
The phenomenon of dispersion proves that:
(A) white light is made up of seven constituent colours
(B) light moves in a straight line
(C) light passes through a transparent medium
(D) light does not pass through an opaque medium and absence of light causes shadow.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The dispersion relates to the property of the light when it passes through the highly refracted material. The white light splits into some colours called spectrum. The medium may be a prism that is a three dimensional object that has two identical ends.
Complete step by step solution:
When the visible light passes through the prism, it splits into the seven consecutive colours called spectrum. This is formed because each component of the light of the incident ray provides the different colours of the different wavelengths that refracts in the different angles. This spectrum is visible to the eye as the seven colours like violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red. Here the prism is the medium in which the white light split into seven colours.
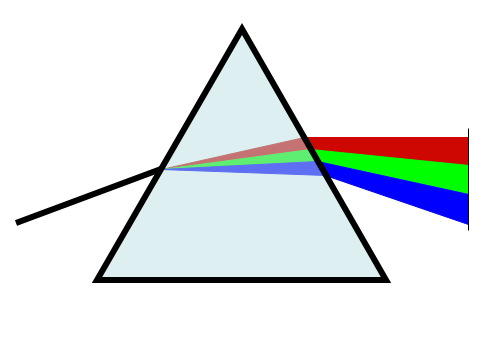
In which the red light has the maximum wavelength so it deviates to the least level in the spectrum where the violet colour has the minimum wavelength so it deviates most. All the other colours lie between them. Let come to the other options. In dispersion, the light bends and does not travel in a straight line. Light cannot pass through the opaque medium since the opaque medium does not produce seven colours instead it absorbs light. If the white light is transmitted in the transparent medium, it again transmits the same white light without any dispersion.
Thus the option (A) is correct.
Note: The rainbow is formed by this process. When the white light from the sun enters the water droplets, it undergoes total internal reflection, refraction and the dispersion to form the seven colours of light. Here the water droplet acts as the prism.
Complete step by step solution:
When the visible light passes through the prism, it splits into the seven consecutive colours called spectrum. This is formed because each component of the light of the incident ray provides the different colours of the different wavelengths that refracts in the different angles. This spectrum is visible to the eye as the seven colours like violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red. Here the prism is the medium in which the white light split into seven colours.

In which the red light has the maximum wavelength so it deviates to the least level in the spectrum where the violet colour has the minimum wavelength so it deviates most. All the other colours lie between them. Let come to the other options. In dispersion, the light bends and does not travel in a straight line. Light cannot pass through the opaque medium since the opaque medium does not produce seven colours instead it absorbs light. If the white light is transmitted in the transparent medium, it again transmits the same white light without any dispersion.
Thus the option (A) is correct.
Note: The rainbow is formed by this process. When the white light from the sun enters the water droplets, it undergoes total internal reflection, refraction and the dispersion to form the seven colours of light. Here the water droplet acts as the prism.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




