
On heating Chloroform with aq. NaOH, the product is
A. Sodium acetate
B. Sodium formate
C. Sodium oxalate
D. Methanol
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Carbon compounds containing more than one halogen atom are called polyhalogen compounds. Chloroform is one of these compounds. The chemical formula of chloroform is \[{\rm{CHC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\]. It is also called trichloromethane.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Chloroform when treated with aqueous NaOH undergoes hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis is the chemical breaking down of a compound by the reaction of water.
A. Sodium acetate
The formula for sodium acetate is \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COONa}}\]. In this compound, there are two carbon atoms.
If we observe the chemical formula of chloroform there is only one carbon atom.
There is no external source like a reagent that provides a carbon atom to the product.
So, there can't be two carbon atoms in the product.
So, A is incorrect.
B. Sodium formate
Aqueous NaOH furnishes the hydroxide ions which act as a nucleophile.
These hydroxide ions attack the chloroform compound replacing the three chloride ions with three hydroxide ions.
This is a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The new compound formed contains one carbon atom carrying three huge oxygen atoms.
Due to this reason, this compound is unstable.
With the loss of a water molecule, it forms formic acid.
Formic acid reacts with sodium ions to form sodium formate.
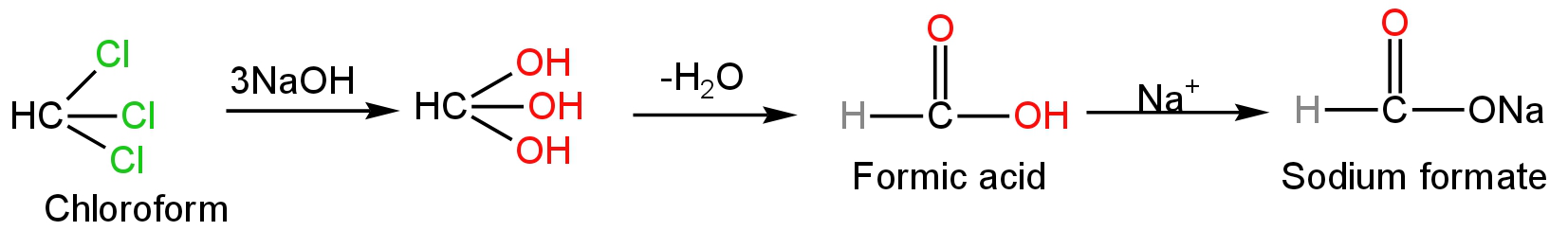
Image: Reaction of chloroform with aqueous NaOH.
So, B is correct.
C. Sodium oxalate
The chemical formula for sodium oxalate is\[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{a}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\].
This has two atoms of carbon.
If we contemplate the chemical formula of chloroform there is only one carbon atom.
There is no external source like a reagent that provides a carbon atom to the product.
So, there cannot be two carbon atoms in the product.
So, C is incorrect.
D. Methanol
Methanol is not formed as a product in this reaction.
So, D is incorrect.
So, option B is correct.
Note: Chloroform has three chlorine atoms which are replaced by the hydroxide ions. This is a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The newly formed product due to its unstable nature loses a water molecule forming formic acid. Formic acid then reacts with sodium ions to form sodium formate.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Chloroform when treated with aqueous NaOH undergoes hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis is the chemical breaking down of a compound by the reaction of water.
A. Sodium acetate
The formula for sodium acetate is \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COONa}}\]. In this compound, there are two carbon atoms.
If we observe the chemical formula of chloroform there is only one carbon atom.
There is no external source like a reagent that provides a carbon atom to the product.
So, there can't be two carbon atoms in the product.
So, A is incorrect.
B. Sodium formate
Aqueous NaOH furnishes the hydroxide ions which act as a nucleophile.
These hydroxide ions attack the chloroform compound replacing the three chloride ions with three hydroxide ions.
This is a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The new compound formed contains one carbon atom carrying three huge oxygen atoms.
Due to this reason, this compound is unstable.
With the loss of a water molecule, it forms formic acid.
Formic acid reacts with sodium ions to form sodium formate.

Image: Reaction of chloroform with aqueous NaOH.
So, B is correct.
C. Sodium oxalate
The chemical formula for sodium oxalate is\[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{a}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\].
This has two atoms of carbon.
If we contemplate the chemical formula of chloroform there is only one carbon atom.
There is no external source like a reagent that provides a carbon atom to the product.
So, there cannot be two carbon atoms in the product.
So, C is incorrect.
D. Methanol
Methanol is not formed as a product in this reaction.
So, D is incorrect.
So, option B is correct.
Note: Chloroform has three chlorine atoms which are replaced by the hydroxide ions. This is a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The newly formed product due to its unstable nature loses a water molecule forming formic acid. Formic acid then reacts with sodium ions to form sodium formate.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




