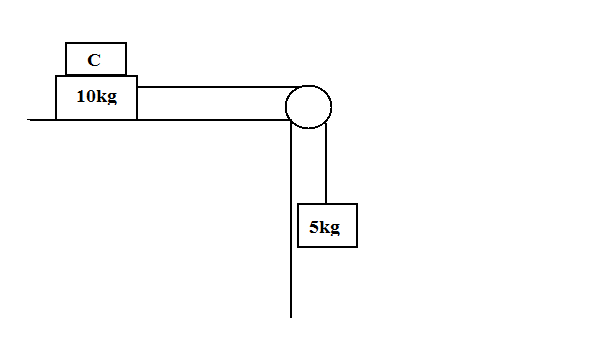
A) ${\text{15kg}}$
B) ${\text{10kg}}$
C) ${\text{5kg}}$
D) ${\text{0kg}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The block will not move unless a force greater than the maximum friction is applied to it. The maximum friction will be the product of the coefficient of static friction times the normal force acting on the block due to the contact surface.
Formula Used::
${f_1} = \mu N$
$\because {{\text{f}}_{\text{1}}}$ is maximum friction
${{\mu }}$ is coefficient of static friction
${\text{N}}$ is the Normal Reaction.
Complete step by step Answer:
Let the mass of block ${\text{C}}$ is ${{\text{M}}_{\text{c}}}$,
And tension on a rope is ${\text{T}}$
Now let us draw the free body diagram for the given situation, this will help us balance all the forces acting on the body.
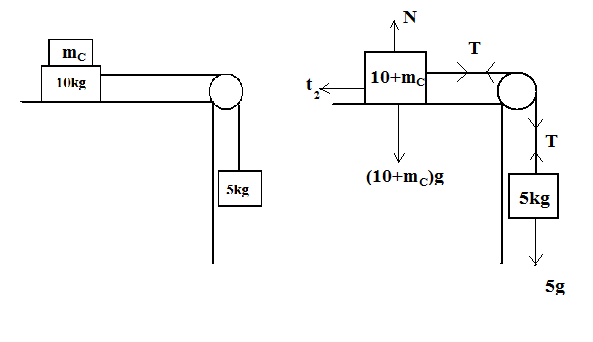
According to the question, we have to find the minimum value of block ${\text{C}}$. So that block A prevents itself from moving.
By seeing Free Body Diagram, We get that the tension T is balancing the mass ${\text{5kg}}$.
So, we can write
$T - 5g = 0$ Or
$
T = mg \\
T = 5g \\
$
$T = 5g - \left( i \right)$
Secondly, the friction ${{\text{f}}_{\text{1}}}$ is balancing the Tension T, So.
$
{f_1} - T = 0 \\
{f_1} = T - \left( {ii} \right) \\
$
The Normal Reaction is balancing the masses of blocks ${\text{C & A}}$. So
$N = \left( {10 + {M_c}} \right)g - \left( {iii} \right)$
Now, we know that, friction can be given as;
${f_1} = \mu N$
Putting the value of ${\text{N}}$ from ${\text{e}}{{\text{q}}^{\text{n}}}\left( {{\text{iii}}} \right)$
${f_1} = \mu \left( {10 + mc} \right)g$
Further from equation $(ii)$ we get;
$T = \mu \left( {10 + mc} \right)g$
$\left[ {\because {f_1} = T} \right]$
Now from equation $(i)$
$5g = \mu \left( {10 + mc} \right)g$
Now calculating further we get;
$ \Rightarrow 5 = \mu \left( {10 + mc} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{5}{\mu } = \left( {10 + mc} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{5}{{0.2}} = \left( {10 + mc} \right)$
$\therefore {m_c} = 15kg$
So, the minimum value of block ${\text{C}}$ such that it prevents block ${\text{A}}$from moving is ${\text{15kg}}$.
Hence, Option (A) is correct, i.e. ${\text{15kg}}$.
Note: The simple way to solve these types of questions is to make a free body diagram of the system, make equations of resulting force and find out the value of quantity which is asked in a question. i.e. Net force $ = 0$ [Newton’s ${{\text{3}}^{{\text{rd}}}}$ law].
Formula Used::
${f_1} = \mu N$
$\because {{\text{f}}_{\text{1}}}$ is maximum friction
${{\mu }}$ is coefficient of static friction
${\text{N}}$ is the Normal Reaction.
Complete step by step Answer:
Let the mass of block ${\text{C}}$ is ${{\text{M}}_{\text{c}}}$,
And tension on a rope is ${\text{T}}$
Now let us draw the free body diagram for the given situation, this will help us balance all the forces acting on the body.

According to the question, we have to find the minimum value of block ${\text{C}}$. So that block A prevents itself from moving.
By seeing Free Body Diagram, We get that the tension T is balancing the mass ${\text{5kg}}$.
So, we can write
$T - 5g = 0$ Or
$
T = mg \\
T = 5g \\
$
$T = 5g - \left( i \right)$
Secondly, the friction ${{\text{f}}_{\text{1}}}$ is balancing the Tension T, So.
$
{f_1} - T = 0 \\
{f_1} = T - \left( {ii} \right) \\
$
The Normal Reaction is balancing the masses of blocks ${\text{C & A}}$. So
$N = \left( {10 + {M_c}} \right)g - \left( {iii} \right)$
Now, we know that, friction can be given as;
${f_1} = \mu N$
Putting the value of ${\text{N}}$ from ${\text{e}}{{\text{q}}^{\text{n}}}\left( {{\text{iii}}} \right)$
${f_1} = \mu \left( {10 + mc} \right)g$
Further from equation $(ii)$ we get;
$T = \mu \left( {10 + mc} \right)g$
$\left[ {\because {f_1} = T} \right]$
Now from equation $(i)$
$5g = \mu \left( {10 + mc} \right)g$
Now calculating further we get;
$ \Rightarrow 5 = \mu \left( {10 + mc} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{5}{\mu } = \left( {10 + mc} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{5}{{0.2}} = \left( {10 + mc} \right)$
$\therefore {m_c} = 15kg$
So, the minimum value of block ${\text{C}}$ such that it prevents block ${\text{A}}$from moving is ${\text{15kg}}$.
Hence, Option (A) is correct, i.e. ${\text{15kg}}$.
Note: The simple way to solve these types of questions is to make a free body diagram of the system, make equations of resulting force and find out the value of quantity which is asked in a question. i.e. Net force $ = 0$ [Newton’s ${{\text{3}}^{{\text{rd}}}}$ law].
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Fluids (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Law of Motion (2025-26)

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




