
The bob A of a simple pendulum is released when the string makes an angle of ${45^ \circ }\] with the vertical. It hits another bob B of the same material and same mass kept at rest on the table. If the collision is elastic:
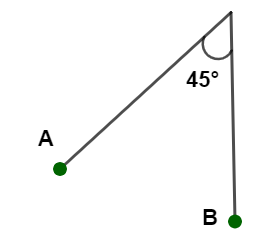
A. both A and B rise to the same height
B. both A and B come to rest at B
C. both A and B move with the velocity of A
D. A comes to rest and B moves with the velocity of A
Answer
239.4k+ views
Hint: A collision between two bodies in physics is referred to as an elastic collision if their combined kinetic energy stays constant. There is no net conversion of kinetic energy into other forms, such as heat, noise, or potential energy, in an ideal, fully elastic collision. According to the law of conservation of momentum, a system's overall momentum remains constant in the absence of an external force.
Formula:
$e =\dfrac{\text{Speed by which the objects separate}}{\text{Speed in which the objects approach}}$
Complete step by step solution:
Let $u$ and $v$ represent the initial and final velocities. After a collision, the velocities of the two spheres switch due to their same masses and the elastic impact. By the law of conservation of momentum,
$m{u_1} = m{v_1} + m{v_2}$
Rewriting the above equation,
${v_1} + {v_2} = {u_1}$.............(1)
Now, equating the value of ‘e’ to 1 and the result is,
$e = \dfrac{{{v_2} - {v_1}}}{{{u_1}}} \\
\Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{{{v_2} - {v_1}}}{{{u_1}}} \\ $
Rewriting the above equation,
${v_2} - {v_1} = {u_1}$...........(2)
By the equations (1) and (2), we get the values
${v_1} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {v_2} = {u_1} $
Therefore, A comes to rest and B will move with the velocity of A.
Hence, option D is correct.
Note: As long as the amplitude is modest, the period of oscillation of a simple pendulum with constant length is independent of the amplitude. A mass of no size fastened to a massless thread serves as a rudimentary pendulum's representation. An actual item that is moving about a point other than its centre of gravity is shown by a compound pendulum.
Formula:
$e =\dfrac{\text{Speed by which the objects separate}}{\text{Speed in which the objects approach}}$
Complete step by step solution:
Let $u$ and $v$ represent the initial and final velocities. After a collision, the velocities of the two spheres switch due to their same masses and the elastic impact. By the law of conservation of momentum,
$m{u_1} = m{v_1} + m{v_2}$
Rewriting the above equation,
${v_1} + {v_2} = {u_1}$.............(1)
Now, equating the value of ‘e’ to 1 and the result is,
$e = \dfrac{{{v_2} - {v_1}}}{{{u_1}}} \\
\Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{{{v_2} - {v_1}}}{{{u_1}}} \\ $
Rewriting the above equation,
${v_2} - {v_1} = {u_1}$...........(2)
By the equations (1) and (2), we get the values
${v_1} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {v_2} = {u_1} $
Therefore, A comes to rest and B will move with the velocity of A.
Hence, option D is correct.
Note: As long as the amplitude is modest, the period of oscillation of a simple pendulum with constant length is independent of the amplitude. A mass of no size fastened to a massless thread serves as a rudimentary pendulum's representation. An actual item that is moving about a point other than its centre of gravity is shown by a compound pendulum.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26




