
The alkyl cyanides are
A. Acidic
B. Basic
C. Neutral
D. Amphoteric
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: When the H atom of HCN is substituted by an alkyl group or aryl group, a cyanide compound is formed. Alkyl cyanide or alkyl nitrile is very much unstable in water. The nature of alkyl cyanide depends upon the nature of the product upon hydrolysis in acidic or basic aqueous solutions.
Complete step by step solution:
Alkyl cyanide groups have a cyanide functional group ($-CN$ group) and are formed when alkyl halide
(R-X) reacts with metal cyanide ( NaCN, KCN, etc.).
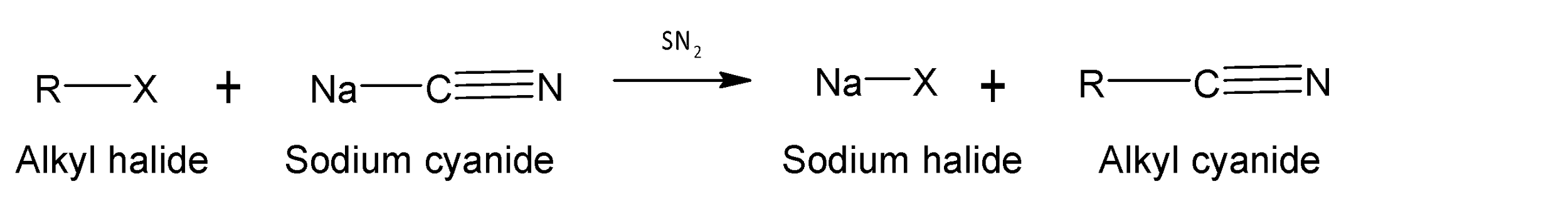
Alkyl cyanides are very unstable in water and undergo rapid hydrolysis both in acidic or basic medium.
In acidic medium: When alkyl cyanide (R-CN) is heated under reflux with dilute acid for example dilute hydrochloric acid, a carboxylic acid (R-COOH) is formed. In the acidic medium, alkyl cyanide acts as an electrophile and activates the C-N triple bond for a nucleophilic attack of water forming an amide as an intermediate, which is then further hydrolyzed to carboxylic acid as the major product.
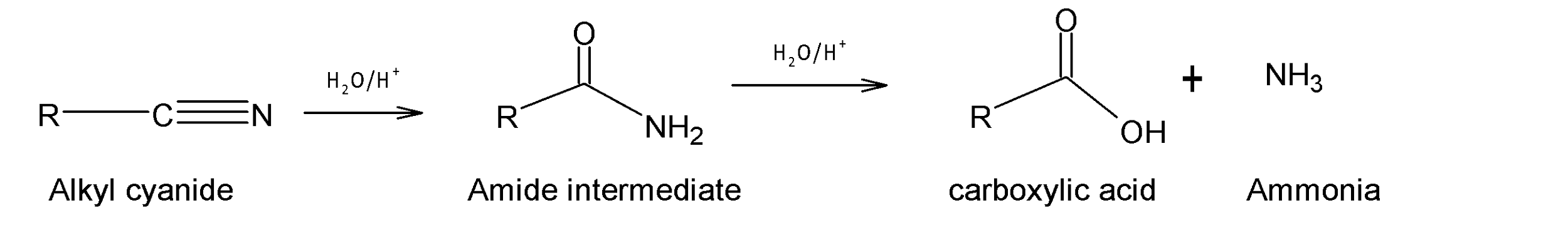
In basic medium: In a basic medium, when alkyl cyanide is heated under reflux with base, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) carboxylic acid salt of sodium is formed. At first nucleophilic addition of the hydroxide ion to the C-N triple bond occurs forming an amide intermediate.
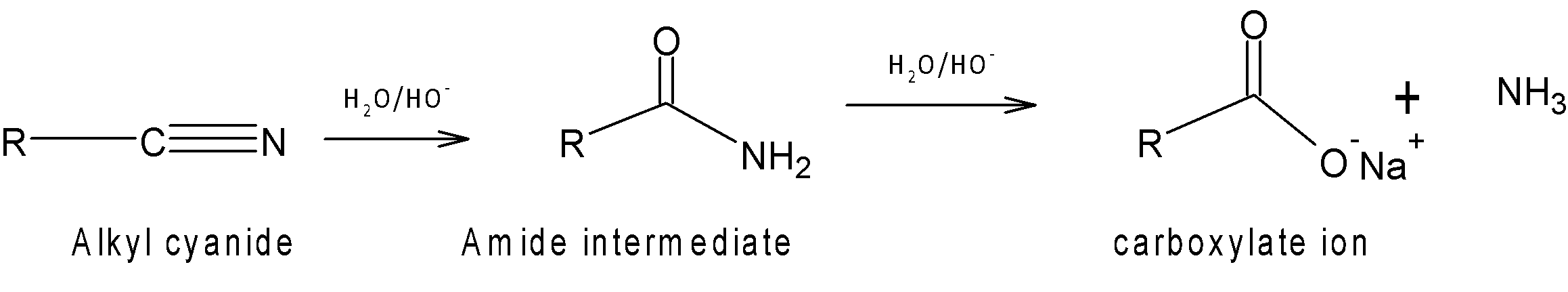
These chemical properties are the reason to consider alkyl nitriles to be acid derivatives.
Thus option (A) is correct.
Note: Cyanide and isocyanide both are functional isomers of each other and they can be synthesized from hydrocyanic acid (HCN). In isocyanides (R-NC) alkyl or aryl groups are attached to the nitrogen atom of the –CN group and for cyanides (R-CN), they are attached to a carbon atom of the –CN group. Isocyanides are only hydrolyzed by dilute acids to give formic acid and a primary amine.
Complete step by step solution:
Alkyl cyanide groups have a cyanide functional group ($-CN$ group) and are formed when alkyl halide
(R-X) reacts with metal cyanide ( NaCN, KCN, etc.).

Alkyl cyanides are very unstable in water and undergo rapid hydrolysis both in acidic or basic medium.
In acidic medium: When alkyl cyanide (R-CN) is heated under reflux with dilute acid for example dilute hydrochloric acid, a carboxylic acid (R-COOH) is formed. In the acidic medium, alkyl cyanide acts as an electrophile and activates the C-N triple bond for a nucleophilic attack of water forming an amide as an intermediate, which is then further hydrolyzed to carboxylic acid as the major product.

In basic medium: In a basic medium, when alkyl cyanide is heated under reflux with base, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) carboxylic acid salt of sodium is formed. At first nucleophilic addition of the hydroxide ion to the C-N triple bond occurs forming an amide intermediate.

These chemical properties are the reason to consider alkyl nitriles to be acid derivatives.
Thus option (A) is correct.
Note: Cyanide and isocyanide both are functional isomers of each other and they can be synthesized from hydrocyanic acid (HCN). In isocyanides (R-NC) alkyl or aryl groups are attached to the nitrogen atom of the –CN group and for cyanides (R-CN), they are attached to a carbon atom of the –CN group. Isocyanides are only hydrolyzed by dilute acids to give formic acid and a primary amine.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




