
Two blocks A and B of masses $2m$ and $m$ respectively are connected by a massless and inextensible string. The whole system is suspended by a massless spring as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the acceleration of A and B immediately after the string is cut are respectively
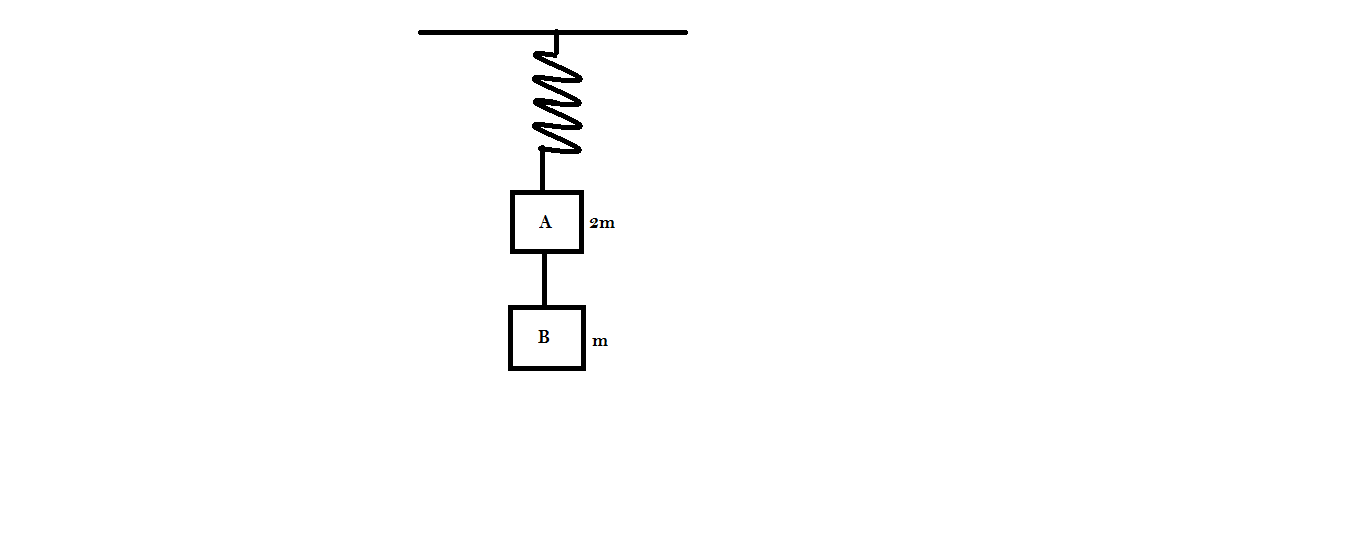
A) $g,\dfrac{g}{2}$
B) $\dfrac{g}{2},g$
C) $g,g$
D) \[\dfrac{g}{2},\dfrac{g}{2}\]
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: Use newton’s second law of motion. In the figure, the system is in equilibrium therefore all the forces are balancing each other. Tension in the string is balanced by the force $mg$ for the B block and the force $2mg + mg$ is balanced by the force $F$ of the spring. Use these equations to find the acceleration for both blocks.
Complete step by step solution:
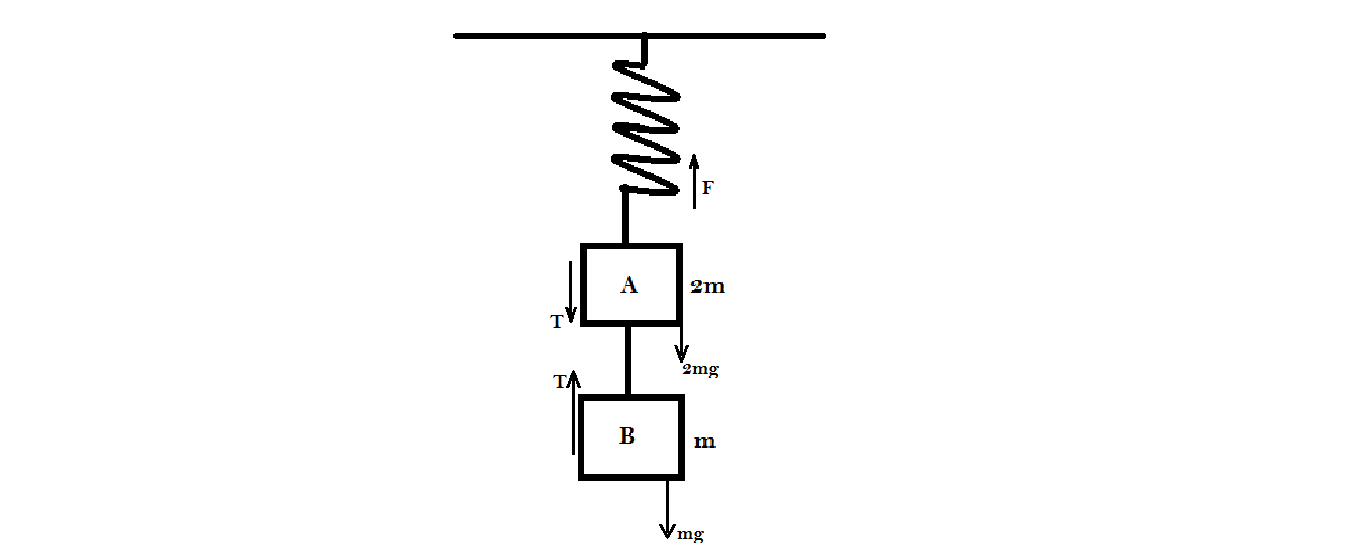 Step 1: In the above figure we can see that the gravitational force on the block B of mass $m$ is balanced out by the tension $T$ in the string because of the mass $m$ . Therefore we can write it as
Step 1: In the above figure we can see that the gravitational force on the block B of mass $m$ is balanced out by the tension $T$ in the string because of the mass $m$ . Therefore we can write it as
$\therefore T = mg$ ……equation (1).
