
The forward biased diode
Answer
240k+ views
Hint: Here, we get the answer by knowing about the PN Junction diode and its characteristics of forward bias current flows from higher potential to lower potential and from opinion you can get the answer.
Complete step by step solution:
The P-N junction diode can be represented by
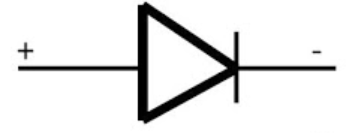
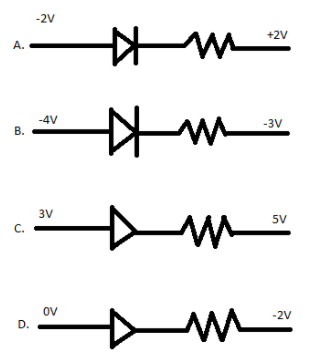
in which the ‘+’ side is called a cathode. In the forward bias current flows from anode to cathode and anode must be connected to higher potential and cathode must be connected to lower potential. When voltage is supplied from the battery source current starts to flow from higher potential to lower potential and is the same way diodes must be inserted that current enter from anode side and leave from cathode side. Anode side is also called P side and cathode side also called N side. Therefore the voltage must be higher at the anode side and voltage must be lower at the cathode side. So, from options we can see in option(D) only, the P side is at higher potential than n side.
P side (anode) at ’0’ volt and n side (cathode) at ‘-2’ volt.
Note: In the case of reverse bias, the polarity of battery change and there current enters to n side (cathode) and leaves from p side (anode). We can see option(C) n side at higher potential (5V) and p side at lower potential (3V). So, it is the case of reverse bias diode circuits.
Complete step by step solution:
The P-N junction diode can be represented by

in which the ‘+’ side is called a cathode. In the forward bias current flows from anode to cathode and anode must be connected to higher potential and cathode must be connected to lower potential. When voltage is supplied from the battery source current starts to flow from higher potential to lower potential and is the same way diodes must be inserted that current enter from anode side and leave from cathode side. Anode side is also called P side and cathode side also called N side. Therefore the voltage must be higher at the anode side and voltage must be lower at the cathode side. So, from options we can see in option(D) only, the P side is at higher potential than n side.
P side (anode) at ’0’ volt and n side (cathode) at ‘-2’ volt.
Note: In the case of reverse bias, the polarity of battery change and there current enters to n side (cathode) and leaves from p side (anode). We can see option(C) n side at higher potential (5V) and p side at lower potential (3V). So, it is the case of reverse bias diode circuits.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 1 (55/1/1) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Marking Scheme




