
Reagent, 1-naphthylamine, and sulfanilic acid in acetic acid are used for the detection of
A. \[{\rm{NO}}\]
B. \[{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}\]
C. \[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{O}}^{\rm{3}}}^{\rm{ - }}\]
D. \[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{O}}^{\rm{2}}}^{\rm{ - }}\]
Answer
241.5k+ views
Hint: When an aromatic amine reacts with nitrous acid at 273-278K forms arene diazonium salt. This arene diazonium salt on treatment with amines forms brightly coloured azo dye.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Nitrite ions combine with acetic acid to form nitrous acid and acetate ions.
\[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{O}}^{{\rm{2 - }}}}{\rm{ + C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOH}} \to {\rm{HN}}{{\rm{O}}_2}{\rm{ + C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CO}}{{\rm{O}}^{\rm{ - }}}\]
This nitrous acid then reacts with sulfanilic acid.
When sulfanilic acid is added to a 1-naphthylamine reagent acidified with acetic acid, sulphanilic acid undergoes diazotization in presence of nitrous acid.
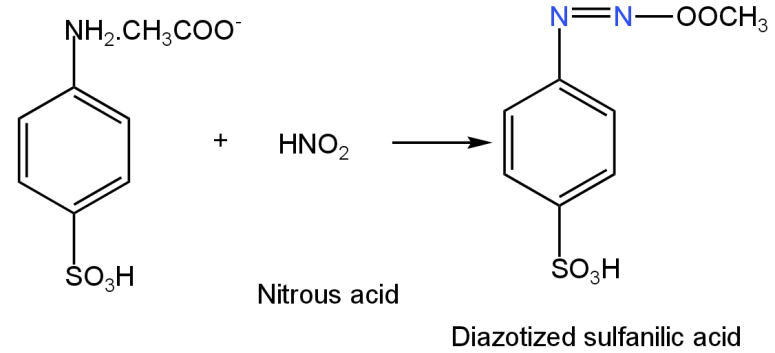
Image: Formation of diazotized sulfanilic acid.
Diazotized sulfanilic acid when treated with 1-naphthyl amine undergo coupling reaction.
Red azo dye is formed as a product. The IUPAC name of the compound is p-sulfobenzene-azo-1-naphthyl amine.
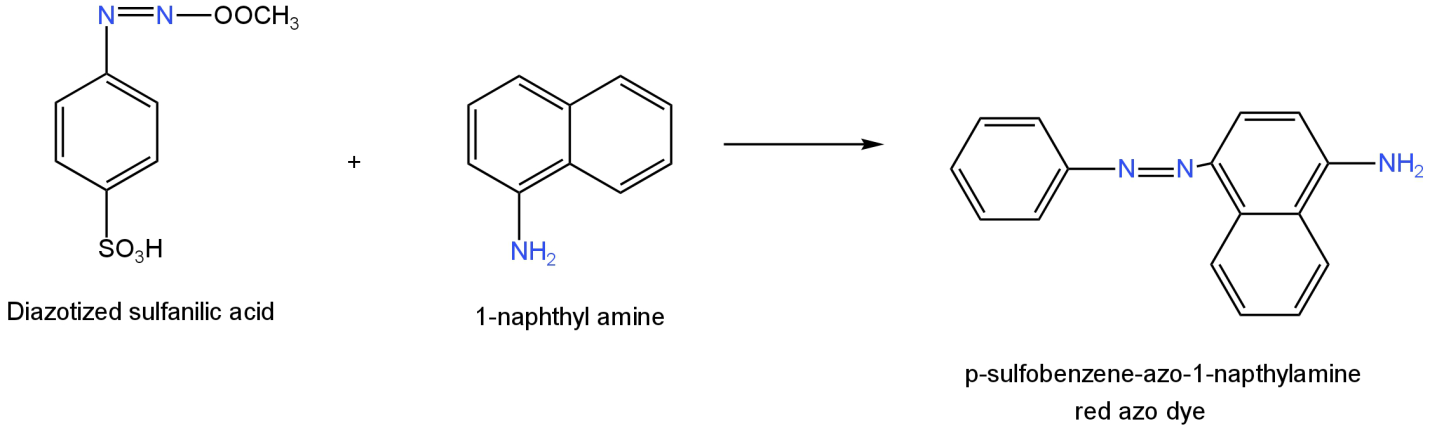
Image: Reaction of diazotized sulfanilic acid with 1-naphthyl amine.
This confirms the presence of nitrite ions in a given solution.
Sulphanilic acid and 1-naphthylamine reagent test or the Griess-Ilosvay test is the test for nitrite ions.
So, option D is correct.
Additional information: The well-known indicator methyl orange which is widely utilized in acid-base titrations is obtained by coupling the diazonium salt of sulfanilic acid with N, N-dimethylaniline.
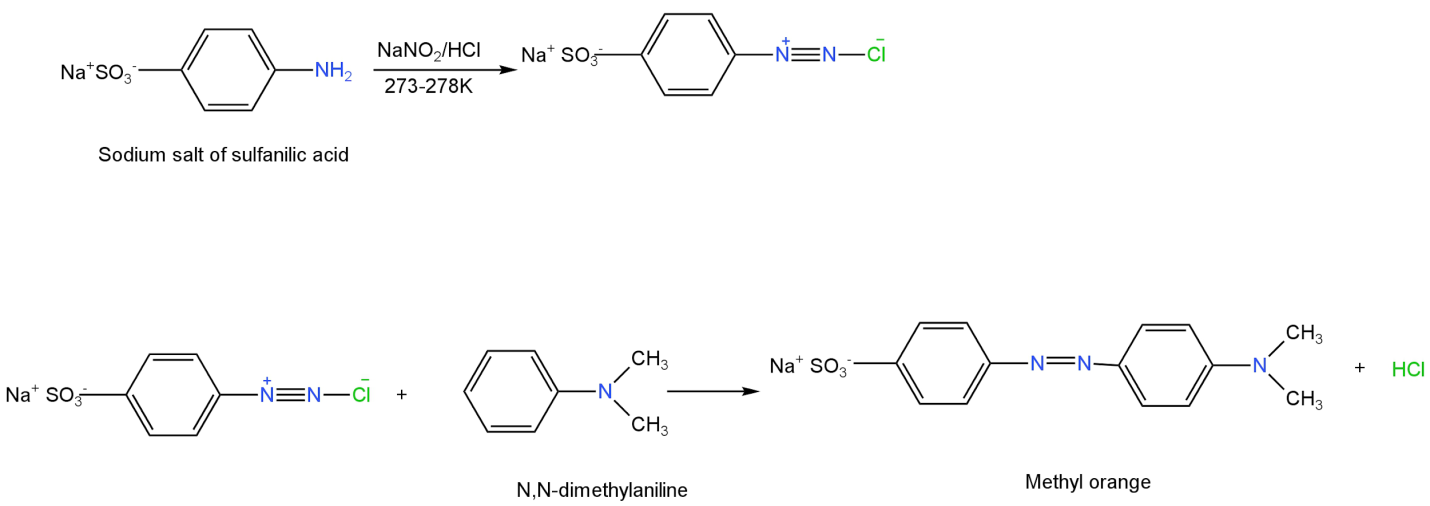
Image: Formation of methyl orange.
Note: The coupling reaction of the arene diazonium salt with amine happens in a faintly acidic medium(pH 4-5) at 273-278K. The coupling reaction is an example of an electrophilic substitution reaction.In this reaction, the diazonium action with the positive charge on the terminal nitrogen acts as the electrophile. The electron-rich compound amine acts as the nucleophile. Coupling occurs at the para position with the amino group. The colour of the azo compounds is due to the extended conjugation involving the double bonds of both the arene (benzene) rings through the \[{\rm{ - N = N - }}\] double bond.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Nitrite ions combine with acetic acid to form nitrous acid and acetate ions.
\[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{O}}^{{\rm{2 - }}}}{\rm{ + C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOH}} \to {\rm{HN}}{{\rm{O}}_2}{\rm{ + C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CO}}{{\rm{O}}^{\rm{ - }}}\]
This nitrous acid then reacts with sulfanilic acid.
When sulfanilic acid is added to a 1-naphthylamine reagent acidified with acetic acid, sulphanilic acid undergoes diazotization in presence of nitrous acid.

Image: Formation of diazotized sulfanilic acid.
Diazotized sulfanilic acid when treated with 1-naphthyl amine undergo coupling reaction.
Red azo dye is formed as a product. The IUPAC name of the compound is p-sulfobenzene-azo-1-naphthyl amine.

Image: Reaction of diazotized sulfanilic acid with 1-naphthyl amine.
This confirms the presence of nitrite ions in a given solution.
Sulphanilic acid and 1-naphthylamine reagent test or the Griess-Ilosvay test is the test for nitrite ions.
So, option D is correct.
Additional information: The well-known indicator methyl orange which is widely utilized in acid-base titrations is obtained by coupling the diazonium salt of sulfanilic acid with N, N-dimethylaniline.

Image: Formation of methyl orange.
Note: The coupling reaction of the arene diazonium salt with amine happens in a faintly acidic medium(pH 4-5) at 273-278K. The coupling reaction is an example of an electrophilic substitution reaction.In this reaction, the diazonium action with the positive charge on the terminal nitrogen acts as the electrophile. The electron-rich compound amine acts as the nucleophile. Coupling occurs at the para position with the amino group. The colour of the azo compounds is due to the extended conjugation involving the double bonds of both the arene (benzene) rings through the \[{\rm{ - N = N - }}\] double bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




