
Oxidation number of oxygen atom in ${O_3} $ molecule is:
(A) 0
(B) -2
(C) +2
(D) +1
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Oxygen being a reactive non- metal occurs in various forms, ozone is also one of the highly reactive gas made up of 3 oxygen atoms. It is both a natural and a man-made product that occurs in the earth’s upper atmosphere (stratosphere) and lower atmosphere (troposphere).
Complete step by step solution:
We have been provided with ${O_3} $ molecule,
As we know the molecular formula of ozone is ${O_3} $, that is 3 oxygen atoms,
The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and its valency is -2, as it requires 2 electrons to complete its octet.
The structure of ozone is:
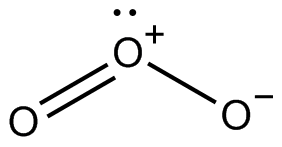
Now, as we know, the oxidation number is the total number of electrons that an atom either gains or loses in order to form a chemical bond with another atom. It is also known as oxidation state.
So, we need to find out the oxidation number of ozone, for that we will be using the formula:
Charge on each atom/ number of atoms
Now, we have 3 oxygens having charges 0, -1 and +1.
So, the oxidation number would be: $\dfrac {{0 + (- 1) + (+ 1)}}{3} $,
On simplifying further, we will get: $\dfrac {0}{3} = 0$,
So, the oxidation number comes out to be 0.
Therefore, we can conclude that option (A) is correct.
Note: Ozone being highly reactive do have resonance structure but it would not change the oxidation number. Also, all the electrons of ozone are paired unlike oxygen and therefore it is diamagnetic.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been provided with ${O_3} $ molecule,
As we know the molecular formula of ozone is ${O_3} $, that is 3 oxygen atoms,
The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and its valency is -2, as it requires 2 electrons to complete its octet.
The structure of ozone is:

Now, as we know, the oxidation number is the total number of electrons that an atom either gains or loses in order to form a chemical bond with another atom. It is also known as oxidation state.
So, we need to find out the oxidation number of ozone, for that we will be using the formula:
Charge on each atom/ number of atoms
Now, we have 3 oxygens having charges 0, -1 and +1.
So, the oxidation number would be: $\dfrac {{0 + (- 1) + (+ 1)}}{3} $,
On simplifying further, we will get: $\dfrac {0}{3} = 0$,
So, the oxidation number comes out to be 0.
Therefore, we can conclude that option (A) is correct.
Note: Ozone being highly reactive do have resonance structure but it would not change the oxidation number. Also, all the electrons of ozone are paired unlike oxygen and therefore it is diamagnetic.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




