
Two different types of rubber are found to have stress-strain curves as shown then-
(A). A is suitable for shock absorber
(B). B is suitable for shock absorber
(C). B is suitable for car types
(D). None of these
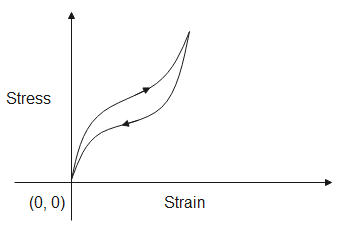
(A)
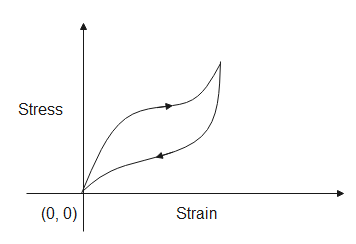
(B)
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The following graphs are stress-strain hysteresis loops for two different types of rubber. It shows that the behavior or material while increasing the load is not the same as when decreasing the load. In order to act as shock absorbers, the material should be good at dissipating energy. The energy dissipated is given by the area of the closed curve.
Complete step-by-step solution
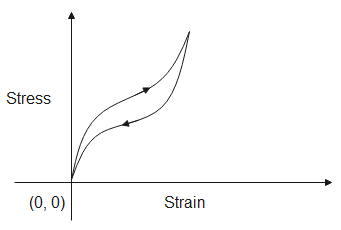
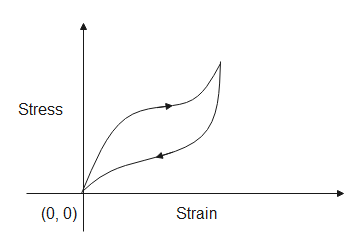
The following graphs show the strain produced in rubber when stress is applied to it. The stress-strain curve gives us information about the elasticity of materials.
The force applied per unit area is called stress.
The deformation caused in the body in the direction of force divided by initial dimensions is called strain.
The area under the above curve gives us the energy absorbed by the material when it is being stretched, while the area under the below curve is the energy released when the stress is being released. Therefore, the area of the close curve gives us energy dissipated. Since the area of the closed curve of fig (B) has a greater area, the energy dissipated in it will be more.
This property of rubber with a curve in fig (B) can be used to absorb the vibrations in machines as most of the absorbed energy will be dissipated.
Since B is more suitable to be a shock absorber due to a larger area of a closed curve, the correct option is (B).
Note: The graph shows that the behavior of rubber when increasing the load is not the same as when decreasing the load, this is called hysteresis and the curves are said to make hysteresis loops. If the stress applied increases the length of the material then it is called tensile stress. If the length decreases due to the stress applied then it is called compressive stress.
Complete step-by-step solution


The following graphs show the strain produced in rubber when stress is applied to it. The stress-strain curve gives us information about the elasticity of materials.
The force applied per unit area is called stress.
The deformation caused in the body in the direction of force divided by initial dimensions is called strain.
The area under the above curve gives us the energy absorbed by the material when it is being stretched, while the area under the below curve is the energy released when the stress is being released. Therefore, the area of the close curve gives us energy dissipated. Since the area of the closed curve of fig (B) has a greater area, the energy dissipated in it will be more.
This property of rubber with a curve in fig (B) can be used to absorb the vibrations in machines as most of the absorbed energy will be dissipated.
Since B is more suitable to be a shock absorber due to a larger area of a closed curve, the correct option is (B).
Note: The graph shows that the behavior of rubber when increasing the load is not the same as when decreasing the load, this is called hysteresis and the curves are said to make hysteresis loops. If the stress applied increases the length of the material then it is called tensile stress. If the length decreases due to the stress applied then it is called compressive stress.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




