
The groups of heterocyclic compounds is :
A.phenol, furan
B.furan, thiophene
C.thiophene, phenol
D.furan, aniline
Answer
243.3k+ views
Hint:Heterocyclic compounds are cyclic structures containing atoms of at least two different elements in its ring structure.
Complete step by step answer:
Cyclic compounds are a category of organic/inorganic compounds in which some or all constituent elements or constituent compounds are arranged in a ring like structure. Although most of these cyclic compounds are organic in nature. If all the atoms that form the ring are carbon, the compound is said to be Carbocyclic; if not, the compound is called heterocyclic. Carbocyclic compounds are more commonly known as homocyclic compounds. Also, a cyclic compound which behaves chemically just as an open-chain aliphatic compound is said to be alicyclic.
In the case of hetero cyclic compounds, as the name suggests, one of the ring members is different in comparison to the remaining ring members. The number of hetero atoms can be more than one as well. Usually, heterocyclic compounds with 5 or 6 member rings are more stable than other possible configurations.
Now, coming back to the question, in order to properly determine the heterocyclic pair out of the given options, we must first understand the molecular structure of these compounds.
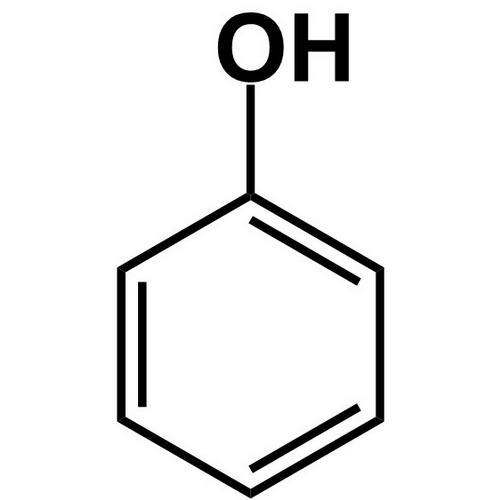
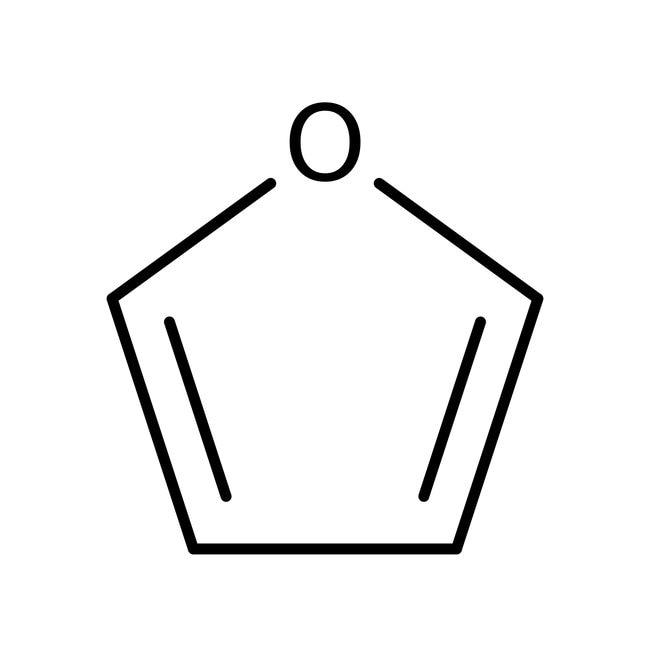
1. Phenol 2. furan
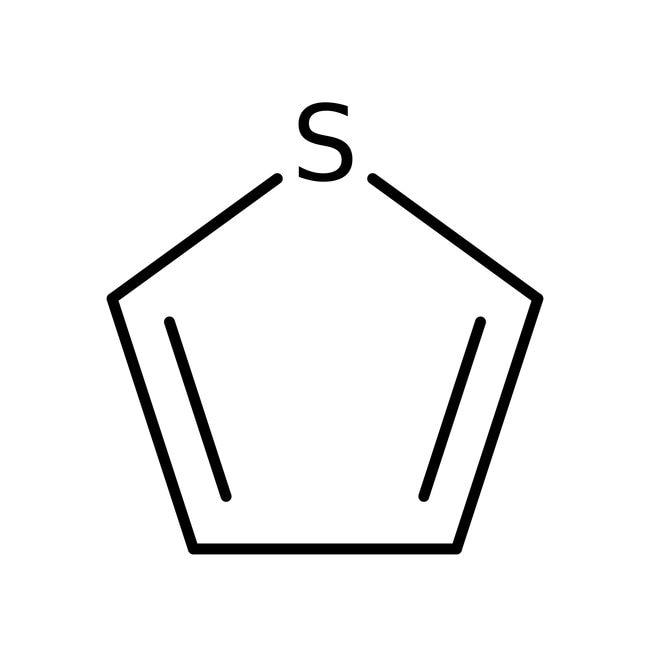
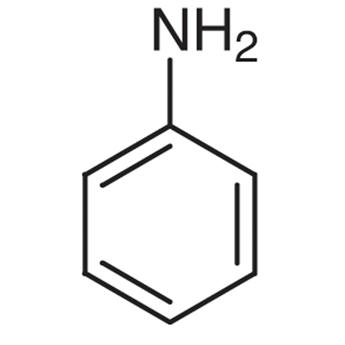
3.thiophene 4. Aniline
From the molecular structures of the given compounds represented above, we can determine the following things:
1.Phenol is NOT a heterocyclic compound because all the members of the ring structure are carbon.
2.Furan is a heterocyclic compound because it contains a hetero atom, i.e. oxygen
3.Thiophene is also a heterocyclic compound because it contains a hetero atom, i.e. sulphur
4.Aniline is NOT a heterocyclic compound because all the members of the ring structure are carbon.
Hence, Option B is the correct answer.
Note: The 3- and 4-member ring structure compounds are not stable and hence cannot be considered heterocyclic in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
Cyclic compounds are a category of organic/inorganic compounds in which some or all constituent elements or constituent compounds are arranged in a ring like structure. Although most of these cyclic compounds are organic in nature. If all the atoms that form the ring are carbon, the compound is said to be Carbocyclic; if not, the compound is called heterocyclic. Carbocyclic compounds are more commonly known as homocyclic compounds. Also, a cyclic compound which behaves chemically just as an open-chain aliphatic compound is said to be alicyclic.
In the case of hetero cyclic compounds, as the name suggests, one of the ring members is different in comparison to the remaining ring members. The number of hetero atoms can be more than one as well. Usually, heterocyclic compounds with 5 or 6 member rings are more stable than other possible configurations.
Now, coming back to the question, in order to properly determine the heterocyclic pair out of the given options, we must first understand the molecular structure of these compounds.


1. Phenol 2. furan


3.thiophene 4. Aniline
From the molecular structures of the given compounds represented above, we can determine the following things:
1.Phenol is NOT a heterocyclic compound because all the members of the ring structure are carbon.
2.Furan is a heterocyclic compound because it contains a hetero atom, i.e. oxygen
3.Thiophene is also a heterocyclic compound because it contains a hetero atom, i.e. sulphur
4.Aniline is NOT a heterocyclic compound because all the members of the ring structure are carbon.
Hence, Option B is the correct answer.
Note: The 3- and 4-member ring structure compounds are not stable and hence cannot be considered heterocyclic in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Exam Dates, Session 2 Updates, City Slip, Admit Card & Latest News

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




