
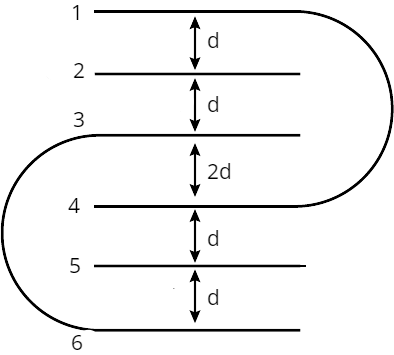
There are six plates of equal are $A$ and separation between the plates is $\mathrm{d}(\mathrm{d} \ll \mathrm{A})$ are arranged as shown in figure. The equivalent capacitance between points 2 and 5 , is $\alpha \dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{~A}}{\mathrm{~d}}$. Then find the value of $\alpha$.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: An electrical device with two terminals known as a capacitor has the capacity to store energy in the form of an electric charge. It is made up of two electrical wires that are spaced apart by a certain amount. Vacuum may be used to fill the space between the conductors, or a dielectric, an insulating substance, may be used instead. Capacitance is the term used to describe a capacitor's capacity to hold charges.
Formula used:
The expression of capacitance is,
$C=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{d}$
Here, A is the area of the cross section of the plate and d is the distance between the plates.
Complete step by step solution:
Rearrange the given plates as shown below
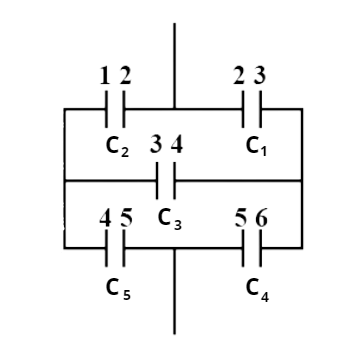
From this we get
${{C}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{d},$
$\Rightarrow {{C}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{2d}$
$\Rightarrow {{C}_{3}}=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{3d},$
$\Rightarrow {{C}_{4}}=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{2d},$
$\Rightarrow {{C}_{5}}=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{d}$
$C_{1}$ and $C_{2}$ are in series and its effective capacity is
$\dfrac{\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d} \times \dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{2 d}}{\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d}+\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{2 d}}=\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{3 d}$
The ratio of a system's electric charge change to the equivalent change in its electric potential is known as capacitance.
The effective capacitance of $C_{4}$ and $C_{3}=\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{3 d}$ is,
${{C}_{AB}}=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{3d}+\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{3d}+\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{3d}$
$\Rightarrow C_{A B}=\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{3 d}+\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{3d}+\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{3 d}$
$\Rightarrow C_{A B}=\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d}$
Substituting values we get
So the value of $\alpha =1$
Hence, the value of $\alpha$ is 1.
Note: The reciprocal of the equivalent capacitance when numerous capacitors are linked in series is equal to the total of the reciprocals of the individual capacitances. The equivalent capacitance is the total of the individual capacitances when many capacitors are connected in a parallel configuration. When numerous capacitors are linked in parallel, the equivalent capacitance is the sum of the individual capacitances. When a network of capacitors comprises a combination of series and parallel connections, we identify the series and parallel networks and compute their equal capacitances stepwise until the entire infrastructure is limited to a single equivalent capacitance.
Formula used:
The expression of capacitance is,
$C=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{d}$
Here, A is the area of the cross section of the plate and d is the distance between the plates.
Complete step by step solution:
Rearrange the given plates as shown below

From this we get
${{C}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{d},$
$\Rightarrow {{C}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{2d}$
$\Rightarrow {{C}_{3}}=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{3d},$
$\Rightarrow {{C}_{4}}=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{2d},$
$\Rightarrow {{C}_{5}}=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{d}$
$C_{1}$ and $C_{2}$ are in series and its effective capacity is
$\dfrac{\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d} \times \dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{2 d}}{\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d}+\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{2 d}}=\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{3 d}$
The ratio of a system's electric charge change to the equivalent change in its electric potential is known as capacitance.
The effective capacitance of $C_{4}$ and $C_{3}=\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{3 d}$ is,
${{C}_{AB}}=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{3d}+\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{3d}+\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{3d}$
$\Rightarrow C_{A B}=\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{3 d}+\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{3d}+\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{3 d}$
$\Rightarrow C_{A B}=\dfrac{\varepsilon_{0} A}{d}$
Substituting values we get
So the value of $\alpha =1$
Hence, the value of $\alpha$ is 1.
Note: The reciprocal of the equivalent capacitance when numerous capacitors are linked in series is equal to the total of the reciprocals of the individual capacitances. The equivalent capacitance is the total of the individual capacitances when many capacitors are connected in a parallel configuration. When numerous capacitors are linked in parallel, the equivalent capacitance is the sum of the individual capacitances. When a network of capacitors comprises a combination of series and parallel connections, we identify the series and parallel networks and compute their equal capacitances stepwise until the entire infrastructure is limited to a single equivalent capacitance.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




