
The circuit shown in the figure contains two diodes each with a forward resistance of $50\Omega $ and the infinite backward resistance. If the battery voltage is $\;6V$ , the current through the $100\Omega $ resistance ( in amperes ) is
(A) zero
(B) $\;0.02$
(C) $\;0.03$
(D) $\;0.036$
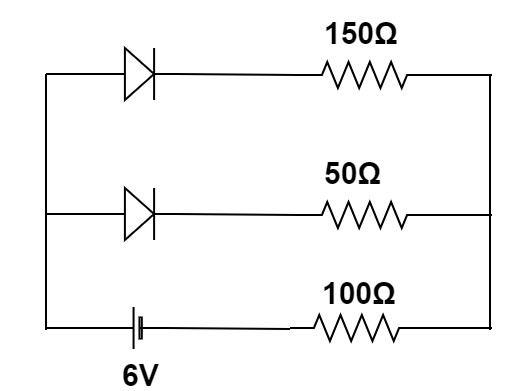
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Knowledge of forward and reverse bias conditions for a PN junction diode is required. Given, the resistance of the diode will be $50\Omega $ in forward biasing condition and infinity in reverse biasing condition. Additionally, ohm’s law would also be required to find the current value.
Formula used:
$V = IR$
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
Complete Step-by-step solution: Let’s remake the circuit, by putting in the signs of the potential of the battery connected, the currents flowing through different arms of the circuit.
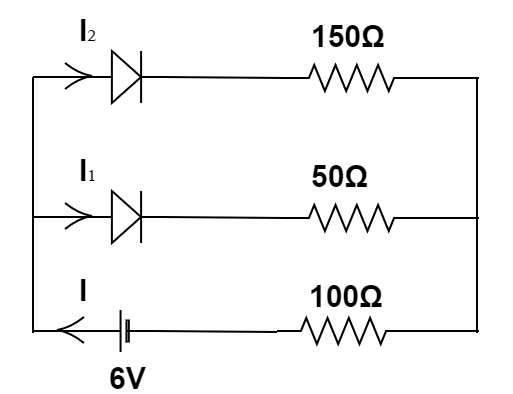
To understand the division of the current flowing through the circuit, we will use Kirchhoff's current law. Hence, considering the amount of current to be flowing through the resistance $100\Omega $ to be $I$ . Then, the circuit breaks into two arms. Hence, the current also gets divided into ${I_1}$ and ${I_2}$ .
Hence, the sum of ${I_1}$ and ${I_2}$ will be $I$ .
We will now discuss the diodes. A PN junction diode is a semiconductor containing excess electrons and holes on each end of the diode and a PN junction interface in between. A common region is formed between the P and the N side having equal amounts of holes and electrons.
In this case, both the diodes are in forward biased condition. Hence the resistance offered by the diode in a forward bias condition is $50\Omega $ .
Taking this into account,
The circuit can be simplified into this form
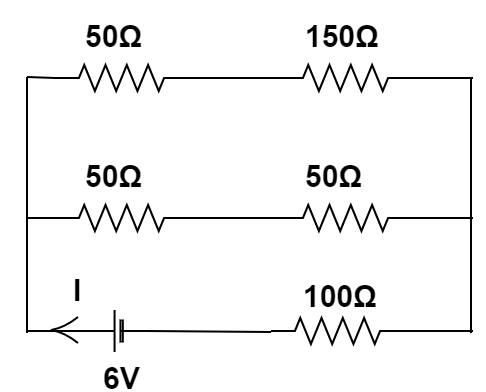
Therefore, we have to find the equivalent resistance of this circuit,
As $50\Omega $ resistor and $150\Omega $ resistor are in series. Therefore, the overall resistance of this arm is $200\Omega $ . Similarly, the overall resistance of the other arm is $100\Omega $ .
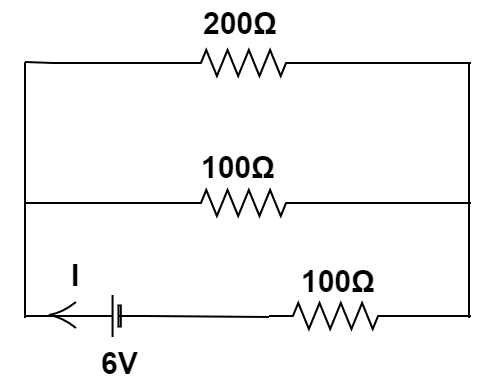
Since $200\Omega $ resistor and $100\Omega $ resistor are in parallel combination,
${R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{200 \times 100}}{{200 + 100}}$
$ \Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{200 \times 100}}{{300}} = \dfrac{{200}}{3}$
Hence, the circuit can be simplified as;
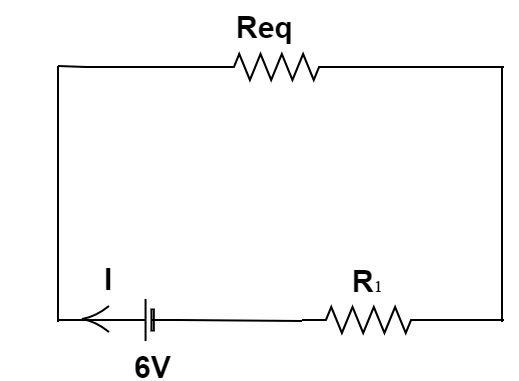
Therefore, the value of current flowing in the circuit can be found using ohm’s law:
$V = IR \Rightarrow 6V = I{R_{net}}$
$ \Rightarrow 6V = I\left( {{R_{eq}} + {R_1}} \right)$
On Substituting the value of ${R_{eq}}$ and ${R_1}$ in the above equation,
$ \Rightarrow 6V = I\left( {\dfrac{{200}}{3} + 100} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 6V = I\left( {\dfrac{{500}}{3}} \right)$
Solve the above equation to determine the value of $I$ ,
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{6 \times 3}}{{500}} = \dfrac{9}{{250}}$
$ \Rightarrow I = 0.036A$
As a result, the amount of current flowing through the resistor $100\Omega $ is $\;0.036A$ .
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note: we consider the value of the net resistance in the above condition to be: ${R_{net}} = {R_{eq}} + {R_1}$ because the resistances are in series to each other. The net resistance of the circuit, when the resistances are connected in series is given by the sum of the resistance values of the resistors connected.
Formula used:
$V = IR$
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
Complete Step-by-step solution: Let’s remake the circuit, by putting in the signs of the potential of the battery connected, the currents flowing through different arms of the circuit.

