
The geometry of the sulfur trioxide molecule is
A. Tetrahedral
B. Trigonal planar
C. Pyramidal
D. Square planar
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:Sulfur trioxide is a chemical compound having the formula SO₃.
It is a combination of one sulfur atom and three oxygen atoms.
Each oxygen atom is doubly bonded to the sulfur atom.
Complete step by step solution:Here in this question, we have to find out the geometry or structure of sulfur trioxide.
We know that the structure of a molecule is predicted by VSEPR theory.
Let us know about it.
VSEPR or valence shell electron pair repulsion theory has some postulates. These can be explained briefly as follows: -
The shape of the molecule relies on the no. of valence shell electron pairs around the main atom even if they are not bonded.
Pairs of electrons in the valence shell all are negatively charged and accordingly, repulsed by one another.
These pairs of electrons try to lessen the repulsion and therefore stay distant and separated from each other.
Lone pair-lone pair repulse each other intensely. Then comes lone pair-bond pair repulsion and bond pair-bond pair repulsion.
The sulfur trioxide molecule has each oxygen doubly bonded to the sulfur atom.
There are six bond pairs of electrons and no lone pairs.
There are three sigma bonds and three pi-bonds.
Thus, there is \[s{p^2}\] hybridization.
The valency of sulfur is fully satisfied.
But while predicting the geometry we can assume that there are 3 bond pairs as multiple bonds are taken as only one electron group.
Using VSEPR theory, we can say that the geometry is a trigonal planar.
The structure is as follows:-
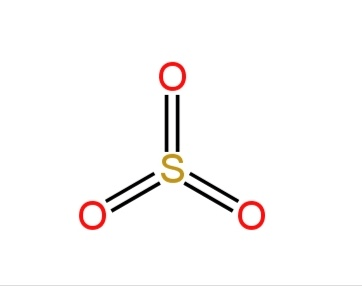
Image: Sulfur trioxide
So, option B is correct.
Note: A molecule whose central atom has only two electron groups is organized so that two groups are as far away from each other. So, these two electron groups are \[180^\circ\] apart. Therefore, the general molecular shape is linear. For example,\[BeC{l_2},C{O_2}\].
It is a combination of one sulfur atom and three oxygen atoms.
Each oxygen atom is doubly bonded to the sulfur atom.
Complete step by step solution:Here in this question, we have to find out the geometry or structure of sulfur trioxide.
We know that the structure of a molecule is predicted by VSEPR theory.
Let us know about it.
VSEPR or valence shell electron pair repulsion theory has some postulates. These can be explained briefly as follows: -
The shape of the molecule relies on the no. of valence shell electron pairs around the main atom even if they are not bonded.
Pairs of electrons in the valence shell all are negatively charged and accordingly, repulsed by one another.
These pairs of electrons try to lessen the repulsion and therefore stay distant and separated from each other.
Lone pair-lone pair repulse each other intensely. Then comes lone pair-bond pair repulsion and bond pair-bond pair repulsion.
The sulfur trioxide molecule has each oxygen doubly bonded to the sulfur atom.
There are six bond pairs of electrons and no lone pairs.
There are three sigma bonds and three pi-bonds.
Thus, there is \[s{p^2}\] hybridization.
The valency of sulfur is fully satisfied.
But while predicting the geometry we can assume that there are 3 bond pairs as multiple bonds are taken as only one electron group.
Using VSEPR theory, we can say that the geometry is a trigonal planar.
The structure is as follows:-

Image: Sulfur trioxide
So, option B is correct.
Note: A molecule whose central atom has only two electron groups is organized so that two groups are as far away from each other. So, these two electron groups are \[180^\circ\] apart. Therefore, the general molecular shape is linear. For example,\[BeC{l_2},C{O_2}\].
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