Step 2: Since both the blocks are connected and are hanged by a spring. Therefore the total amount of force balanced out by the spring will be $mg + 2mg$ . If the force applied by the spring is $F$ to keep the system in equilibrium then
$\therefore F = mg + 2mg$
$ \Rightarrow F = 3mg$…….equation (2).
Step 3: Now if the string is cut then the tension in the string will disappear and block B start falling. The force which is acting on block B is the only gravitational force. Therefore we can write
$\therefore mg = ma$ , where $a$ is the acceleration of the block
$ \Rightarrow a = g$
Step 4: When the string is cut, immediately the spring pulls block A upwards. Now because the direction of the motion is opposite to the direction of the gravitational force, therefore if the acceleration of the block is $a$ then,
$\therefore F - 2mg = 2ma$
But $F = 3mg$ . Therefore, substitute the value of $F$ in the above equation
$\therefore 3mg - 2mg = 2ma$
$ \Rightarrow mg = 2ma$
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{g}{2}$
Therefore the magnitude of the acceleration of A and B immediately after the string is cut are respectively $\dfrac{g}{2}$ and $g$ .
Hence the option B is correct.
Note: In the question, the magnitude of the acceleration is asked for both blocks. For block A the acceleration will be negative as the gravitational force works downwards while the block is moving upwards. But when we take the magnitude of a negative quantity it becomes positive since the negative sign is only for the direction. The magnitude of the acceleration is a scalar quantity that does not have the direction.
Complete step by step solution:
 Step 1: In the above figure we can see that the gravitational force on the block B of mass $m$ is balanced out by the tension $T$ in the string because of the mass $m$ . Therefore we can write it as
Step 1: In the above figure we can see that the gravitational force on the block B of mass $m$ is balanced out by the tension $T$ in the string because of the mass $m$ . Therefore we can write it as$\therefore T = mg$ ……equation (1).
Step 2: Since both the blocks are connected and are hanged by a spring. Therefore the total amount of force balanced out by the spring will be $mg + 2mg$ . If the force applied by the spring is $F$ to keep the system in equilibrium then
$\therefore F = mg + 2mg$
$ \Rightarrow F = 3mg$…….equation (2).
Step 3: Now if the string is cut then the tension in the string will disappear and block B start falling. The force which is acting on block B is the only gravitational force. Therefore we can write
$\therefore mg = ma$ , where $a$ is the acceleration of the block
$ \Rightarrow a = g$
Step 4: When the string is cut, immediately the spring pulls block A upwards. Now because the direction of the motion is opposite to the direction of the gravitational force, therefore if the acceleration of the block is $a$ then,
$\therefore F - 2mg = 2ma$
But $F = 3mg$ . Therefore, substitute the value of $F$ in the above equation
$\therefore 3mg - 2mg = 2ma$
$ \Rightarrow mg = 2ma$
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{g}{2}$
Therefore the magnitude of the acceleration of A and B immediately after the string is cut are respectively $\dfrac{g}{2}$ and $g$ .
Hence the option B is correct.
Note: In the question, the magnitude of the acceleration is asked for both blocks. For block A the acceleration will be negative as the gravitational force works downwards while the block is moving upwards. But when we take the magnitude of a negative quantity it becomes positive since the negative sign is only for the direction. The magnitude of the acceleration is a scalar quantity that does not have the direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




