
\[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{6}}}\] on treatment with alcoholic KOH yields
A. \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}\]
B. \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
C. \[\left( {{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_6}} \right){\rm{OH}}\]
D. \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{4}}}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Alcoholic KOH is a special reagent used in the Dehydrohalogenation of haloalkane. This results in the product Alkenes. Also, we can say that Alcoholic KOH gives an elimination reaction. The products are different when haloalkane reacts with aqueous KOH.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let’s first draw the structure of \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{6}}}\].
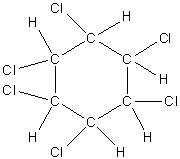
Image: structure of \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{6}}}\]
When \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{6}}}\]undergoes reaction with alcoholic KOH, elimination reaction occurs. So, the reaction is,
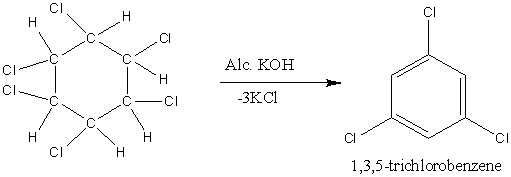
Image: Reaction of \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{6}}}\] with alcoholic KOH.
So, the product obtained is \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\].
Hence, the right answer is option B.
Additional Information:
Let’s discuss the elimination reaction in detail. An elimination reaction is one where an atom or a group of atoms is removed from the molecule. Usually, the removal occurs because of the action of bases or acids on metals. The removal also takes place because of the heating of the compound at a high temperature. Elimination reactions are of two types, E1 and E2 reactions. Let’s discuss both reactions one by one.
• E2 reaction is also termed bimolecular elimination and it is one step elimination reaction.. This reaction follows second-order kinetics.
Note: Students might get confused between the reaction of haloalkane with Alcoholic KOH and aqueous KOH. When haloalkane undergoes a reaction with aqueous KOH, the substitution reaction occurs and the reaction of haloalkane with aqueous KOH results in the elimination reaction.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let’s first draw the structure of \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{6}}}\].

Image: structure of \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{6}}}\]
When \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{6}}}\]undergoes reaction with alcoholic KOH, elimination reaction occurs. So, the reaction is,

Image: Reaction of \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{6}}}\] with alcoholic KOH.
So, the product obtained is \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_3}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\].
Hence, the right answer is option B.
Additional Information:
Let’s discuss the elimination reaction in detail. An elimination reaction is one where an atom or a group of atoms is removed from the molecule. Usually, the removal occurs because of the action of bases or acids on metals. The removal also takes place because of the heating of the compound at a high temperature. Elimination reactions are of two types, E1 and E2 reactions. Let’s discuss both reactions one by one.
- • E1 reaction is also termed unimolecular elimination. Two steps are involved in this type of elimination, that is ionisation and deprotonation. It has similar features to the SN1 reaction.
Note: Students might get confused between the reaction of haloalkane with Alcoholic KOH and aqueous KOH. When haloalkane undergoes a reaction with aqueous KOH, the substitution reaction occurs and the reaction of haloalkane with aqueous KOH results in the elimination reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




