
Propyl ester reacts with isopropyl magnesium bromide to give ${{2}^{\circ }}$ alcohol. The ester is:
(A) propyl methanoate
(B) isopropyl formate
(C) propyl ethanoate
(D) isopropyl ethanoate
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Secondary alcohol is a hydroxyl group which is attached to a secondary carbon atom. The carbon atom that is attached to the other two carbon atoms is called a secondary carbon atom. The structure of the isopropyl group is as shown below.

Complete step by step solution:
Let’s see how these all esters will react with the given Grignard reagent one by one.
- Any ester will react with the Grignard reagent to first give a ketone and then the ketone will further react with the Grignard reagent to give alcohol as a final product.
i) Propyl methanoate
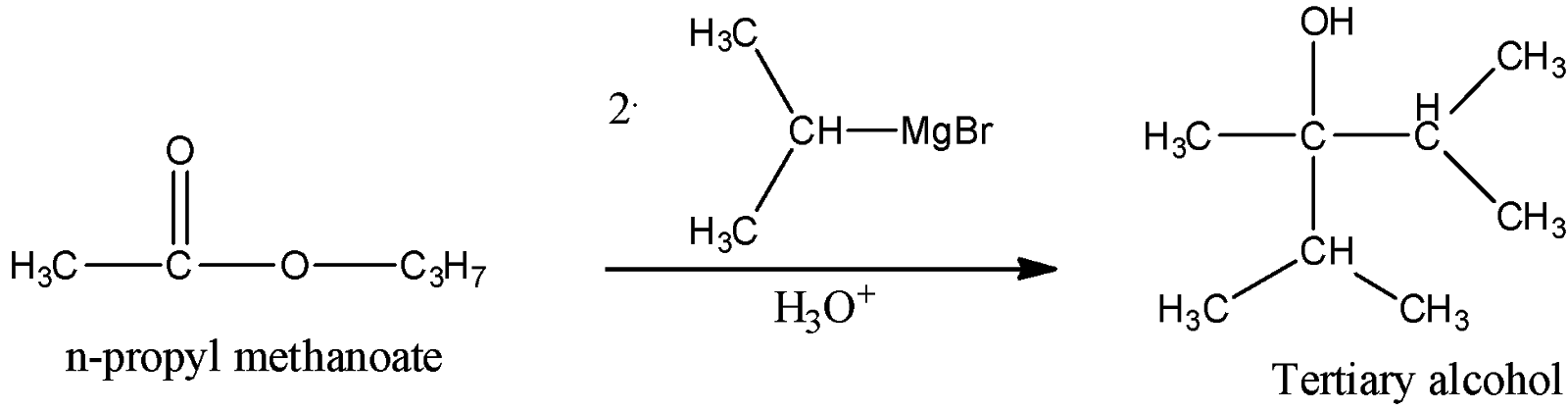
Thus, here we can see that propyl stands for the n-propyl group and it will react with two moles of the given Grignard reagent to give tertiary alcohol as a product. We can see that the hydroxyl group bearing carbon is attached with other three carbon atoms, hence the product is a tertiary alcohol.
ii) Isopropyl formate
