
The number of dative bonds in sulphuric acid molecule is:
(A) $0$
(B) $1$
(C) $2$
(D) $4$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Dative bond is another name for coordinate bond. It is also a type of covalent bond in which both the electrons are donated by one atom at another, unlike an ordinary covalent bond where there is mutual sharing. Each of the atoms brings an electron to form a bond.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Sulphuric acid, also called as oil of vitriol has chemical formula\[{H_2}S{O_4}\]. Sulphur has a very high affinity for oxygen. The tendency of pπ−dπ bonding increases which increases the back bonding tendency as we move along the period from carbon to chlorine. Thus, from carbon to chlorine the formation of double bonds with oxygen tendency increases. Hence, sulphur has a very tendency to form pi bonds with oxygen.(before carbon the elements do not show covalent bonding).
Pi bond between sulphur and oxygen releases more energy and leads to more stability than a single bond between $S$ and $O$. Thus, when drawing the structure of sulphuric acid first priority is given to double bond with oxygen.
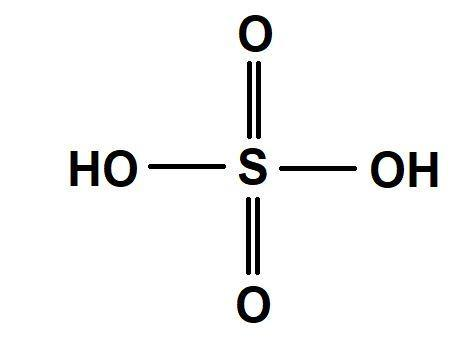
This double bond is actually back bonding which is a dative bond. Thus, there are $2$ dative bonds in sulphuric acid.
Hence, The correct answer is C.
Note: Sometimes, a dative bond is misunderstood as an ionic bond because the atom accepting the electron is represented by negative charge while donation of electron by the atom bears negative charge. sulphuric acid has zero charge on it but it is a charged molecule due to the electronegativity difference between \[S\]and\[O\]. The molecule has sp3 hybridization and it is tetrahedral in shape.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Sulphuric acid, also called as oil of vitriol has chemical formula\[{H_2}S{O_4}\]. Sulphur has a very high affinity for oxygen. The tendency of pπ−dπ bonding increases which increases the back bonding tendency as we move along the period from carbon to chlorine. Thus, from carbon to chlorine the formation of double bonds with oxygen tendency increases. Hence, sulphur has a very tendency to form pi bonds with oxygen.(before carbon the elements do not show covalent bonding).
Pi bond between sulphur and oxygen releases more energy and leads to more stability than a single bond between $S$ and $O$. Thus, when drawing the structure of sulphuric acid first priority is given to double bond with oxygen.

This double bond is actually back bonding which is a dative bond. Thus, there are $2$ dative bonds in sulphuric acid.
Hence, The correct answer is C.
Note: Sometimes, a dative bond is misunderstood as an ionic bond because the atom accepting the electron is represented by negative charge while donation of electron by the atom bears negative charge. sulphuric acid has zero charge on it but it is a charged molecule due to the electronegativity difference between \[S\]and\[O\]. The molecule has sp3 hybridization and it is tetrahedral in shape.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




