
Pulley mass system is shown in figure string and pulleys and strings are ideal. Acceleration of \[{m_2}\] and ${m_1}$ will be:
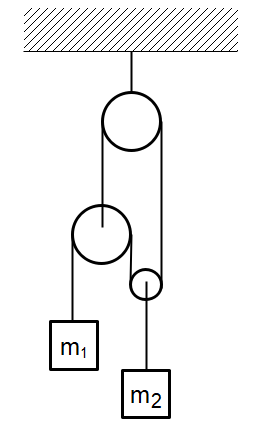
A) ${a_1} = 2{a_2}$
B) ${a_1} = 2{a_1}$
C) ${a_1} = {a_2} = g$
D) ${a_1} = 3{a_2}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In this solution, we will draw the free body diagram of the string pulley system. Then we will calculate the tension in the strings to calculate the acceleration in the two blocks.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us start by drawing a free body diagram of the tension in the different strings.
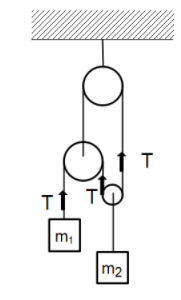
AS we can see, for the mass ${m_1}$ the mass it experiences is associated with only the bottom left pulley. Hence, we can write the equation of motion for the first mass as:
$T = m{a_1}$
Now the string connecting the lower two pulleys is the same so the net displacement will be zero. Also, we can see that for the pulley in the bottom right, the tension in the two strings will be $2T$ as can be seen from the diagram. Also, the tension in the string can be represented as the acceleration of the object which will be
$T = 2m{a_2}$
Since the tension will be the same in the string for both the bottom pulleys, we have
$m{a_1} = 2m{a_2}$
So, the relation of the acceleration of the two blocks will be
${a_1} = 2{a_2}$
Hence the correct choice will be choice (A).
Note: We can intuitively expect the first mass to have higher acceleration since it will have to compensate for the tension exerted by the other mass as it is connected by two pulleys. As a result, the displacement of the first block will always be higher than the displacement of the second block. We shouldn’t worry about the movement of individual pulleys but only the tension in the strings as it simplifies our calculations.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us start by drawing a free body diagram of the tension in the different strings.

AS we can see, for the mass ${m_1}$ the mass it experiences is associated with only the bottom left pulley. Hence, we can write the equation of motion for the first mass as:
$T = m{a_1}$
Now the string connecting the lower two pulleys is the same so the net displacement will be zero. Also, we can see that for the pulley in the bottom right, the tension in the two strings will be $2T$ as can be seen from the diagram. Also, the tension in the string can be represented as the acceleration of the object which will be
$T = 2m{a_2}$
Since the tension will be the same in the string for both the bottom pulleys, we have
$m{a_1} = 2m{a_2}$
So, the relation of the acceleration of the two blocks will be
${a_1} = 2{a_2}$
Hence the correct choice will be choice (A).
Note: We can intuitively expect the first mass to have higher acceleration since it will have to compensate for the tension exerted by the other mass as it is connected by two pulleys. As a result, the displacement of the first block will always be higher than the displacement of the second block. We shouldn’t worry about the movement of individual pulleys but only the tension in the strings as it simplifies our calculations.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




