
The image of the point with position vector $[ \vec{i}+3\vec{k} ]$ in the plane $[\vec{r}.(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})=1 ]$ is-
A. $\vec{i}+2\vec{j}+\vec{k}$
B. $ \vec{i}-2\vec{j}+\vec{k}$
C. $-\vec{i}-2\vec{j}+\vec{k}$
D. $\vec{i}+2\vec{j}-\vec{k}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The object having both magnitude and direction are called vectors. The position vector is that vector that locates the position of any point on any plane from any origin. The direction of the position vector is from the origin towards the point. The point can also be a moving body.
Complete step by step solution: Let on the plane $[\vec{r}.(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})=1 ]$ the image of point P$ [ (\vec{i}+3\vec{k}) ]$ is Q.
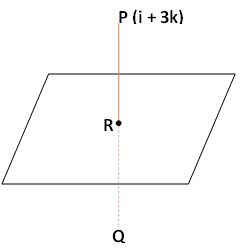
Hence, we can see that the PQ is normal/perpendicular to the plane$ [ \vec{r}.(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})=1 ]$. Since PQ is passing through P and is perpendicular to the given plane, the coordinates of P is (1,0,3), so the equation of PQ will be –
r=$(\vec{i}+3\vec{k})+\lambda(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})$
Since Q also lies on the line PQ, so the position vector of Q is$ [ (\vec{i}+3\vec{k})+\lambda(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})]$
⇒ $ (1+\lambda)\vec{i}+\lambda\vec{j}+(3+\lambda)\vec{k}$
As we know that the R is the midpoint of PQ, therefore position vector of R is
⇒ $\dfrac{(1+\lambda)\vec{i}+\lambda\vec{j}+(3+\lambda)\vec{k}+\vec{i}+3\vec{k}}{2}$
Or, $ (\dfrac{\lambda+2}{2})\vec{i}+(\dfrac{\lambda}{2})\vec{j}+(3+\dfrac{\lambda}{2})\ \vec{k}$
Or, $(\dfrac{\lambda}{2}+1)\vec{i}+(\dfrac{\lambda}{2})\vec{j}+(3+\dfrac{\lambda}{2})\ \vec{k}$
Since, R lies on plane$ [ \vec{r}.(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})=1]$
Hence,
⇒ $\left[(\dfrac{\lambda}{2}+1)\vec{i}+(\dfrac{\lambda}{2})\vec{j}+(3+\dfrac{\lambda}{2})\ \vec{k}\right].(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})=1$
⇒ $\left[(\dfrac{\lambda}{2}+1+\dfrac{\lambda}{2}+3+\dfrac{\lambda}{2})\ \right]=1$
⇒ λ = ―2
So, the position vector of Q is-
$(\vec{i}+3\vec{k})-2(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})=\ -\vec{i}-2\vec{j}+\vec{k} $
The image Q of the point with position vector$ [(\vec{i}+3\vec{k}) ]$ in the plane $[ \vec{r}.(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})=1 ] is [ -\vec{i}-2\vec{j}+\vec{k}]$
Thus, Option (C) is correct.
Note: When there is a change in the position of the position vector the difference in the change in the position of position vector is called displacement vector. The direction of the displacement vector is from the initial towards the final position. There are different types of vectors like unit vector, zero vector, collinear vector, equal vector, etc.
Complete step by step solution: Let on the plane $[\vec{r}.(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})=1 ]$ the image of point P$ [ (\vec{i}+3\vec{k}) ]$ is Q.

Hence, we can see that the PQ is normal/perpendicular to the plane$ [ \vec{r}.(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})=1 ]$. Since PQ is passing through P and is perpendicular to the given plane, the coordinates of P is (1,0,3), so the equation of PQ will be –
r=$(\vec{i}+3\vec{k})+\lambda(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})$
Since Q also lies on the line PQ, so the position vector of Q is$ [ (\vec{i}+3\vec{k})+\lambda(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})]$
⇒ $ (1+\lambda)\vec{i}+\lambda\vec{j}+(3+\lambda)\vec{k}$
As we know that the R is the midpoint of PQ, therefore position vector of R is
⇒ $\dfrac{(1+\lambda)\vec{i}+\lambda\vec{j}+(3+\lambda)\vec{k}+\vec{i}+3\vec{k}}{2}$
Or, $ (\dfrac{\lambda+2}{2})\vec{i}+(\dfrac{\lambda}{2})\vec{j}+(3+\dfrac{\lambda}{2})\ \vec{k}$
Or, $(\dfrac{\lambda}{2}+1)\vec{i}+(\dfrac{\lambda}{2})\vec{j}+(3+\dfrac{\lambda}{2})\ \vec{k}$
Since, R lies on plane$ [ \vec{r}.(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})=1]$
Hence,
⇒ $\left[(\dfrac{\lambda}{2}+1)\vec{i}+(\dfrac{\lambda}{2})\vec{j}+(3+\dfrac{\lambda}{2})\ \vec{k}\right].(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})=1$
⇒ $\left[(\dfrac{\lambda}{2}+1+\dfrac{\lambda}{2}+3+\dfrac{\lambda}{2})\ \right]=1$
⇒ λ = ―2
So, the position vector of Q is-
$(\vec{i}+3\vec{k})-2(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})=\ -\vec{i}-2\vec{j}+\vec{k} $
The image Q of the point with position vector$ [(\vec{i}+3\vec{k}) ]$ in the plane $[ \vec{r}.(\vec{i}+\vec{j}+\vec{k})=1 ] is [ -\vec{i}-2\vec{j}+\vec{k}]$
Thus, Option (C) is correct.
Note: When there is a change in the position of the position vector the difference in the change in the position of position vector is called displacement vector. The direction of the displacement vector is from the initial towards the final position. There are different types of vectors like unit vector, zero vector, collinear vector, equal vector, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits




