
On complete hydrogenation, natural rubber produces
(A) ethylene-propylene copolymer
(B) vulcanised rubber
(C) polypropylene
(D) polybutylene
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: For this problem, we have to study the formation of the natural polymer and its formula which will then undergo hydrogenation in the presence of hydrogen and a catalyst. Then we will get the correct answer.
Complete step by step solution:
-In the given question we have to determine the correct product which is formed after the hydrogenation of the natural rubber.
-Hydrogenation is a chemical in which the addition of hydrogen takes place by the breaking of unsaturated bonds with the help of metal catalysts such as nickel.
-The process helps in converting the unsaturated hydrocarbon into saturated hydrogen.
-As we know that natural rubber is a polymer because it is by the polymerisation reaction of the monomer isoprene or 2-methyl - 1,3 butadiene.
-When so many molecules of isoprene make bonds with each other they yield cis - 1,4 polyisoprene.
- The balanced chemical reaction is shown below:
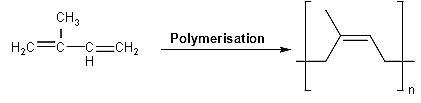
-When this natural rubber undergoes complete hydrogenation reaction, the double bond break and it yields copolymer of ethylene and propylene i.e.
$\text{Natural rubber }\xrightarrow{{{\text{H}}_{2}}/\text{Ni}}\text{ -C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ - CH (C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{) - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{- }\to \text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ = C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\ \text{+ C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ = CH - C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}$
-Here, nickel, palladium, etc will act as a catalyst which will increase the rate of reaction.
Therefore, option A is the correct answer.
Note: Copolymer is the type of polymer which is made up by the polymerisation of different types of monomer. The process of hydrogenation is also known as reduction reaction because the reduction of molecules takes place by addition of hydrogen.
Complete step by step solution:
-In the given question we have to determine the correct product which is formed after the hydrogenation of the natural rubber.
-Hydrogenation is a chemical in which the addition of hydrogen takes place by the breaking of unsaturated bonds with the help of metal catalysts such as nickel.
-The process helps in converting the unsaturated hydrocarbon into saturated hydrogen.
-As we know that natural rubber is a polymer because it is by the polymerisation reaction of the monomer isoprene or 2-methyl - 1,3 butadiene.
-When so many molecules of isoprene make bonds with each other they yield cis - 1,4 polyisoprene.
- The balanced chemical reaction is shown below:

-When this natural rubber undergoes complete hydrogenation reaction, the double bond break and it yields copolymer of ethylene and propylene i.e.
$\text{Natural rubber }\xrightarrow{{{\text{H}}_{2}}/\text{Ni}}\text{ -C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ - CH (C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{) - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ - C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{- }\to \text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ = C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\ \text{+ C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ = CH - C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}$
-Here, nickel, palladium, etc will act as a catalyst which will increase the rate of reaction.
Therefore, option A is the correct answer.
Note: Copolymer is the type of polymer which is made up by the polymerisation of different types of monomer. The process of hydrogenation is also known as reduction reaction because the reduction of molecules takes place by addition of hydrogen.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




