
The following compound can be classified as N-N dimethyl propanamine, N- methyl aniline, and aniline.
a. Primary, Secondary, Tertiary
b. Primary, Tertiary, Secondary
c. Secondary, Tertiary, Primary
d. Tertiary, Primary, Secondary
e. None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The IUPAC names given in the question are of different types of amines. The IUPAC of primary amine does not contain N in its nomenclature. The secondary and tertiary amine contains one and two N in their name respectively.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Amines are the ammonia derivatives which are formed by replacing hydrogen atoms. Amine compounds can be shown as $RN{{H}_{2}}$ where, R is any alkyl group.
Amines are further classified into three types: Primary, Secondary and Tertiary.
All the three have different rules for their nomenclature.
$RN{{H}_{2}}$ is considered as primary amine because it has two replaceable hydrogen atoms and its IUPAC name is alkanamine.
${{R}_{2}}NH$ is considered as the secondary amine because it has one replaceable hydrogen atom and its IUPAC name is N-alkyl alkanamine.
${{R}_{3}}N$ is considered as the tertiary amine because it has no replaceable hydrogen atom and its IUPAC name is N-N dialkylalkanamine
Now according to the question the first compound is N-N dimethyl propanamine, therefore according to the rules it’s a tertiary amine.
The next compound is N-methylaniline and the structure of the compound is given as
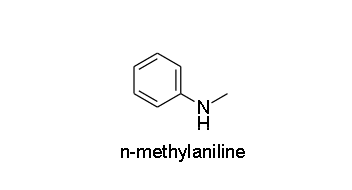
As you can see there is only one replaceable hydrogen atom, so it is a secondary amine.
The next compound is aniline and the structure of the compound is given as
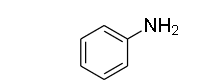
As you can see there are two replaceable hydrogen atoms, it is a primary amine.
So the first compound is tertiary amine, second compound is secondary amine and the third compound is primary amine.
So the answer is e. None of these
Note: The most important thing is to remember the IUPAC nomenclature rules for primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Another thing to remember is the number of replaceable H atoms, it also helps in differentiating between different amines.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Amines are the ammonia derivatives which are formed by replacing hydrogen atoms. Amine compounds can be shown as $RN{{H}_{2}}$ where, R is any alkyl group.
Amines are further classified into three types: Primary, Secondary and Tertiary.
All the three have different rules for their nomenclature.
$RN{{H}_{2}}$ is considered as primary amine because it has two replaceable hydrogen atoms and its IUPAC name is alkanamine.
${{R}_{2}}NH$ is considered as the secondary amine because it has one replaceable hydrogen atom and its IUPAC name is N-alkyl alkanamine.
${{R}_{3}}N$ is considered as the tertiary amine because it has no replaceable hydrogen atom and its IUPAC name is N-N dialkylalkanamine
Now according to the question the first compound is N-N dimethyl propanamine, therefore according to the rules it’s a tertiary amine.
The next compound is N-methylaniline and the structure of the compound is given as

As you can see there is only one replaceable hydrogen atom, so it is a secondary amine.
The next compound is aniline and the structure of the compound is given as

As you can see there are two replaceable hydrogen atoms, it is a primary amine.
So the first compound is tertiary amine, second compound is secondary amine and the third compound is primary amine.
So the answer is e. None of these
Note: The most important thing is to remember the IUPAC nomenclature rules for primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Another thing to remember is the number of replaceable H atoms, it also helps in differentiating between different amines.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




