
Propene when heated with chlorine at about 773K forms
A.
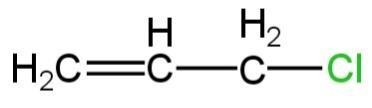
B.
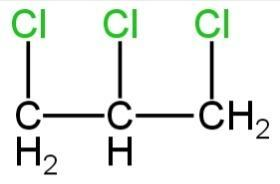
C.
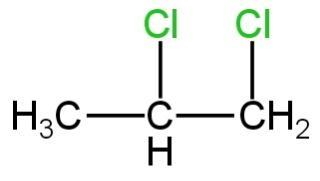
D. All of these
Answer
242.1k+ views
Hint: Halogenation of alkenes is the reaction of alkenes with chlorine, bromine, or iodine to produce a vicinal dihalide. This reaction happens in the existence of inert and non-nucleophilic solvents like methylene chloride, chloroform, or carbon tetrachloride.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In this question, it is given that propene is undergoing a reaction with chlorine at about 773K. We have to find out the product it will form.
We know that propene will react with chlorine and will undergo halogenation.
It is because halogens can act as electrophiles to attack a double bond in an alkene.
A double bond depicts an area of electron density and thus acts as a nucleophile.
As chlorine approaches the double bond, electrons in the double bond are repelled by the electrons in the bromine molecule resulting in a polarization of the halogen bond.
This establishes a dipolar moment in the halogen molecule bond.
Then heterolytic bond division happens and one of the halogens acquires a positive charge and reacts as an electrophile.
This reaction ensues in two steps.
This reaction occurs at low temperatures.
But at high temperatures, chlorine undergoes homolytic cleavage to form chlorine free radicals.
This reaction occurs in three steps.
Initiation step
In the initial step of the addition, the Cl-Cl bond undergoes homolytic cleavage.
Chlorine free radicals are formed.
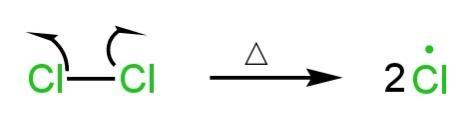
Image: Initiation step
Propagation step
One chlorine radical generated by homolytic cleavage in the initiation step eliminates allylic hydrogen from propane.
A radical intermediate is produced, which is stabilised by resonance.
So, allylic halogenation is preferred.
The intermediate radical then reacts with a chlorine molecule to produce the allylic chloride product which again forms the chlorine radical, which starts again the radical chain mechanism.
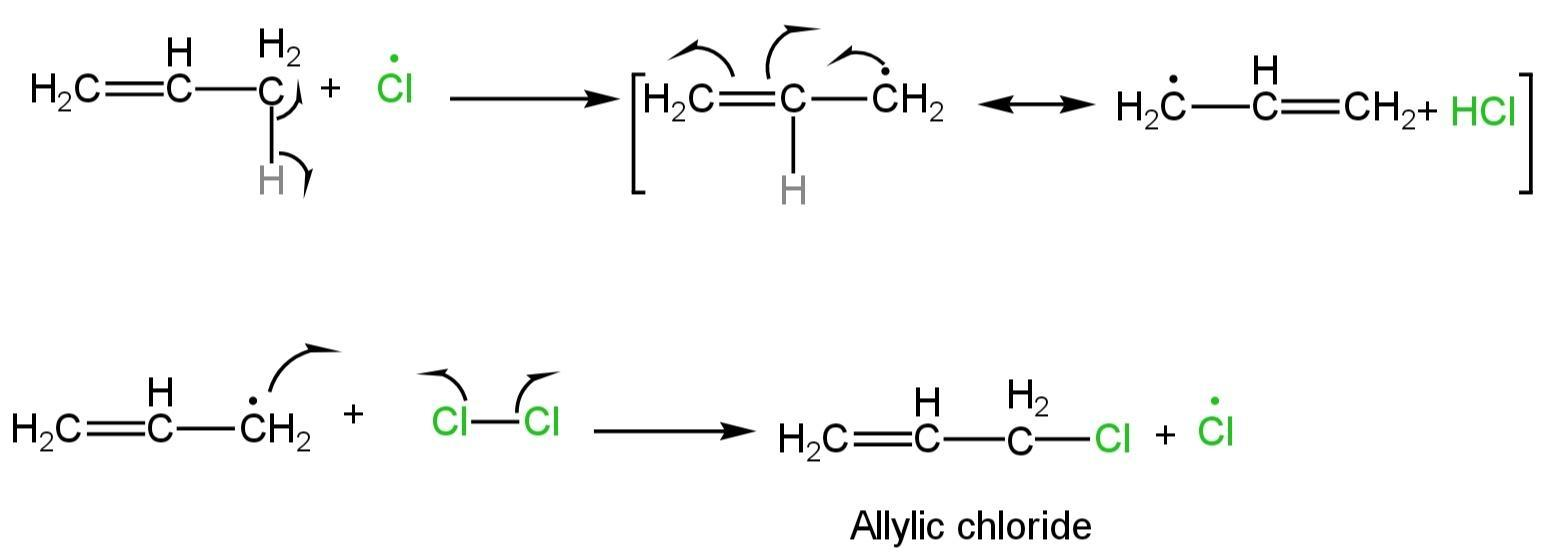
Image: Propagation step
Termination step
Termination happens by the combination of bromine radicals, one bromine radical with one allylic radical, and two allylic radicals.
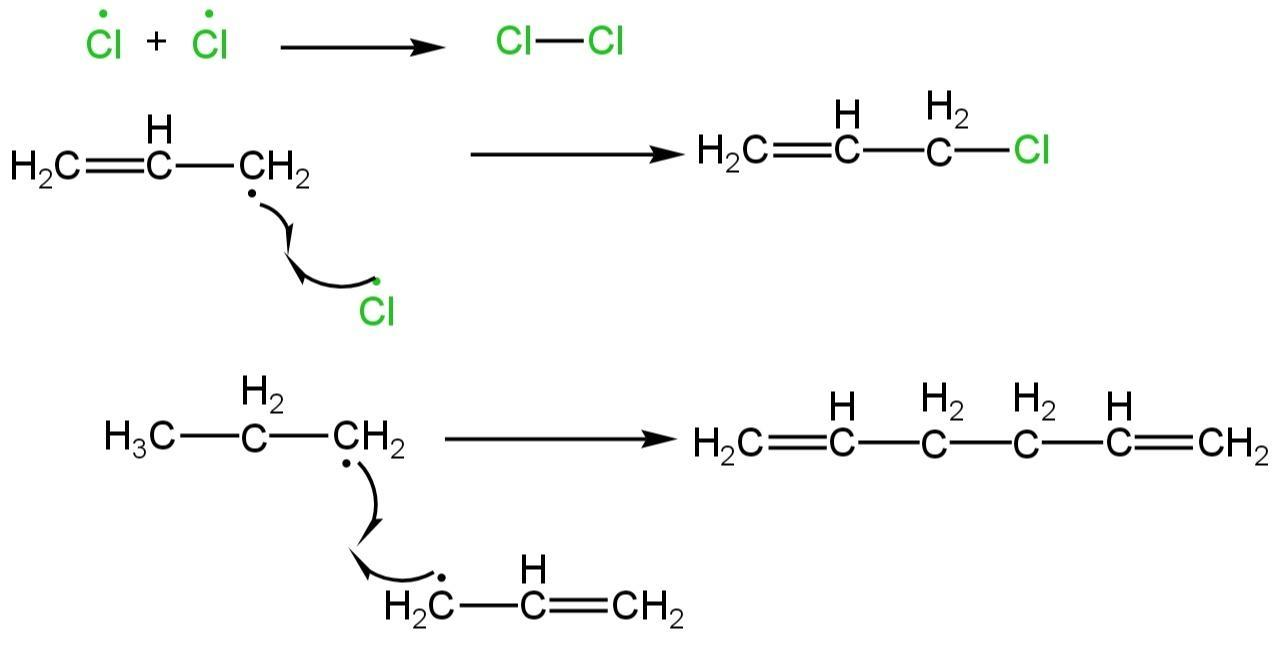
Image: Termination step
So, the product formed in this reaction is A.
So, option A is correct.
Note: Numerous routes exist for the halogenation of organic compounds, comprising free radical halogenation, ketone halogenation, electrophilic halogenation, and halogen addition reaction. The nature of the substrate specifies the pathway. Fluorination with elemental fluorine is extremely exothermic so highly specialised conditions and devices are employed.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In this question, it is given that propene is undergoing a reaction with chlorine at about 773K. We have to find out the product it will form.
