
The phase change in reflected wave, when light wave suffers reflection at the interface from air to glass is
(A) $0$
(B) $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
(C) $\pi $
(D) $2\pi $
Answer
242.7k+ views
Hint: A phase change occurs when a wave is reflected and for light waves it occurs only when reflection is taking place at a surface of higher refractive index than the medium it is travelling in.
Complete step-by-step solution
When light waves are passing from one medium to another the phase associated with the wave also changes. But phase change does not occur for every reflection. In light waves a phase change of 180o takes place when they reflect from the surface whose refractive index of the medium is higher than the medium they are travelling.
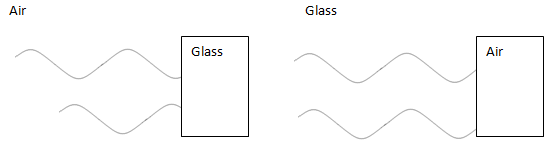
A light wave undergoes a phase change by π when travelling in air suffers reflection at glass but no phase change occurs when it is moving in glass and gets reflected at the surface of air.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: This is the reason why the optical boundaries are in ordered pairs mentioned as glass-air suggesting from which material the light is moving out and into. This phase change also plays an important role in thin film interference.
Complete step-by-step solution
When light waves are passing from one medium to another the phase associated with the wave also changes. But phase change does not occur for every reflection. In light waves a phase change of 180o takes place when they reflect from the surface whose refractive index of the medium is higher than the medium they are travelling.

A light wave undergoes a phase change by π when travelling in air suffers reflection at glass but no phase change occurs when it is moving in glass and gets reflected at the surface of air.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: This is the reason why the optical boundaries are in ordered pairs mentioned as glass-air suggesting from which material the light is moving out and into. This phase change also plays an important role in thin film interference.
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Important Questions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 Units and Measurement - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26