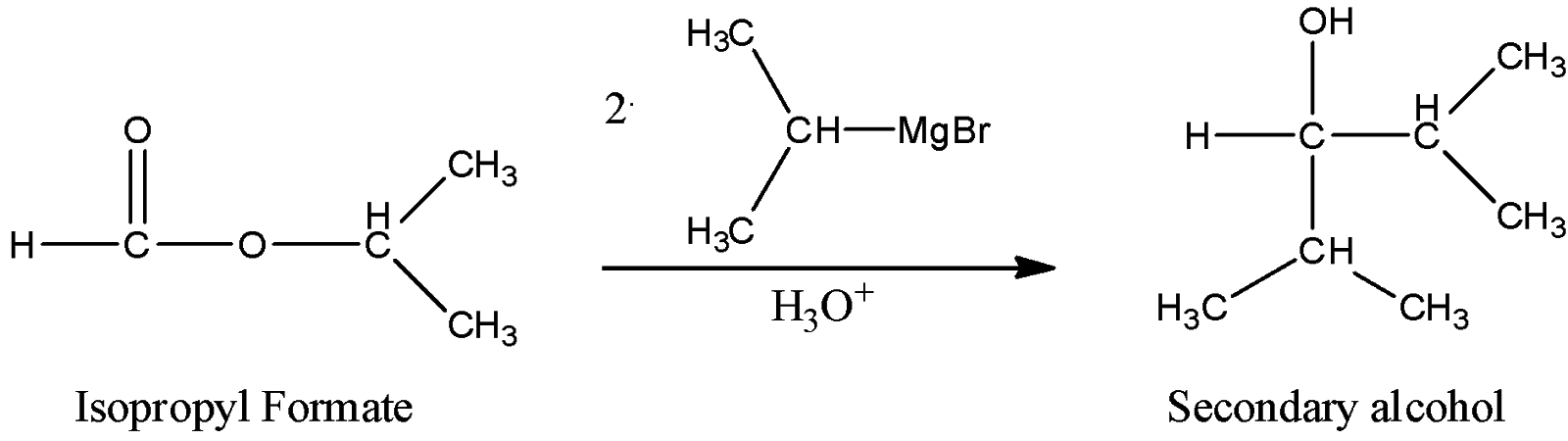
Here, we can see that as a hydrogen atom is bonded to the carbonyl carbon, the resulting alcohol bearing carbon will have one carbon atom less than the first example, so here the carbon-bearing hydroxyl group is bonded with only two carbon atoms, so it can be categorized as secondary alcohol.
iii) Propyl Ethanoate
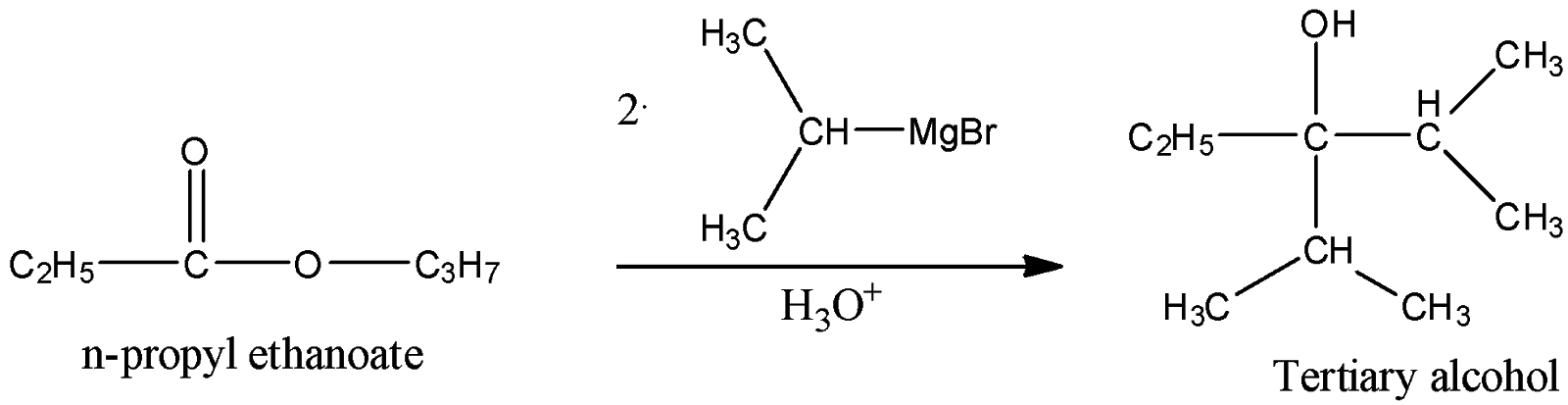
Here, we can see that as the ethyl group is bonded with the carbonyl carbon, the resulting alcohol will have a hydroxyl group which will be bonded to a carbon atom which is a tertiary carbon. Hence, alcohol is a tertiary alcohol.
iv) isopropyl Ethanoate
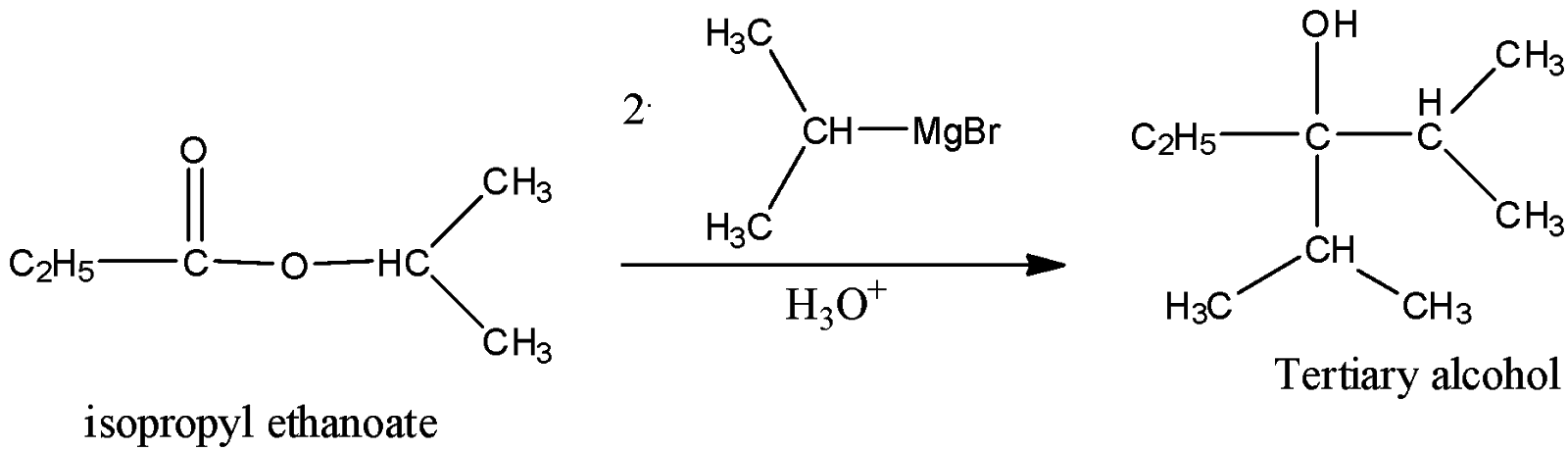
Here, also the resulting alcohol will be tertiary alcohol as the carbon attached to it is a tertiary alcohol.
Thus, we can conclude from the above discussion that option (B) is correct.
Note: Note that any ester that is derivative of formic acid means it is formate, then it will always give secondary alcohol upon its reaction with two moles of Grignard reagent. Any ester that is not formatted, will always give tertiary alcohol as a final product with the reaction with the Grignard reagent.

