
The ruff degradation used to reduce the carbon chain in an –
(A) Alcohol
(B) Alkene
(C) Ketose
(D) Aldose
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Ruff degradation is a synthetic method to shorten the carbon-chain. It was first studied by Otto Ruff on glucose molecules.
Complete solution:
If we will add an aldehydic group to an acyclic form of monosaccharide, the resulting monosaccharide will be an aldose.
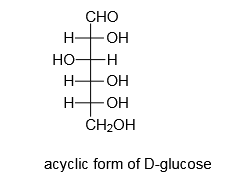
Ruff degradation will shorten the above chain by removing one carbon atom.
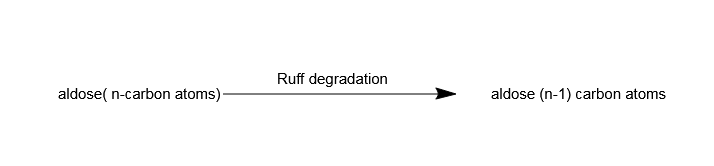
The overall conversion mechanism can be stated as follows-
The terminal aldehydic group is made to undergo selective oxidation, by using bromine water, and then it is converted to gluconate ion. In the next step, $Fe(OAc)3$ with 30% of $H2O2$ is added. This will result in the formation of $CO2$ along with a stereo selective compound from COO- ion. And in the downside, $ - CH2OH$will get converted to $ - CHO$ group. This conversion is achieved by the reduction of iron $Fe$ from its +3 state to +2 state. In this way, we get the product, D-Arabinose.
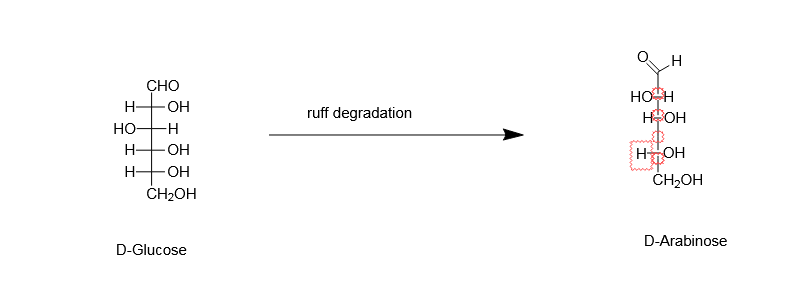
So, the correct option is D.
Note:
Ruff degradation has been named after its discoverer, Otto Ruff.
Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) is the enzyme that can break down alcohol into acetaldehyde. This enzyme can be found in the liver cells.
Arabinose acts as an inhibitor of enzyme Sucrase. This enzyme is present in the small intestine and helps to break down sucrose into fructose and glucose. Because of this ability, it is commercialized as a sweetener.
Arabinose is also used as a reversible switch for protein expression in E.coli
Complete solution:
If we will add an aldehydic group to an acyclic form of monosaccharide, the resulting monosaccharide will be an aldose.

Ruff degradation will shorten the above chain by removing one carbon atom.

The overall conversion mechanism can be stated as follows-
The terminal aldehydic group is made to undergo selective oxidation, by using bromine water, and then it is converted to gluconate ion. In the next step, $Fe(OAc)3$ with 30% of $H2O2$ is added. This will result in the formation of $CO2$ along with a stereo selective compound from COO- ion. And in the downside, $ - CH2OH$will get converted to $ - CHO$ group. This conversion is achieved by the reduction of iron $Fe$ from its +3 state to +2 state. In this way, we get the product, D-Arabinose.

So, the correct option is D.
Note:
Ruff degradation has been named after its discoverer, Otto Ruff.
Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) is the enzyme that can break down alcohol into acetaldehyde. This enzyme can be found in the liver cells.
Arabinose acts as an inhibitor of enzyme Sucrase. This enzyme is present in the small intestine and helps to break down sucrose into fructose and glucose. Because of this ability, it is commercialized as a sweetener.
Arabinose is also used as a reversible switch for protein expression in E.coli
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




