
The work done by the frictional force on a surface in drawing a circle of radius r on the surface by a pencil of negligible mass with a normal pressing force N (coefficient of friction ${\mu _k}$) is:
A) $4\pi {r^2}{\mu _k}N$
B) $ - 2\pi {r^2}{\mu _k}N$
C) $ - 2\pi r{\mu _k}N$
D) Zero
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In this question, the concept of friction force is applied, that is the friction force is the product of the coefficient of friction and the normal force exerted on the body or the object. First, draw the diagram using all the information given in the question and then find out the work done by the frictional force in drawing a circle of radius and discuss the derivation.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given question first, we will draw the diagram as per the given situation.
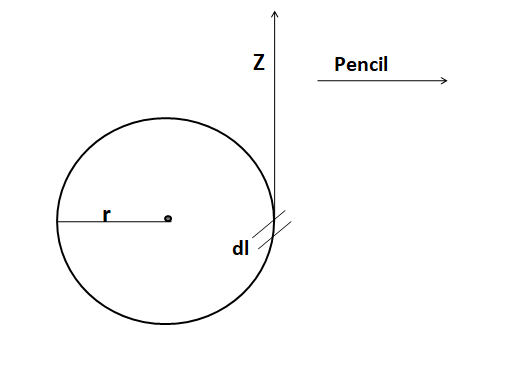
The motion of the pencil is in the $z$ direction. The given radius of the circle is $r$. The friction of motion will be tangentially.
So, we have to derive the work done at $dl$ length.
We know that the work done at length $dl$ can be written as
${\rm{dw = }}\;{\rm{ - }}{{\rm{f}}_k}.dl$
Here, the force of friction is ${{\rm{f}}_k}$.
As we know that the frictional force is always opposing the relative motion of the body so it is negative. Now, we integrate the above equation as,
$\int {dw\; = \;w} $
$ \Rightarrow \;w\, = - \int {{{\rm{f}}_k}.dl} $
We know that the friction force is the product of the coefficient of friction and the normal force exerted on the body or the object so,
${{\rm{f}}_k}\; = \;{\mu _k}{\rm{k}}$
Where, ${\mu _k}$is coefficient of friction and N is the pressing force.
Now we will substitute the value of friction force in the work done equation as,
$w\; = \, - \int {{\mu _k}{\rm{Ndl}}} $
The total length of the circle is $2\pi r$ . So to find out the total work done at length $dl$,we have to integrate from $0$ to $2\pi r$, so the above equation become,
$w\, = \, - \int\limits_0^{2\pi r} {{\mu _k}{\rm{Ndl}}} $
We integrate the above equation as,
$w\, = \, - {\mu _k}{\rm{N}}\left[ {2\pi r - 0} \right]$
$w\, = \, - 2\pi r{\mu _k}N$
Hence the correct option is (C).
Note: When a body is dragged along a rough surface, the frictional force will be acting in the direction opposite to the displacement of the body. And the angle between the displacement of the body and frictional force will be $180^\circ $. Hence the total work done by the frictional force will be negative.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given question first, we will draw the diagram as per the given situation.

The motion of the pencil is in the $z$ direction. The given radius of the circle is $r$. The friction of motion will be tangentially.
So, we have to derive the work done at $dl$ length.
We know that the work done at length $dl$ can be written as
${\rm{dw = }}\;{\rm{ - }}{{\rm{f}}_k}.dl$
Here, the force of friction is ${{\rm{f}}_k}$.
As we know that the frictional force is always opposing the relative motion of the body so it is negative. Now, we integrate the above equation as,
$\int {dw\; = \;w} $
$ \Rightarrow \;w\, = - \int {{{\rm{f}}_k}.dl} $
We know that the friction force is the product of the coefficient of friction and the normal force exerted on the body or the object so,
${{\rm{f}}_k}\; = \;{\mu _k}{\rm{k}}$
Where, ${\mu _k}$is coefficient of friction and N is the pressing force.
Now we will substitute the value of friction force in the work done equation as,
$w\; = \, - \int {{\mu _k}{\rm{Ndl}}} $
The total length of the circle is $2\pi r$ . So to find out the total work done at length $dl$,we have to integrate from $0$ to $2\pi r$, so the above equation become,
$w\, = \, - \int\limits_0^{2\pi r} {{\mu _k}{\rm{Ndl}}} $
We integrate the above equation as,
$w\, = \, - {\mu _k}{\rm{N}}\left[ {2\pi r - 0} \right]$
$w\, = \, - 2\pi r{\mu _k}N$
Hence the correct option is (C).
Note: When a body is dragged along a rough surface, the frictional force will be acting in the direction opposite to the displacement of the body. And the angle between the displacement of the body and frictional force will be $180^\circ $. Hence the total work done by the frictional force will be negative.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Fluids (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Law of Motion (2025-26)

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