We know that propene will react with chlorine and will undergo halogenation.
It is because halogens can act as electrophiles to attack a double bond in an alkene.
A double bond depicts an area of electron density and thus acts as a nucleophile.
As chlorine approaches the double bond, electrons in the double bond are repelled by the electrons in the bromine molecule resulting in a polarization of the halogen bond.
This establishes a dipolar moment in the halogen molecule bond.
Then heterolytic bond division happens and one of the halogens acquires a positive charge and reacts as an electrophile.
This reaction ensues in two steps.
This reaction occurs at low temperatures.
But at high temperatures, chlorine undergoes homolytic cleavage to form chlorine free radicals.
This reaction occurs in three steps.
Initiation step
In the initial step of the addition, the Cl-Cl bond undergoes homolytic cleavage.
Chlorine free radicals are formed.
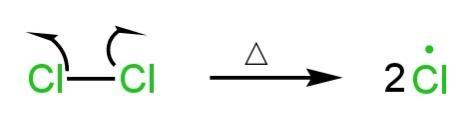
Image: Initiation step
Propagation step
One chlorine radical generated by homolytic cleavage in the initiation step eliminates allylic hydrogen from propane.
A radical intermediate is produced, which is stabilised by resonance.
So, allylic halogenation is preferred.
The intermediate radical then reacts with a chlorine molecule to produce the allylic chloride product which again forms the chlorine radical, which starts again the radical chain mechanism.

Image: Propagation step
Termination step
Termination happens by the combination of bromine radicals, one bromine radical with one allylic radical, and two allylic radicals.

Image: Termination step
So, the product formed in this reaction is A.
So, option A is correct.
Note: Numerous routes exist for the halogenation of organic compounds, comprising free radical halogenation, ketone halogenation, electrophilic halogenation, and halogen addition reaction. The nature of the substrate specifies the pathway. Fluorination with elemental fluorine is extremely exothermic so highly specialised conditions and devices are employed.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Set 2 (56/5/2) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Notes Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 - The D and F Block Elements - 2025-26

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Set 3 56/4/3 2025 Question Paper PDF & Answer Key

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Set 3 2025 with Answers

What is Glucose in Chemistry? Structure, Properties & Uses