Complete step by step solution:
Let’s see how these all esters will react with the given Grignard reagent one by one.
- Any ester will react with the Grignard reagent to first give a ketone and then the ketone will further react with the Grignard reagent to give alcohol as a final product.
i) Propyl methanoate

Thus, here we can see that propyl stands for the n-propyl group and it will react with two moles of the given Grignard reagent to give tertiary alcohol as a product. We can see that the hydroxyl group bearing carbon is attached with other three carbon atoms, hence the product is a tertiary alcohol.
ii) Isopropyl formate

Here, we can see that as a hydrogen atom is bonded to the carbonyl carbon, the resulting alcohol bearing carbon will have one carbon atom less than the first example, so here the carbon-bearing hydroxyl group is bonded with only two carbon atoms, so it can be categorized as secondary alcohol.
iii) Propyl Ethanoate

Here, we can see that as the ethyl group is bonded with the carbonyl carbon, the resulting alcohol will have a hydroxyl group which will be bonded to a carbon atom which is a tertiary carbon. Hence, alcohol is a tertiary alcohol.
iv) isopropyl Ethanoate

Here, also the resulting alcohol will be tertiary alcohol as the carbon attached to it is a tertiary alcohol.
Thus, we can conclude from the above discussion that option (B) is correct.
Note: Note that any ester that is derivative of formic acid means it is formate, then it will always give secondary alcohol upon its reaction with two moles of Grignard reagent. Any ester that is not formatted, will always give tertiary alcohol as a final product with the reaction with the Grignard reagent.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