To understand the division of the current flowing through the circuit, we will use Kirchhoff's current law. Hence, considering the amount of current to be flowing through the resistance $100\Omega $ to be $I$ . Then, the circuit breaks into two arms. Hence, the current also gets divided into ${I_1}$ and ${I_2}$ .
Hence, the sum of ${I_1}$ and ${I_2}$ will be $I$ .
We will now discuss the diodes. A PN junction diode is a semiconductor containing excess electrons and holes on each end of the diode and a PN junction interface in between. A common region is formed between the P and the N side having equal amounts of holes and electrons.
In this case, both the diodes are in forward biased condition. Hence the resistance offered by the diode in a forward bias condition is $50\Omega $ .
Taking this into account,
The circuit can be simplified into this form

Therefore, we have to find the equivalent resistance of this circuit,
As $50\Omega $ resistor and $150\Omega $ resistor are in series. Therefore, the overall resistance of this arm is $200\Omega $ . Similarly, the overall resistance of the other arm is $100\Omega $ .

Since $200\Omega $ resistor and $100\Omega $ resistor are in parallel combination,
${R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{200 \times 100}}{{200 + 100}}$
$ \Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = \dfrac{{200 \times 100}}{{300}} = \dfrac{{200}}{3}$
Hence, the circuit can be simplified as;

Therefore, the value of current flowing in the circuit can be found using ohm’s law:
$V = IR \Rightarrow 6V = I{R_{net}}$
$ \Rightarrow 6V = I\left( {{R_{eq}} + {R_1}} \right)$
On Substituting the value of ${R_{eq}}$ and ${R_1}$ in the above equation,
$ \Rightarrow 6V = I\left( {\dfrac{{200}}{3} + 100} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 6V = I\left( {\dfrac{{500}}{3}} \right)$
Solve the above equation to determine the value of $I$ ,
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{6 \times 3}}{{500}} = \dfrac{9}{{250}}$
$ \Rightarrow I = 0.036A$
As a result, the amount of current flowing through the resistor $100\Omega $ is $\;0.036A$ .
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note: we consider the value of the net resistance in the above condition to be: ${R_{net}} = {R_{eq}} + {R_1}$ because the resistances are in series to each other. The net resistance of the circuit, when the resistances are connected in series is given by the sum of the resistance values of the resistors connected.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry




