
The final product formed by the ozonolysis of compound $RCH=C{{R}_{2}}$ is
(A) $RCHO$
(B) ${{R}_{2}}CO$
(C) Both A and B
(D) None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The method of producing ozonides and then reducing them to produce carbonyl compounds is known as ozonolysis. By adding an ozone molecule to the double bond of alkenes or triple bond of alkynes, ozonides are created. The process of cleaving a double bond by creating a five-membered ring is known as ozonolysis. The ring has five members, three of which are oxygens, and two of which are carbons which were doubly bonded.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The ozone molecule is added to the double bond of $RCH=C{{R}_{2}}$ in the ozonolysis reaction and forms an ozonide. Ozone (${{O}_{3}}$), a powerful oxidant, may easily transform alkenes into carbonyl compounds. Both the sigma and pi bonds are broken in this reaction. In the presence of $Zn/{{H}_{2}}O$, hydrolysis of the synthesised ozonide occurs.
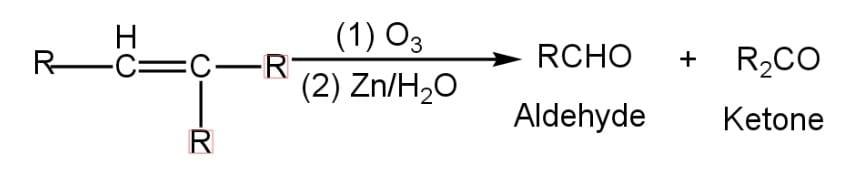
One of the products formed is an aldehyde and the other is a ketone.
Hence, the final product formed by the ozonolysis of compound $RCH=C{{R}_{2}}$is $RCHO$ and${{R}_{2}}CO$.
Correct Option: (C) Both A and B.
Note: While symmetrical alkenes yield two moles of the same product molecule, unsymmetrical alkenes yield two moles of different molecules. This reaction can further produce carboxylic acids and alcohols. When an oxidizing agent is treated with the carbonyl compound formed in the above reaction, a carboxylic acid is formed. Similarly, when a reducing agent is treated with the carbonyl compound, an alcohol is formed.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The ozone molecule is added to the double bond of $RCH=C{{R}_{2}}$ in the ozonolysis reaction and forms an ozonide. Ozone (${{O}_{3}}$), a powerful oxidant, may easily transform alkenes into carbonyl compounds. Both the sigma and pi bonds are broken in this reaction. In the presence of $Zn/{{H}_{2}}O$, hydrolysis of the synthesised ozonide occurs.

One of the products formed is an aldehyde and the other is a ketone.
Hence, the final product formed by the ozonolysis of compound $RCH=C{{R}_{2}}$is $RCHO$ and${{R}_{2}}CO$.
Correct Option: (C) Both A and B.
Note: While symmetrical alkenes yield two moles of the same product molecule, unsymmetrical alkenes yield two moles of different molecules. This reaction can further produce carboxylic acids and alcohols. When an oxidizing agent is treated with the carbonyl compound formed in the above reaction, a carboxylic acid is formed. Similarly, when a reducing agent is treated with the carbonyl compound, an alcohol is formed.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




