
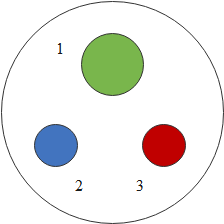
The diagram shows a three-pin socket marked as 1, 2 and 3. Identify live (L), neural (N) and earth (E) against the correct number.
(A) $1 \to {\text{E, 2}} \to {\text{N, 3}} \to {\text{L}}$
(B) $1 \to {\text{N, 2}} \to {\text{E, 3}} \to {\text{L}}$
(C) $1 \to {\text{E, 2}} \to {\text{L, 3}} \to {\text{N}}$
(D) $1 \to {\text{L, 2}} \to {\text{N, 3}} \to {\text{E}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint To answer this question we should be having knowledge about the three kinds of wire that makes up the three pin socket. Each wire has got its known use and for easy identification each wire is painted in a different colour. Depending on the position of the wiring we can predict whether the wiring is neutral, earth or live. This will give us the required answer.
Complete step by step answer
We should know that in the given diagram, the marking 1 indicates the earth wire, marking 2 indicates the neutral wire and the marking 3 indicates the live wire.
The LIVE wire RED or BROWN in colour. This wire is connected to the fuse which is present on the live pin. The electric current uses the live wire as its route in.
The NEUTRAL wire is BLUE or BLACK in colour. This is the route the electric current is taken whenever there exists an appliance that is attached to it. It is for this reason that the neutral wire has a voltage close to that of zero.
The EARTH wire is GREEN or YELLOW in colour. This is connected to the earth pin. This wire is used when the appliance that is attached to it has a metal casting that is to be take away if the live wire comes in contact with that of the casting,
Hence in the diagram the correct representation of the three pin socket is $1 \to {\text{E, 2}} \to {\text{N, 3}} \to {\text{L}}$.
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note We should know that the live wire always comes out from the output terminals of the kWh meter. This consists of the fuse which is called the main fuse. The fuse is connected in series with the live wire. This is performed because it is only the live wire which has a potential of 220 volts unlike the neutral wire. This neutral wire carries zero potential.
It is to be known that the fuse has a high rating which is about 50 amperes. This is done because it prevents any damage which can be caused by a fire to the entire electrical wiring of any house or that of a building. Such situations usually happen because of the short- circuit or overloading.
Complete step by step answer
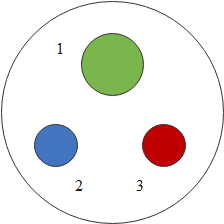
We should know that in the given diagram, the marking 1 indicates the earth wire, marking 2 indicates the neutral wire and the marking 3 indicates the live wire.

The LIVE wire RED or BROWN in colour. This wire is connected to the fuse which is present on the live pin. The electric current uses the live wire as its route in.
The NEUTRAL wire is BLUE or BLACK in colour. This is the route the electric current is taken whenever there exists an appliance that is attached to it. It is for this reason that the neutral wire has a voltage close to that of zero.
The EARTH wire is GREEN or YELLOW in colour. This is connected to the earth pin. This wire is used when the appliance that is attached to it has a metal casting that is to be take away if the live wire comes in contact with that of the casting,
Hence in the diagram the correct representation of the three pin socket is $1 \to {\text{E, 2}} \to {\text{N, 3}} \to {\text{L}}$.
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note We should know that the live wire always comes out from the output terminals of the kWh meter. This consists of the fuse which is called the main fuse. The fuse is connected in series with the live wire. This is performed because it is only the live wire which has a potential of 220 volts unlike the neutral wire. This neutral wire carries zero potential.
It is to be known that the fuse has a high rating which is about 50 amperes. This is done because it prevents any damage which can be caused by a fire to the entire electrical wiring of any house or that of a building. Such situations usually happen because of the short- circuit or overloading.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




