
The chord joining two points ${\theta _1}{\text{ and }}{\theta _2}$on the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ such that $\tan {\theta _1}\tan {\theta _2} = - \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{{{b^2}}}$ will subtend a right angle at
$
(a){\text{ focus}} \\
(b){\text{ center}} \\
(c){\text{ end of the major axis}} \\
(d){\text{ end of the minor axis}} \\
$
Answer
240k+ views
Hint: In this question suppose two points ${\theta _1}$ and ${\theta _2}$ such that ${\theta _1} = \left( {a\cos {\theta _1},b\sin {\theta _1}} \right)$ and ${\theta _2} = \left( {a\cos {\theta _2},b\sin {\theta _2}} \right)$through which the chord passes. Then use the concept of slope of line passing through two given points to find the slope of $O{\theta _1}{\text{ and O}}{\theta _2}$ where O is the origin. Use the concept that if two lines are perpendicular then their slopes are related as ${m_1} \times {m_2} = - 1$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
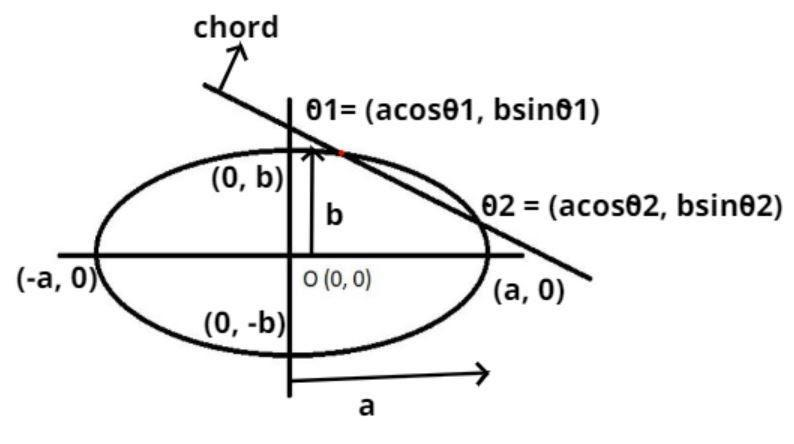
The chord joining two points $\left( {{\theta _1},{\theta _2}} \right)$ on the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ is shown above.
As we know that the ellipse is having a center (O) = (0, 0) is also shown in the figure.
Let us suppose the point ${\theta _1} = \left( {a\cos {\theta _1},b\sin {\theta _1}} \right)$ and ${\theta _2} = \left( {a\cos {\theta _2},b\sin {\theta _2}} \right)$ is also shown in the figure.
Now as we know that the slope between two points $(x_1, y_1)$ and $(x_2, y_2)$ is given as
Slope (m) = $\dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$
So find out the slopes of $\left( {O{\theta _1}} \right)$ and $\left( {O{\theta _2}} \right)$.
Let O = $(x_1, y_1)$ = (0, 0)
${\theta _1} = \left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( {a\cos {\theta _1},b\sin {\theta _1}} \right)$
${\theta _2} = \left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {a\cos {\theta _2},b\sin {\theta _2}} \right)$
So let the slope of $\left( {0{\theta _1}} \right)$ be m1.
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{b\sin {\theta _1} - 0}}{{a\cos {\theta _1} - 0}} = \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _1}$
Now let the slope of $\left( {O{\theta _2}} \right)$ be m2.
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} = \dfrac{{{y_3} - {y_1}}}{{{x_3} - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{b\sin {\theta _2} - 0}}{{a\cos {\theta _2} - 0}} = \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _2}$
Now multiply the slopes we have
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} \times {m_2} = \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _1} \times \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}\tan {\theta _1}\tan {\theta _2}$........................ (1)
Now it is given that
$\tan {\theta _1}\tan {\theta _2} = - \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{{{b^2}}}$
Now substitute this value in equation (1) we have,
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} \times {m_2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}\tan {\theta _1}\tan {\theta _2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}} \times \dfrac{{ - {a^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = - 1$
So multiplication of slopes is (-1) which is the condition of the right angle.
Therefore the chord joining two points $\left( {{\theta _1},{\theta _2}} \right)$ on the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ will subtend a right angle at origin or center.
Hence option (B) is correct.
Note: The center of the given ellipse that is $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ is (0, 0) that is the origin that’s why option (c) is correct. The equation of shifted ellipse or the ellipse whose center is not at origin is given by $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - p} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - q} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ here the center is at (p, q).
Complete step-by-step answer:

The chord joining two points $\left( {{\theta _1},{\theta _2}} \right)$ on the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ is shown above.
As we know that the ellipse is having a center (O) = (0, 0) is also shown in the figure.
Let us suppose the point ${\theta _1} = \left( {a\cos {\theta _1},b\sin {\theta _1}} \right)$ and ${\theta _2} = \left( {a\cos {\theta _2},b\sin {\theta _2}} \right)$ is also shown in the figure.
Now as we know that the slope between two points $(x_1, y_1)$ and $(x_2, y_2)$ is given as
Slope (m) = $\dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$
So find out the slopes of $\left( {O{\theta _1}} \right)$ and $\left( {O{\theta _2}} \right)$.
Let O = $(x_1, y_1)$ = (0, 0)
${\theta _1} = \left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( {a\cos {\theta _1},b\sin {\theta _1}} \right)$
${\theta _2} = \left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( {a\cos {\theta _2},b\sin {\theta _2}} \right)$
So let the slope of $\left( {0{\theta _1}} \right)$ be m1.
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{b\sin {\theta _1} - 0}}{{a\cos {\theta _1} - 0}} = \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _1}$
Now let the slope of $\left( {O{\theta _2}} \right)$ be m2.
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} = \dfrac{{{y_3} - {y_1}}}{{{x_3} - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{b\sin {\theta _2} - 0}}{{a\cos {\theta _2} - 0}} = \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _2}$
Now multiply the slopes we have
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} \times {m_2} = \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _1} \times \dfrac{b}{a}\tan {\theta _2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}\tan {\theta _1}\tan {\theta _2}$........................ (1)
Now it is given that
$\tan {\theta _1}\tan {\theta _2} = - \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{{{b^2}}}$
Now substitute this value in equation (1) we have,
$ \Rightarrow {m_1} \times {m_2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}\tan {\theta _1}\tan {\theta _2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}} \times \dfrac{{ - {a^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = - 1$
So multiplication of slopes is (-1) which is the condition of the right angle.
Therefore the chord joining two points $\left( {{\theta _1},{\theta _2}} \right)$ on the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ will subtend a right angle at origin or center.
Hence option (B) is correct.
Note: The center of the given ellipse that is $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ is (0, 0) that is the origin that’s why option (c) is correct. The equation of shifted ellipse or the ellipse whose center is not at origin is given by $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - p} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - q} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ here the center is at (p, q).
Recently Updated Pages
Geometry of Complex Numbers Explained

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

JEE Main Correction Window 2026 Session 1 Dates Announced - Edit Form Details, Dates and Link

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




