
Seven homogeneous bricks each of length L, mass M are arranged as shown. Projection $x = \dfrac{L}{{10}}$ then x coordinate of center of mass is:
Answer
232.8k+ views
- Hint: In order to solve this question, firstly we will assume that the bricks are placed on one another and length, mass be L, m respectively. Then we will apply the formula of center of mass i.e. ${X_{cm}} = \dfrac{{{M_1}{X_1} + {M_2}{X_2} + {M_3}{X_3}.....}}{{{M_1} + {M_2} + {M_3}.......}}$ to get the required answer.
Formula used-
${X_{cm}} = \dfrac{{{M_1}{X_1} + {M_2}{X_2} + {M_3}{X_3}.....}}{{{M_1} + {M_2} + {M_3}.......}}$
Complete step-by-step solution -
The center of mass is a point in a system that responds to outside forces as if at this point the total mass of the system was concentrated. The center of mass can be determined by taking the masses from which you seek to locate the center of mass, and by multiplying them by their locations. You then add these together, and divide it by the sum of all the masses.
Let mass of brick be M and length be L.
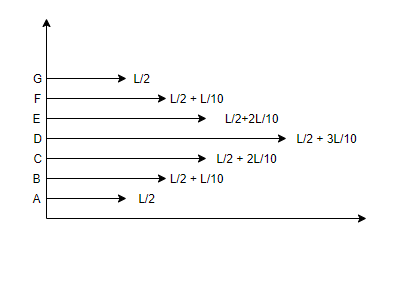
Assuming that each brick is in contact by distance $x = \dfrac{L}{{10}}$. In addition, the bricks are put on each other and the first and last bricks have the same center of mass, the second and sixth having the same center of mass, the third and fifth having the same center of mass, the fourth having a different center of mass.
Let the bricks be called A, B , C, D, E, F, G
$ \Rightarrow Com{\text{ of A,G = }}\dfrac{L}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow Com{\text{ of B,F = }}\dfrac{L}{2} + \dfrac{L}{{10}}$
$ \Rightarrow Com{\text{ of C, E = }}\dfrac{L}{2} + \dfrac{{2L}}{{10}}$
$ \Rightarrow Com{\text{ of D = }}\dfrac{L}{2} + \dfrac{{3L}}{{10}}$
Using the formula of center of mass i.e.${X_{cm}} = \dfrac{{{M_1}{X_1} + {M_2}{X_2} + {M_3}{X_3}.....}}{{{M_1} + {M_2} + {M_3}.......}}$
Now, center of mass of X coordinate is-
$X = \dfrac{{\left( {{M_1}{X_1} + {M_2}{X_2} + {M_3}{X_3} + {M_4}{X_4} + {M_5}{X_5} + {M_6}{X_6} + {M_7}{X_7}} \right)}}{{{M_1} + {M_2} + {M_3} + {M_4} + {M_5} + {M_6} + {M_7}}}$
$X = \dfrac{{\left\{ {2 \times \dfrac{{ML}}{2} + 2 \times M\left( {\dfrac{L}{2} + \dfrac{L}{{10}}} \right) + 2 \times M\left( {\dfrac{L}{2} + \dfrac{{2L}}{{10}}} \right) + M \times \left( {\dfrac{L}{2} + \dfrac{{3L}}{{10}}} \right)} \right\}}}{{7M}}$
$X = \dfrac{{\left[ {ML + 2M\left\{ {\dfrac{{\left( {5L + L} \right)}}{{10}}} \right\} + 2M\left\{ {\dfrac{{\left( {5L + 2L} \right)}}{{10}}} \right\} + M \times \left\{ {\dfrac{{\left( {5L + 3L} \right)}}{{10}}} \right\}} \right]}}{{7M}}$
$X = \dfrac{{\left( {10ML + 12ML + 14ML + 8ML} \right)}}{{10 \times 7M}}$
$\Rightarrow X = \dfrac{{44ML}}{{70M}}$
$\Rightarrow X = \dfrac{{44L}}{{70}}$
$\Rightarrow X = \dfrac{{22L}}{{35}}$
Therefore, we conclude that the X coordinate of center of mass, $X = \dfrac{{22L}}{{35}}$.
Note- While solving this question, we must know the concept of center of mass i.e. it is a position defined relative to an object or system of objects. It is the average location of all components of the system, weighted by their masses.
Formula used-
${X_{cm}} = \dfrac{{{M_1}{X_1} + {M_2}{X_2} + {M_3}{X_3}.....}}{{{M_1} + {M_2} + {M_3}.......}}$
Complete step-by-step solution -
The center of mass is a point in a system that responds to outside forces as if at this point the total mass of the system was concentrated. The center of mass can be determined by taking the masses from which you seek to locate the center of mass, and by multiplying them by their locations. You then add these together, and divide it by the sum of all the masses.
Let mass of brick be M and length be L.
Assuming that each brick is in contact by distance $x = \dfrac{L}{{10}}$. In addition, the bricks are put on each other and the first and last bricks have the same center of mass, the second and sixth having the same center of mass, the third and fifth having the same center of mass, the fourth having a different center of mass.
Let the bricks be called A, B , C, D, E, F, G
$ \Rightarrow Com{\text{ of A,G = }}\dfrac{L}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow Com{\text{ of B,F = }}\dfrac{L}{2} + \dfrac{L}{{10}}$
$ \Rightarrow Com{\text{ of C, E = }}\dfrac{L}{2} + \dfrac{{2L}}{{10}}$
$ \Rightarrow Com{\text{ of D = }}\dfrac{L}{2} + \dfrac{{3L}}{{10}}$
Using the formula of center of mass i.e.${X_{cm}} = \dfrac{{{M_1}{X_1} + {M_2}{X_2} + {M_3}{X_3}.....}}{{{M_1} + {M_2} + {M_3}.......}}$
Now, center of mass of X coordinate is-
$X = \dfrac{{\left( {{M_1}{X_1} + {M_2}{X_2} + {M_3}{X_3} + {M_4}{X_4} + {M_5}{X_5} + {M_6}{X_6} + {M_7}{X_7}} \right)}}{{{M_1} + {M_2} + {M_3} + {M_4} + {M_5} + {M_6} + {M_7}}}$
$X = \dfrac{{\left\{ {2 \times \dfrac{{ML}}{2} + 2 \times M\left( {\dfrac{L}{2} + \dfrac{L}{{10}}} \right) + 2 \times M\left( {\dfrac{L}{2} + \dfrac{{2L}}{{10}}} \right) + M \times \left( {\dfrac{L}{2} + \dfrac{{3L}}{{10}}} \right)} \right\}}}{{7M}}$
$X = \dfrac{{\left[ {ML + 2M\left\{ {\dfrac{{\left( {5L + L} \right)}}{{10}}} \right\} + 2M\left\{ {\dfrac{{\left( {5L + 2L} \right)}}{{10}}} \right\} + M \times \left\{ {\dfrac{{\left( {5L + 3L} \right)}}{{10}}} \right\}} \right]}}{{7M}}$
$X = \dfrac{{\left( {10ML + 12ML + 14ML + 8ML} \right)}}{{10 \times 7M}}$
$\Rightarrow X = \dfrac{{44ML}}{{70M}}$
$\Rightarrow X = \dfrac{{44L}}{{70}}$
$\Rightarrow X = \dfrac{{22L}}{{35}}$
Therefore, we conclude that the X coordinate of center of mass, $X = \dfrac{{22L}}{{35}}$.
Note- While solving this question, we must know the concept of center of mass i.e. it is a position defined relative to an object or system of objects. It is the average location of all components of the system, weighted by their masses.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




