
The hybridization of carbon and oxygen in CO are respectively:
(A) sp, sp
(B) $s{p^2}$, sp
(C) $s{p^2}$, $s{p^2}$
(D) sp, $s{p^2}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: There are mainly three types of atomic orbital hybridization: $s{p^3}$, $s{p^2}$ and $sp$. By evaluating the steric number of an atom, the hybridization of that atom in a molecule can be determined.
Complete step by step solution:
-Before determining the states of hybridization of carbon and oxygen atoms in $CO$ molecules, let us know about hybridization first.
According to the valence bond theory, hybridization of orbitals is defined as the mixing of different atomic orbitals to produce new orbitals that are suitable for creating new chemical bonds. These new orbitals are called hybrid orbitals and they have different energies, shapes, and other properties than the parent orbitals.
-In order to determine the hybridization of an atom in a molecule, the steric number of that particular atom can be used.
-Steric number: The steric number of an atom is the summation of the number of lone pairs of electrons present in that atom and number of atoms that are directly attached to that atom. Hence, we can write,
SN = (number of lone pairs of electrons) + (number of atoms directly bonded to the atom)
-The Lewis structure of a molecule provides us with the complete overview of a molecule (how many lone pairs each has, the bonding pattern of each atom etc.).
-Let’s now look at the structure of carbon monoxide (CO) molecule:
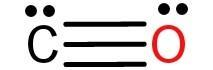
-From the structure of CO, we can write the following points:
1) The carbon atom has one lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to one oxygen atom.
2) The oxygen atom also has one lone pair of electrons and it is only bonded to a carbon atom.
3) The carbon and oxygen atom are attached by a triple bond with each other.
The steric number of carbon atom:
SN = 1 + 1 = 2
The steric number of oxygen atom:
SN = 1 + 1 = 2
-Now, the relation between steric number and the state of hybridization is as follows:
Hence, steric number 2 of an atom implies that the atom is sp hybridized. Here, both the carbon and oxygen atom have steric number 2, thus both of them will be sp hybridized.
Hence the correct answer is: (A) sp, sp.
Note: While calculating the steric number, the charges should not be included or excluded. Only two parameters are required to calculate the steric number of a particular atom in a molecule: lone pairs available on that atom and how many other atoms it is currently bonded with. To find out the accurate steric number, students have to draw the accurate Lewis structure of the molecule.
Complete step by step solution:
-Before determining the states of hybridization of carbon and oxygen atoms in $CO$ molecules, let us know about hybridization first.
According to the valence bond theory, hybridization of orbitals is defined as the mixing of different atomic orbitals to produce new orbitals that are suitable for creating new chemical bonds. These new orbitals are called hybrid orbitals and they have different energies, shapes, and other properties than the parent orbitals.
-In order to determine the hybridization of an atom in a molecule, the steric number of that particular atom can be used.
-Steric number: The steric number of an atom is the summation of the number of lone pairs of electrons present in that atom and number of atoms that are directly attached to that atom. Hence, we can write,
SN = (number of lone pairs of electrons) + (number of atoms directly bonded to the atom)
-The Lewis structure of a molecule provides us with the complete overview of a molecule (how many lone pairs each has, the bonding pattern of each atom etc.).
-Let’s now look at the structure of carbon monoxide (CO) molecule:
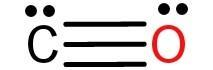
-From the structure of CO, we can write the following points:
1) The carbon atom has one lone pair of electrons and it is bonded to one oxygen atom.
2) The oxygen atom also has one lone pair of electrons and it is only bonded to a carbon atom.
3) The carbon and oxygen atom are attached by a triple bond with each other.
The steric number of carbon atom:
SN = 1 + 1 = 2
The steric number of oxygen atom:
SN = 1 + 1 = 2
-Now, the relation between steric number and the state of hybridization is as follows:
| Steric Number | Hybridization |
| 2 | $sp$ |
| 3 | $s{p^2}$ |
| 4 | $s{p^3}$ |
Hence, steric number 2 of an atom implies that the atom is sp hybridized. Here, both the carbon and oxygen atom have steric number 2, thus both of them will be sp hybridized.
Hence the correct answer is: (A) sp, sp.
Note: While calculating the steric number, the charges should not be included or excluded. Only two parameters are required to calculate the steric number of a particular atom in a molecule: lone pairs available on that atom and how many other atoms it is currently bonded with. To find out the accurate steric number, students have to draw the accurate Lewis structure of the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




