
The most acidic of the following is [J & K $2005$]
A.$ClC{{H}_{2}}COOH$
B.${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COOH$
C.$C{{D}_{3}}COOH$
D.$C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The most acidic compound refers to the more stable conjugate base which means the more stable the conjugate base, the more likely the acid donates a proton. Here we have to determine the most acidic compound among the given four acids, so we will have to find the most stable conjugate base.
Complete answer:Stronger acid tends to lose a proton ${{H}^{+}}$ion to a base. Here in (A), we have $ClC{{H}_{2}}COOH$ which chlorine atoms,$Cl$is a highly electron-withdrawing group. Due to this electronegative nature, it withdraws the electron density from the negatively charged oxygen atom, and as a result, a proton from the $-OH$ group can easily be closed. Therefore the produced conjugate base gains stability through resonance.
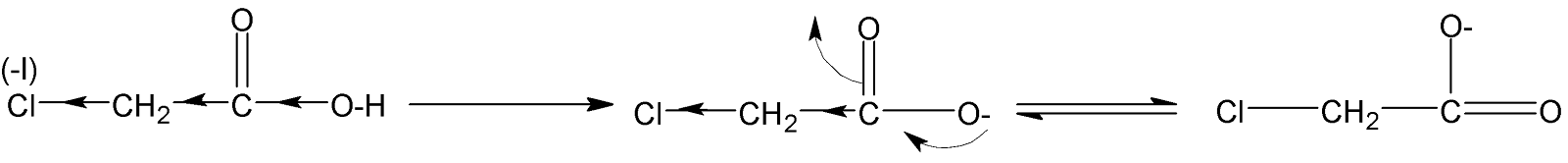
Therefore it is the most acidic as compared to other given acids.
When benzoic acid,${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COOH$forms a conjugate anion by donating one ${{H}^{+}}$ that is only stabilized by the inductive effect of the carbonyl group $(C=O)$ , as well as a negative charge on the oxygen atom, participates in resonance with double-bonded carbonyl oxygen. Also, the attached phenyl group with carboxylate ion further decreases the electron density on oxygen atoms making the benzoic acid more acidic. But it is less acidic than $ClC{{H}_{2}}COOH$as the inductive effect of a phenyl group($-{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}$) is less than $Cl$.
Again the more acidic compound is $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH$than the compound $C{{D}_{3}}COOH$ because protium$(H)$ is more electronegative than deuterium$(D)$. $-C{{D}_{3}}$the group has more $+I$effect than $-C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}$the group hence more electronegative $-C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}$group is better able to stabilize the carboxylate anion.
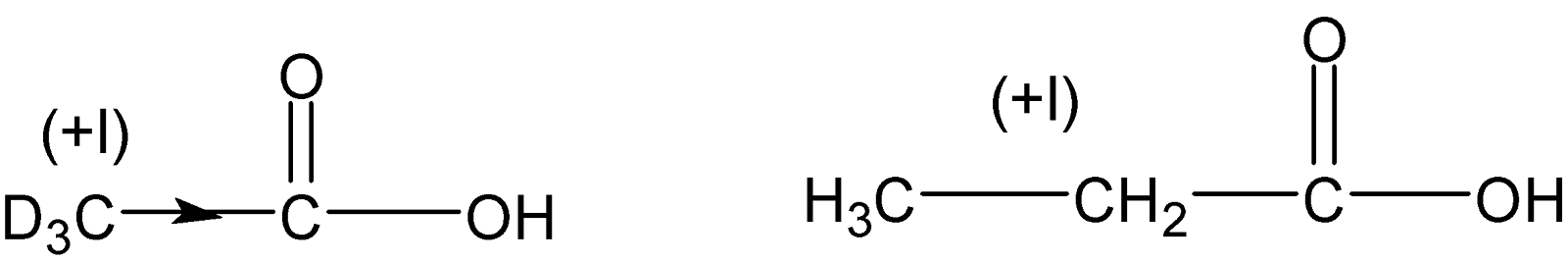
Therefore the decreasing order of acidity is $ClC{{H}_{2}}COOH>{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COOH>C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH>C{{D}_{3}}COOH$ .
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Note: To find the most acidic or most basic compound, we have to notice whether the electron donating group or electron withdrawing group is attached to that compound. In general, the acidity of a compound increases in the presence of the electron-withdrawing group, similarly electron donating group increases the basicity of a compound. Most importantly resonance and mesomeric effects dominate over inductive effects.
Complete answer:Stronger acid tends to lose a proton ${{H}^{+}}$ion to a base. Here in (A), we have $ClC{{H}_{2}}COOH$ which chlorine atoms,$Cl$is a highly electron-withdrawing group. Due to this electronegative nature, it withdraws the electron density from the negatively charged oxygen atom, and as a result, a proton from the $-OH$ group can easily be closed. Therefore the produced conjugate base gains stability through resonance.

Therefore it is the most acidic as compared to other given acids.
When benzoic acid,${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COOH$forms a conjugate anion by donating one ${{H}^{+}}$ that is only stabilized by the inductive effect of the carbonyl group $(C=O)$ , as well as a negative charge on the oxygen atom, participates in resonance with double-bonded carbonyl oxygen. Also, the attached phenyl group with carboxylate ion further decreases the electron density on oxygen atoms making the benzoic acid more acidic. But it is less acidic than $ClC{{H}_{2}}COOH$as the inductive effect of a phenyl group($-{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}$) is less than $Cl$.
Again the more acidic compound is $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH$than the compound $C{{D}_{3}}COOH$ because protium$(H)$ is more electronegative than deuterium$(D)$. $-C{{D}_{3}}$the group has more $+I$effect than $-C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}$the group hence more electronegative $-C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}$group is better able to stabilize the carboxylate anion.
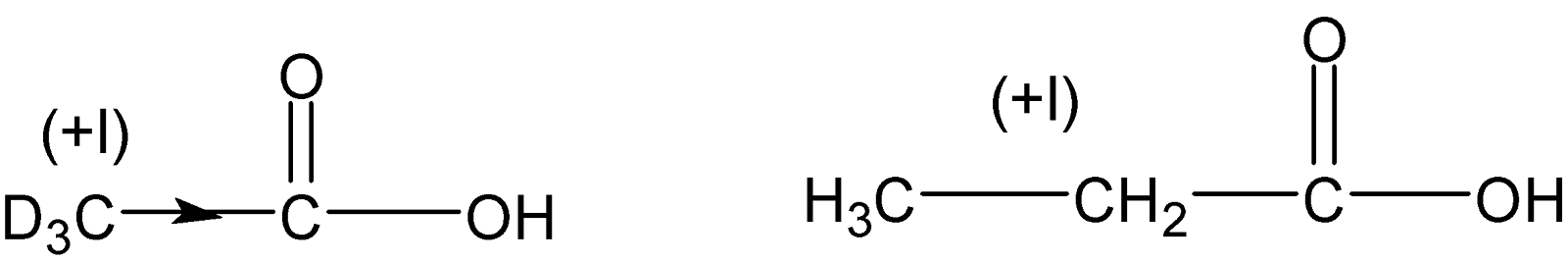
Therefore the decreasing order of acidity is $ClC{{H}_{2}}COOH>{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COOH>C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH>C{{D}_{3}}COOH$ .
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Note: To find the most acidic or most basic compound, we have to notice whether the electron donating group or electron withdrawing group is attached to that compound. In general, the acidity of a compound increases in the presence of the electron-withdrawing group, similarly electron donating group increases the basicity of a compound. Most importantly resonance and mesomeric effects dominate over inductive effects.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




