
The area (in sq.units) of the part of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=36\], which is outside the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=9x$, is:
a) $24\pi +3\sqrt{3}$
b) $12\pi +3\sqrt{3}$
c) $12\pi -3\sqrt{3}$
d) $24\pi -3\sqrt{3}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:
For the question, we are provided with equation of circle which is \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=36\] and also the equation for the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=9x$. We need to evaluate the area of the part of the circle that lies outside parabola. We calculate the area of the circle and subtract the area of the parabola lying in the circle.
Complete step by step solution:
For better understanding, let us create the figure for given question;
We know standard equation for circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\]
Comparing with given equation \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=36\]; we get r = 6units
Solving \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=36\] and ${{y}^{2}}=9x$ simultaneously;
${{x}^{2}}+9x-36=0$
Solving above quadratic equation
${{x}^{2}}-3x+12x-36=0$
$x\left( x-3 \right)+12\left( x-3 \right)=0$
$\left( x-3 \right)\left( x+12 \right)=0$
$\left( x-3 \right)=0$ Or $\left( x+12 \right)=0$
The above equations give value for x as \[x=3, -12\]
x cannot be negative as it will not satisfy the given equation for parabola
Thus, we have x=3
Figure:
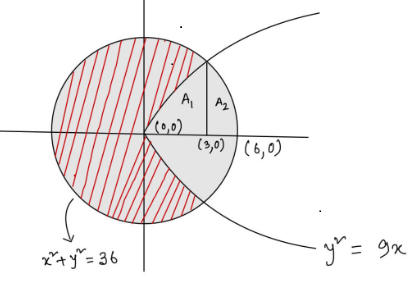
Area of circle = \[\pi r^{2}\]
Now, Required area(A) can be calculated by deducting the area of the parabola inside the circle from the area of the circle. It can be given as;
$A=\pi {{r}^{2}}-2\left[ A_1+A_2 \right]$
\[A=\pi {{6}^{2}}-2\left[ \left( \int\limits_{0}^{3}{\sqrt{9x}dx} \right)+\left( \int\limits_{3}^{6}{\sqrt{36-{{x}^{2}}}dx} \right) \right]\]
\[A=36\pi -2\left[ \left[ 3\times \frac{2}{3}{{x}^{\frac{3}{2}}} \right]_{0}^{3}+\left[ \frac{x}{2}\sqrt{{{36}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}+\frac{36}{2}{{\sin }^{-1}}\frac{x}{6} \right]_{3}^{6} \right]\]
\[A=36\pi -2\left[ \left[ 6\sqrt{3}-0 \right]+\left[ \left( 0+18{{\sin }^{-1}}\frac{6}{6} \right)-\left( \frac{3}{2}\times 3\sqrt{3}+18{{\sin }^{-1}}\frac{3}{6} \right) \right] \right]\]
\[A=36\pi -2\left[ \left[ 6\sqrt{3} \right]+\left[ \left( \frac{3}{2}\times 3\sqrt{3}+\frac{18\pi }{6} \right) \right] \right]\]
Simplifying further we get,
\[A=36\pi -\left( 12\sqrt{3}+18\pi -9\sqrt{3}-6\pi \right)\]
Opening brackets to simplify
\[A=24\pi -3\sqrt{3}\]
Thus we get area of circle outside the given parabola as \[A=24\pi -3\sqrt{3}\]
Correct Option: (d) $24\pi -3\sqrt{3}$
Note: It is mandatory to understand the given equations. Plotting a diagram would help better understanding. Such types of questions could be solved with basic knowledge of curves and finding areas using integration. Following mentioned are some of the important formulas to remember.
$1.\int{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}}dx=\frac{1}{2}\left[ x\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}+{{a}^{2}}\log \left( \left| x+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}} \right| \right) \right]+C$
$2.\int{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}}dx=\frac{1}{2}\left[ x\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}+{{a}^{2}}{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \frac{x}{a} \right) \right]+C$
$3.\int{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}}dx=\frac{1}{2}\left[ x\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}-{{a}^{2}}\log \left( \left| x+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}} \right| \right) \right]+C$
For the question, we are provided with equation of circle which is \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=36\] and also the equation for the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=9x$. We need to evaluate the area of the part of the circle that lies outside parabola. We calculate the area of the circle and subtract the area of the parabola lying in the circle.
Complete step by step solution:
For better understanding, let us create the figure for given question;
We know standard equation for circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\]
Comparing with given equation \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=36\]; we get r = 6units
Solving \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=36\] and ${{y}^{2}}=9x$ simultaneously;
${{x}^{2}}+9x-36=0$
Solving above quadratic equation
${{x}^{2}}-3x+12x-36=0$
$x\left( x-3 \right)+12\left( x-3 \right)=0$
$\left( x-3 \right)\left( x+12 \right)=0$
$\left( x-3 \right)=0$ Or $\left( x+12 \right)=0$
The above equations give value for x as \[x=3, -12\]
x cannot be negative as it will not satisfy the given equation for parabola
Thus, we have x=3
Figure:

Area of circle = \[\pi r^{2}\]
Now, Required area(A) can be calculated by deducting the area of the parabola inside the circle from the area of the circle. It can be given as;
$A=\pi {{r}^{2}}-2\left[ A_1+A_2 \right]$
\[A=\pi {{6}^{2}}-2\left[ \left( \int\limits_{0}^{3}{\sqrt{9x}dx} \right)+\left( \int\limits_{3}^{6}{\sqrt{36-{{x}^{2}}}dx} \right) \right]\]
\[A=36\pi -2\left[ \left[ 3\times \frac{2}{3}{{x}^{\frac{3}{2}}} \right]_{0}^{3}+\left[ \frac{x}{2}\sqrt{{{36}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}+\frac{36}{2}{{\sin }^{-1}}\frac{x}{6} \right]_{3}^{6} \right]\]
\[A=36\pi -2\left[ \left[ 6\sqrt{3}-0 \right]+\left[ \left( 0+18{{\sin }^{-1}}\frac{6}{6} \right)-\left( \frac{3}{2}\times 3\sqrt{3}+18{{\sin }^{-1}}\frac{3}{6} \right) \right] \right]\]
\[A=36\pi -2\left[ \left[ 6\sqrt{3} \right]+\left[ \left( \frac{3}{2}\times 3\sqrt{3}+\frac{18\pi }{6} \right) \right] \right]\]
Simplifying further we get,
\[A=36\pi -\left( 12\sqrt{3}+18\pi -9\sqrt{3}-6\pi \right)\]
Opening brackets to simplify
\[A=24\pi -3\sqrt{3}\]
Thus we get area of circle outside the given parabola as \[A=24\pi -3\sqrt{3}\]
Correct Option: (d) $24\pi -3\sqrt{3}$
Note: It is mandatory to understand the given equations. Plotting a diagram would help better understanding. Such types of questions could be solved with basic knowledge of curves and finding areas using integration. Following mentioned are some of the important formulas to remember.
$1.\int{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}}dx=\frac{1}{2}\left[ x\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}+{{a}^{2}}\log \left( \left| x+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}} \right| \right) \right]+C$
$2.\int{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}}dx=\frac{1}{2}\left[ x\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}+{{a}^{2}}{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \frac{x}{a} \right) \right]+C$
$3.\int{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}}dx=\frac{1}{2}\left[ x\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}-{{a}^{2}}\log \left( \left| x+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}} \right| \right) \right]+C$
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole




